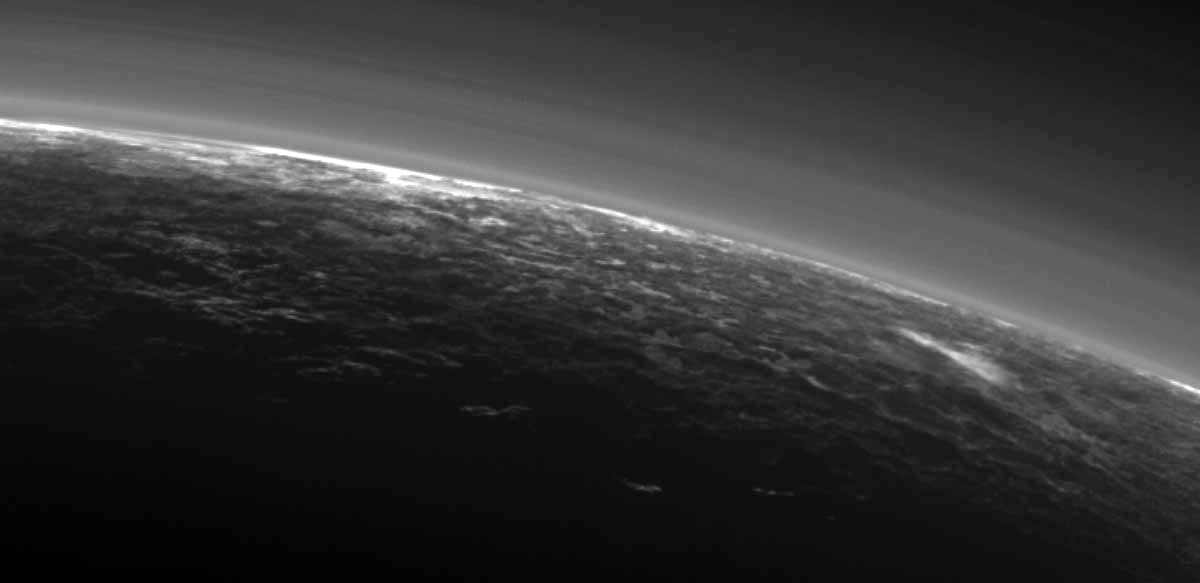
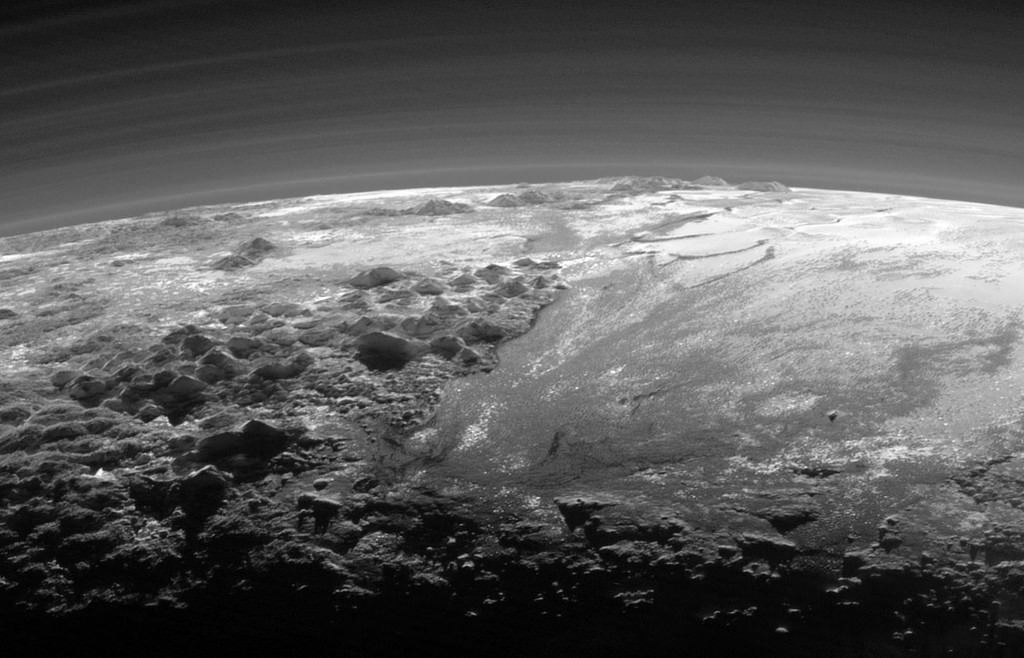
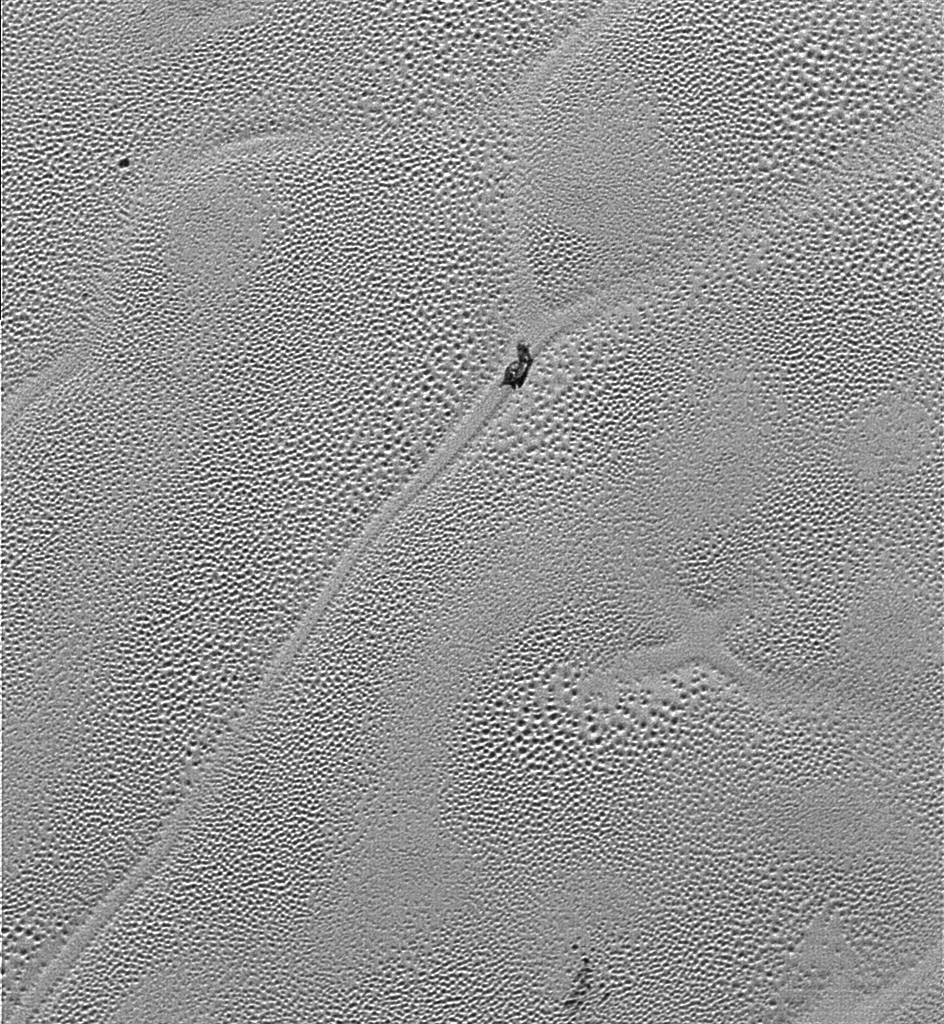
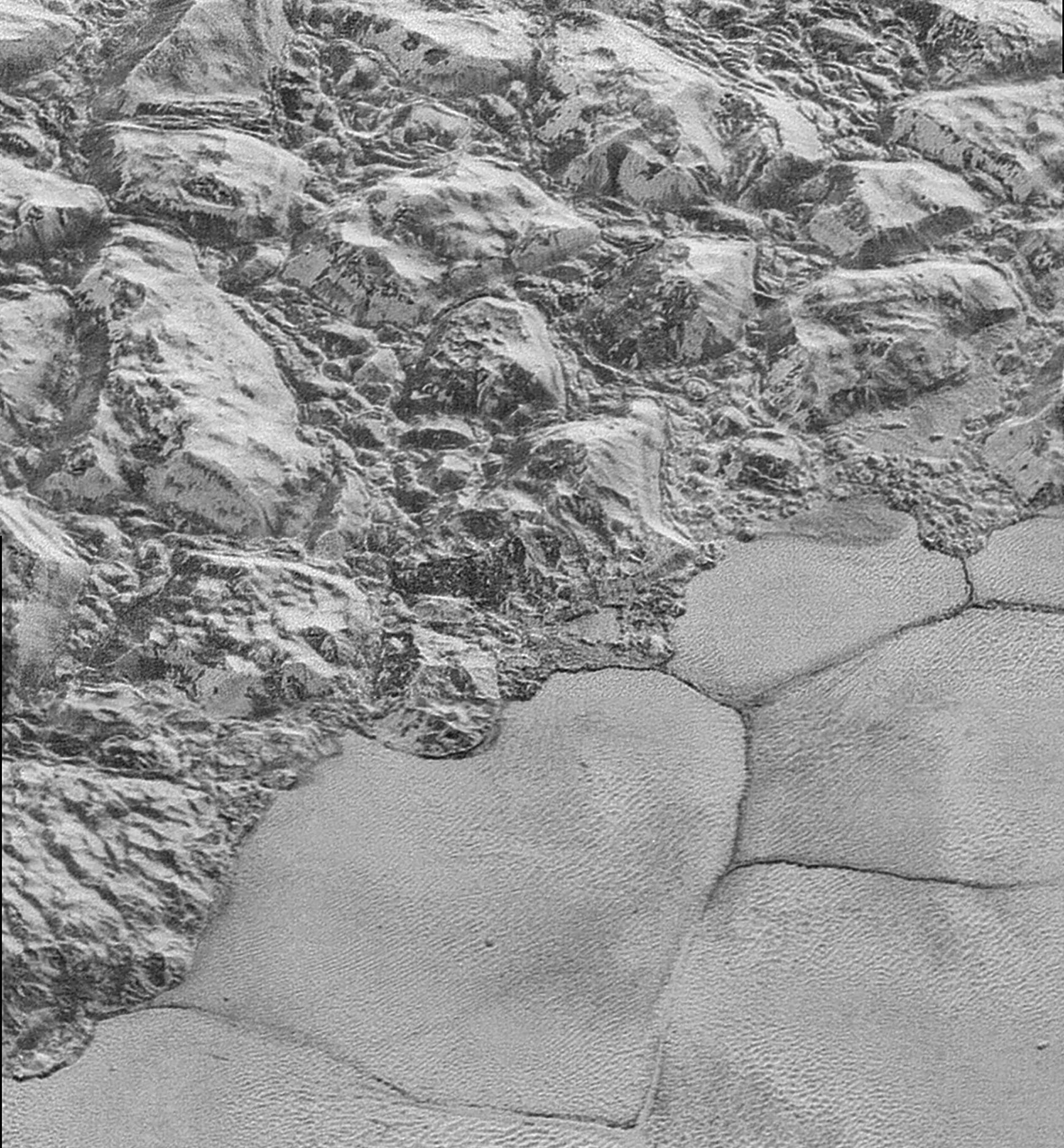
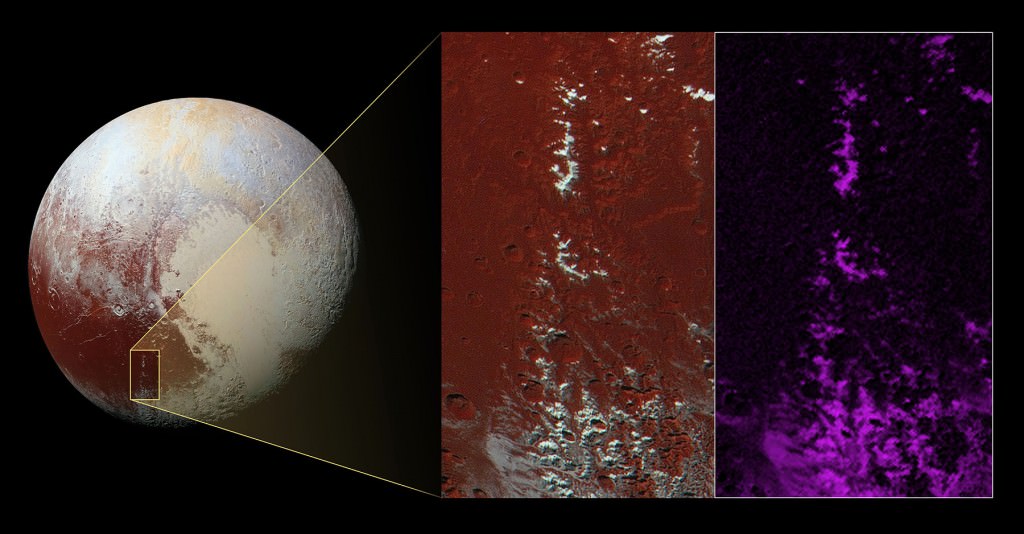
Images from the New Horizons spacecraft show a bite-mark shaped feature on the surface of Pluto. Scientists think that the feature is caused by the sublimation of methane ice, causing cliffs to erode and leaving a flat plain in their place. The images were captured just prior to New Horizon’s closest approach to Pluto on July 14th, 2015.
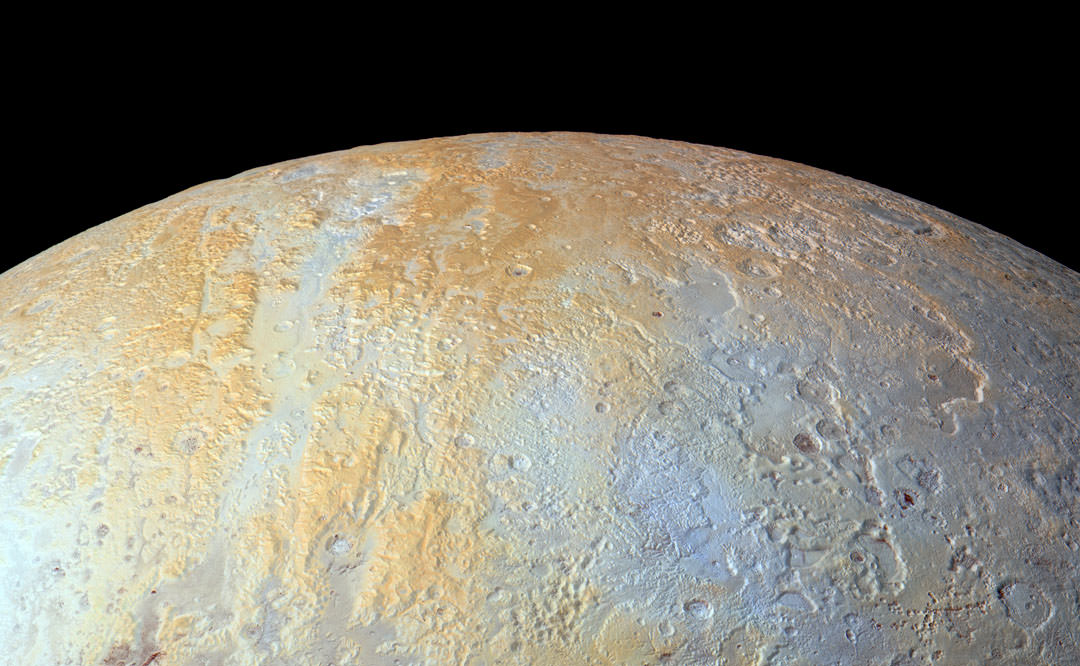
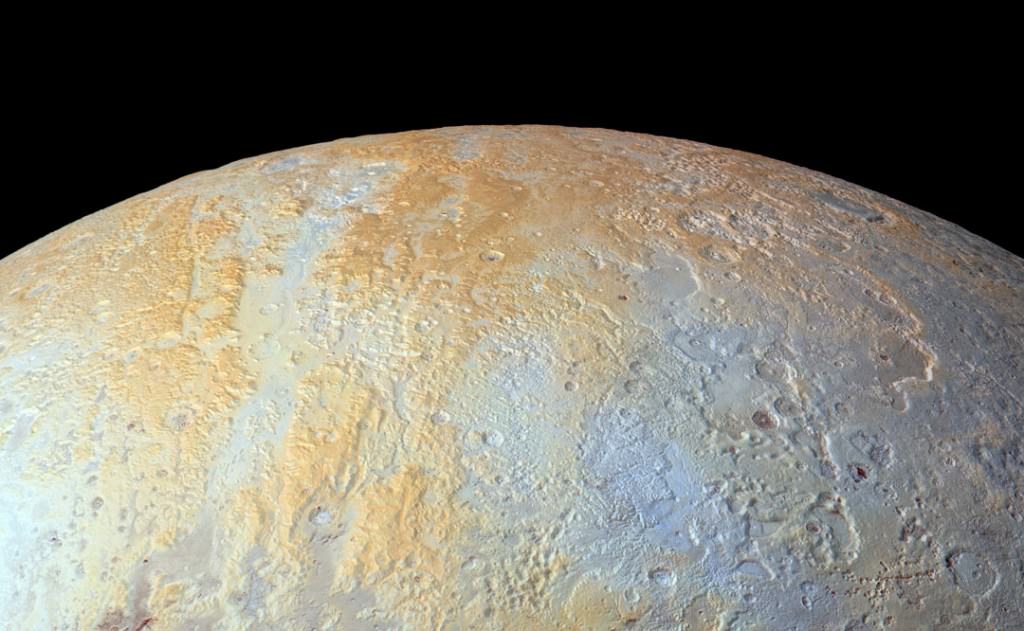
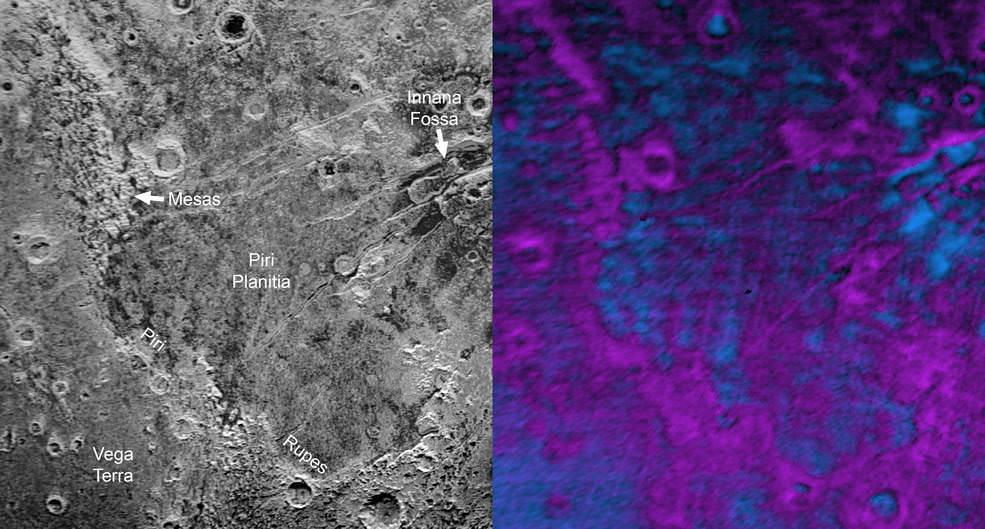
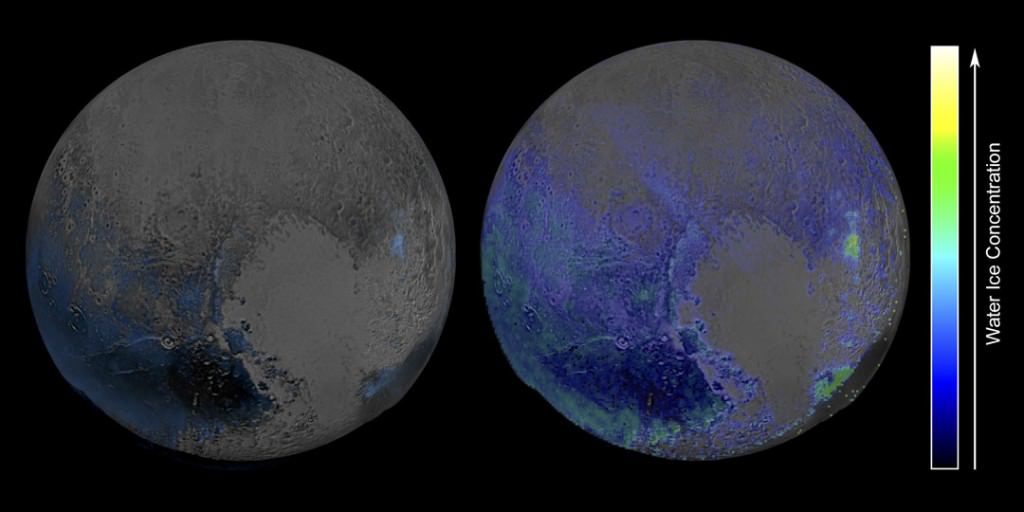
In the image above, which is of Pluto’s western hemisphere, three main features are shown. The first is Vega Terra, which as a raised plateau area. The second is the Piri Planitia, which is a flatter and lower area of plains. Piri Planitia shows an absence of craters, meaning it is geologically younger. Dividing Terra and Planitia are the Piri Rupes, the cliffs which have the bite-mark shaped feature that caught the interest of scientist.
The colored image on the right shows methane-rich areas in purple. Scientists think that as the methane ice of Piri Rupes is sublimated away into the atmosphere, the cliffs are removed and the flat plains of Piri Planitia take their place. The image also shows some methane mesas which have not sublimated away yet.

New Horizons’ data also shows that Piri Planitia has a higher content of water ice, which is shown in blue. Because of the frigid temperature on Pluto, it’s thought that this water ice is like bedrock. It is immobile, and as the methane ice is sublimated away, the water ice bedrock of Piri Planitia is left exposed.
Prior to New Horizons’ arrival at Pluto, it was generally thought that not much was happening at Pluto. But as these images show, and as New Horizons keeps proving, Pluto is far from an inactive place, and there’s a lot to hold the interest of planetary scientists.