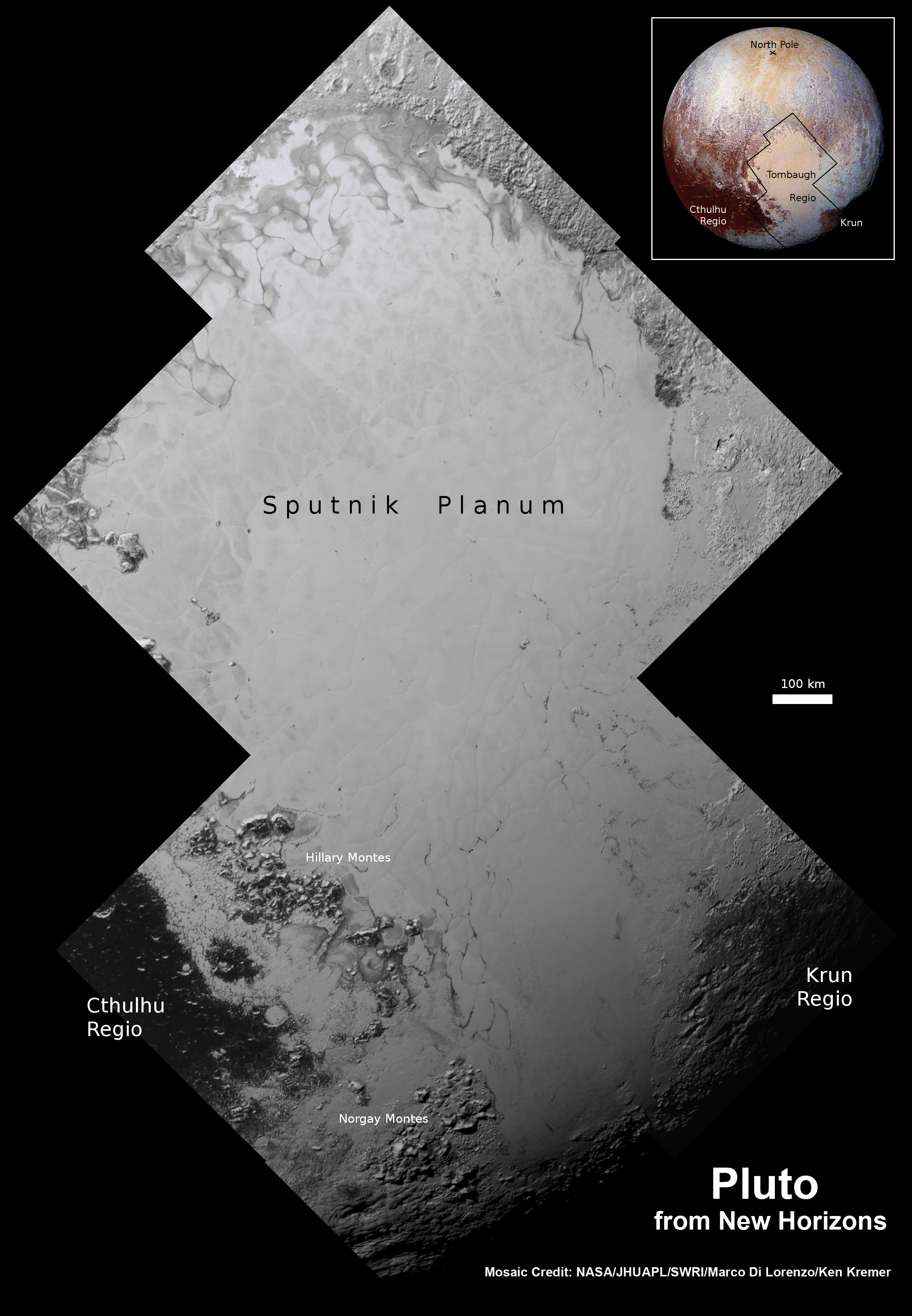
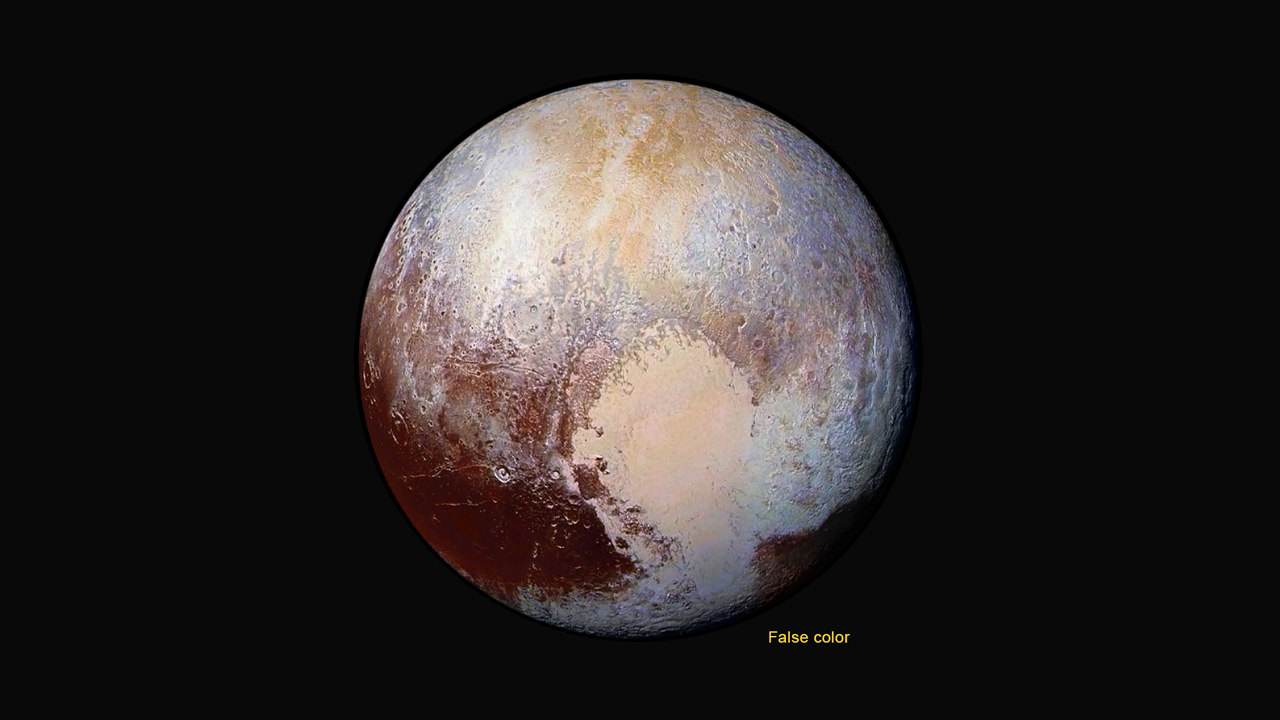
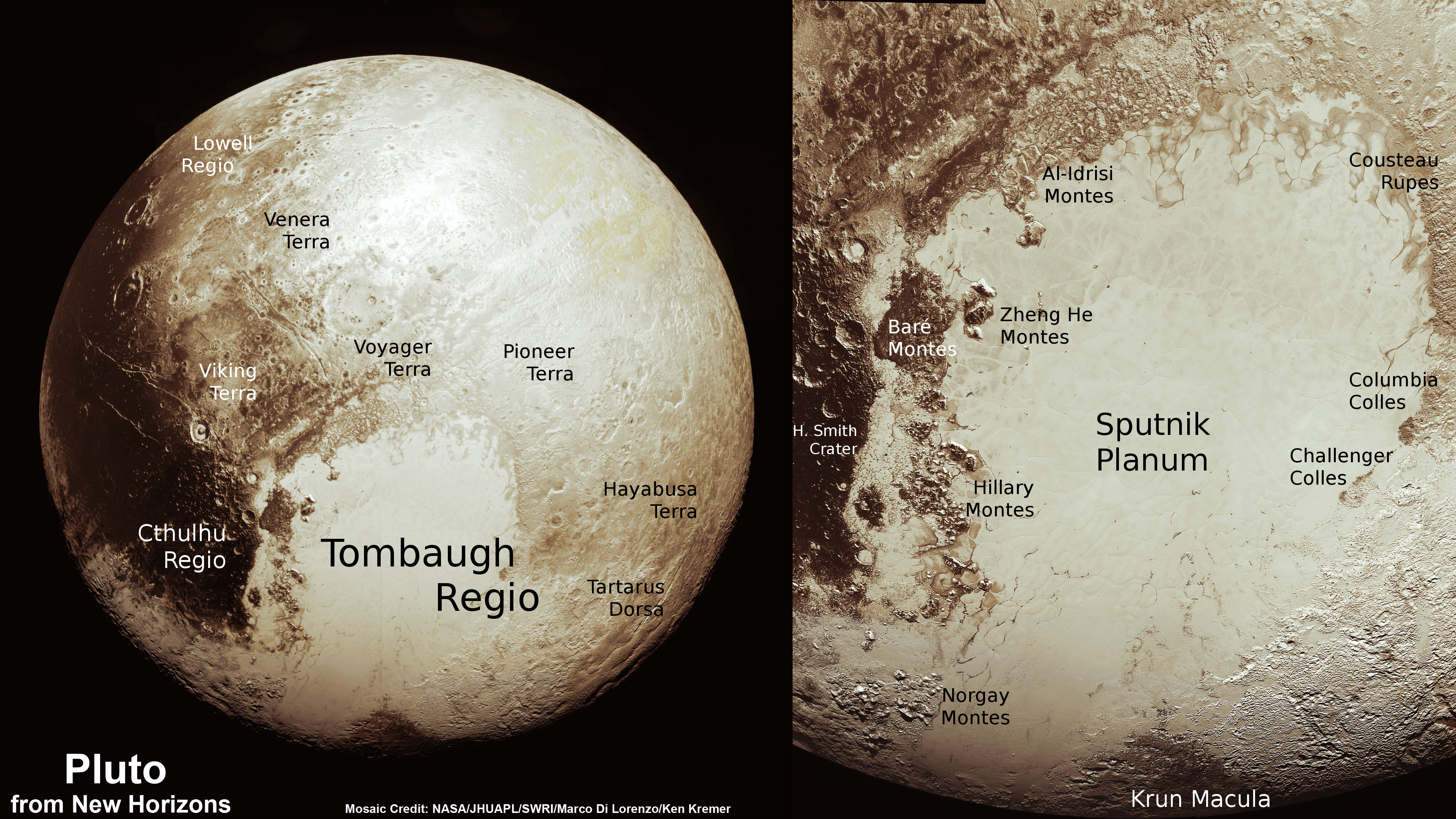
This new global mosaic view of Pluto was created from the latest high-resolution images to be downlinked from NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft and released on Sept. 11, 2015. The images were taken as New Horizons flew past Pluto on July 14, 2015, from a distance of 50,000 miles (80,000 kilometers). This new mosaic was stitched from over two dozen raw images captured by the LORRI imager and colorized. Credits: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Southwest Research Institute/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com
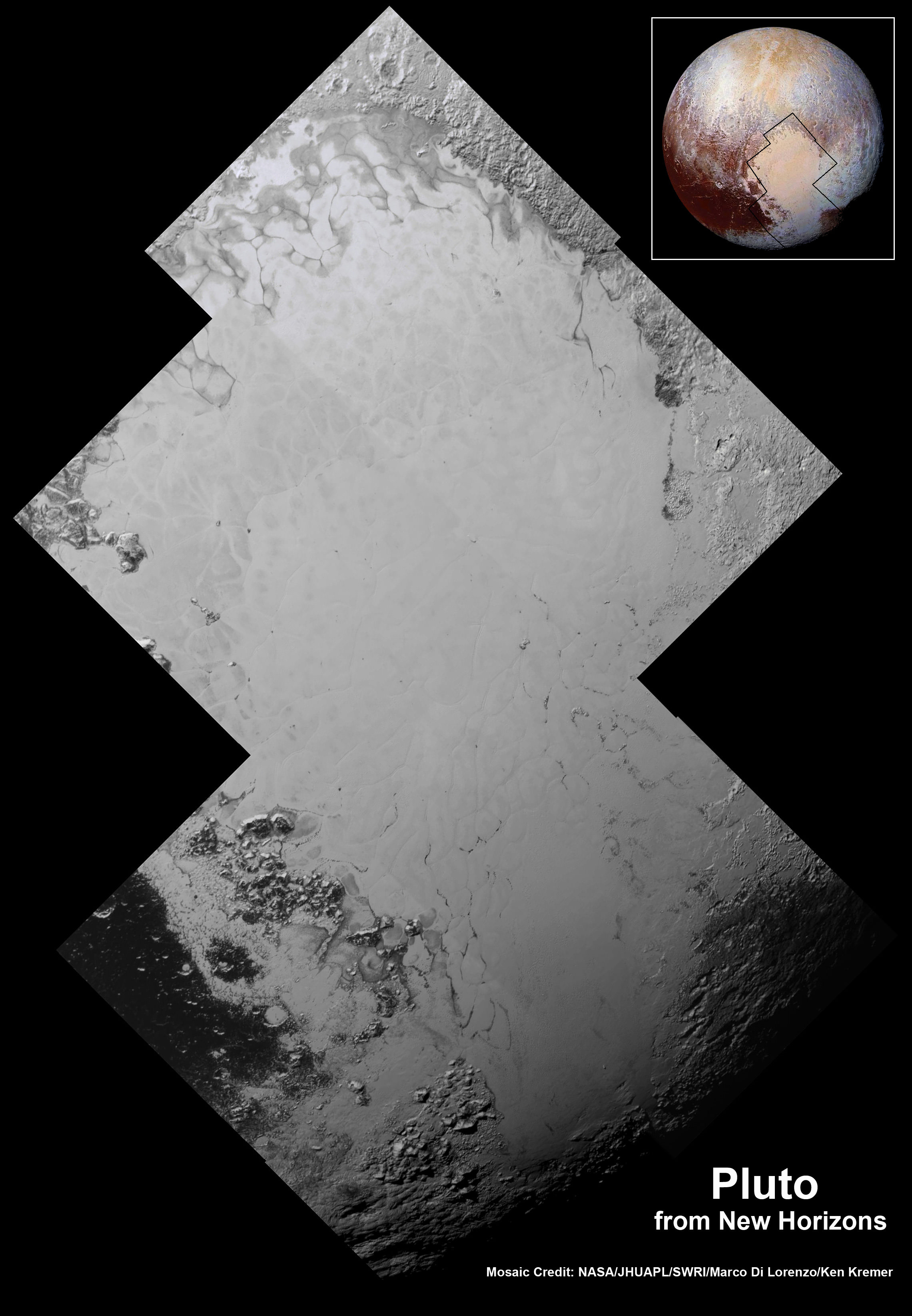
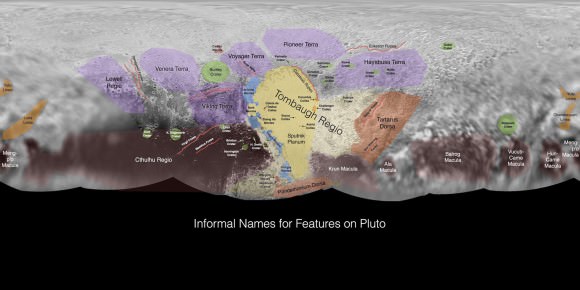
See annotated version and new hi res Tombaugh Regio mosaic below[/caption]
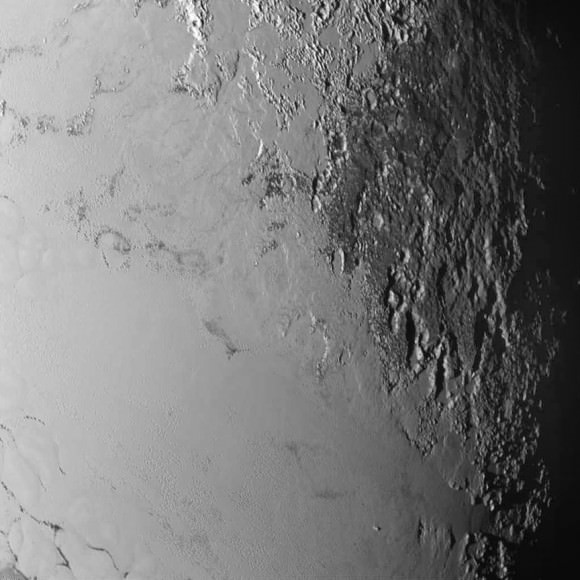
A new global mosaic of Pluto created from the latest high resolution images just beamed back from NASA’s New Horizons probe reveals a bewildering diversity of planetary landforms with unimaginable complexity – yielding undreamed of science discoveries.
But because of limited bandwidth the new image data sets were stored onboard the probe until days ago when they were transmitted back to Earth and released by the New Horizons team late in the day on Friday, Sept. 11.
This best yet view of far flung Pluto comes from raw images taken as New Horizons conducted the history making first flyby past Pluto on July 14, 2015, at a distance of 50,000 miles (80,000 kilometers).
The global Pluto mosaic was generated from over two dozen raw images captured by New Horizons’ Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) and stitched together by the image processing team of Marco Di Lorenzo and Ken Kremer.
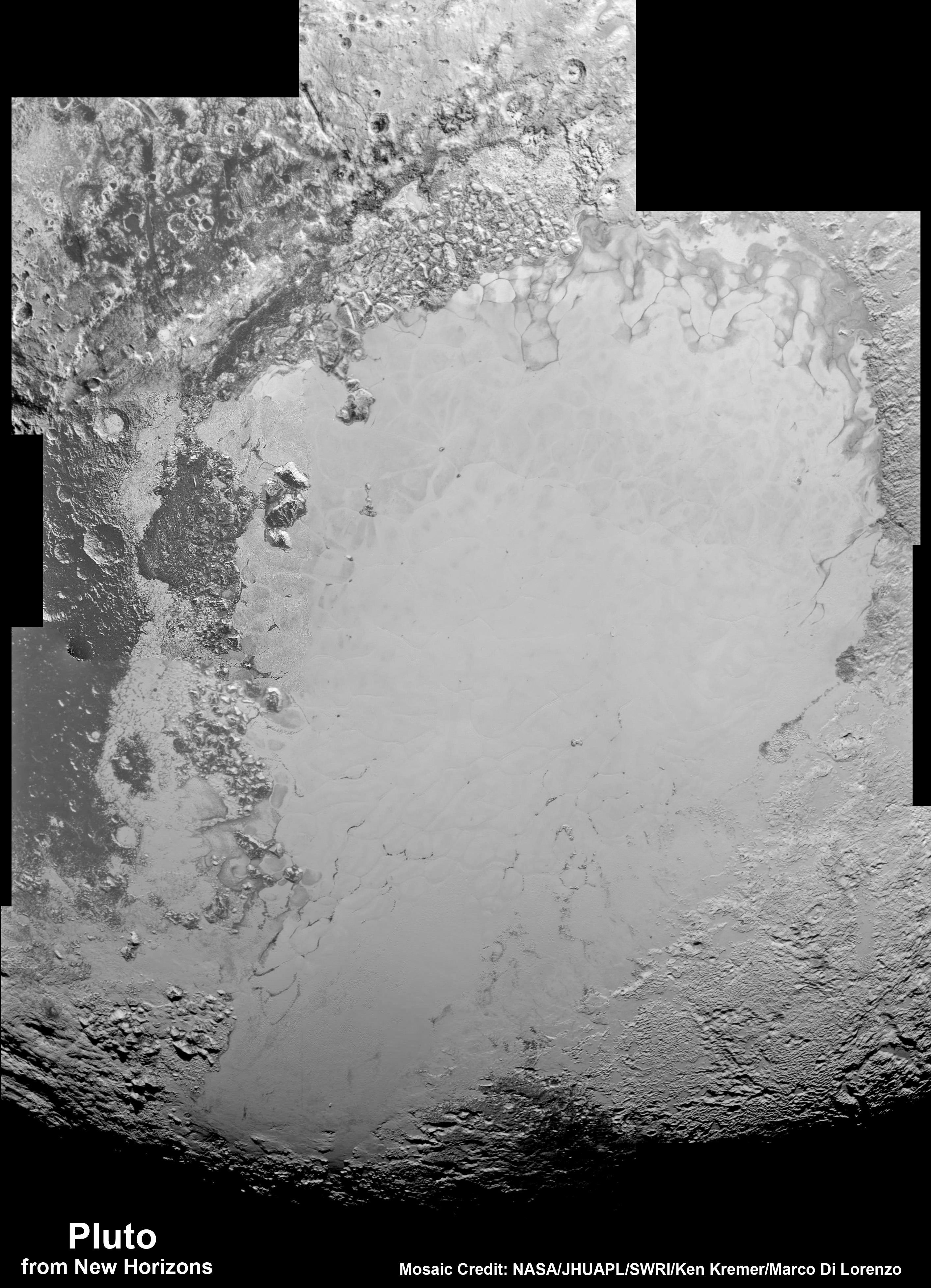
See also our expanded hi res Tombaugh Regio mosaic below showing features as small as 0.5 miles (0.8 kilometers) in size.
After transmitting carefully selected high priority images and science measurements across over 3 billion miles (about 5 billion kilometers) of interplanetary space in the days around the history making flyby, the team elected to temporarily pause the transmission of new images for several weeks in favor of sending other data important for helping place the entire Pluto planetary system into context.
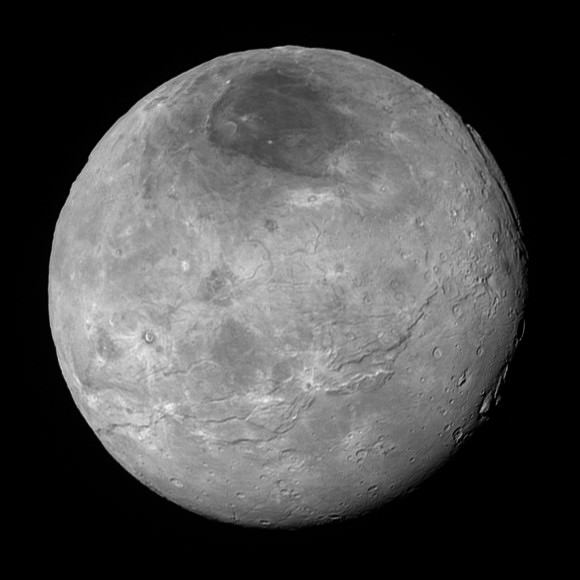
Altogether, over 50 gigabits of data were collected during the July 14 encounter and flyby periods of the highest scientific activity – which includes the most critical hours before and after the spacecrafts closest approach to Pluto, its largest moon Charon and its quartet of smaller moons.

Data from the flyby continues streaming back to Earth, but rather slowly due to limited bandwidth amounting to an average “downlink” of only about 2 kilobits per second via its two transmitters.
New Horizon’s unveiled Pluto as a surprising vibrant and geologically active “icy world of wonders” as it barreled past the Pluto-Charon double planet system on July 14 at over 31,000 mph (49,600 kph) and collected unprecedented high resolution imagery and spectral measurements of the utterly alien worlds.
Since the flyby, the team has been busy analyzing the science data returned thus far and “making some discoveries” said New Horizons Principal Investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute, Boulder, Colorado, during the Weekly Space Hangout on Sept 11.
The team is ecstatic with all the new images and created what they call a synthetic global view of a portion of Pluto.
“We created a synthetic global mosaic view of more than a dozen frames from the LORRI camera, and wrapped it on a sphere and then projected the view as if you were suspended about a thousand miles above the planet – looking back.”
Each LORRI frame is about 400 km across.
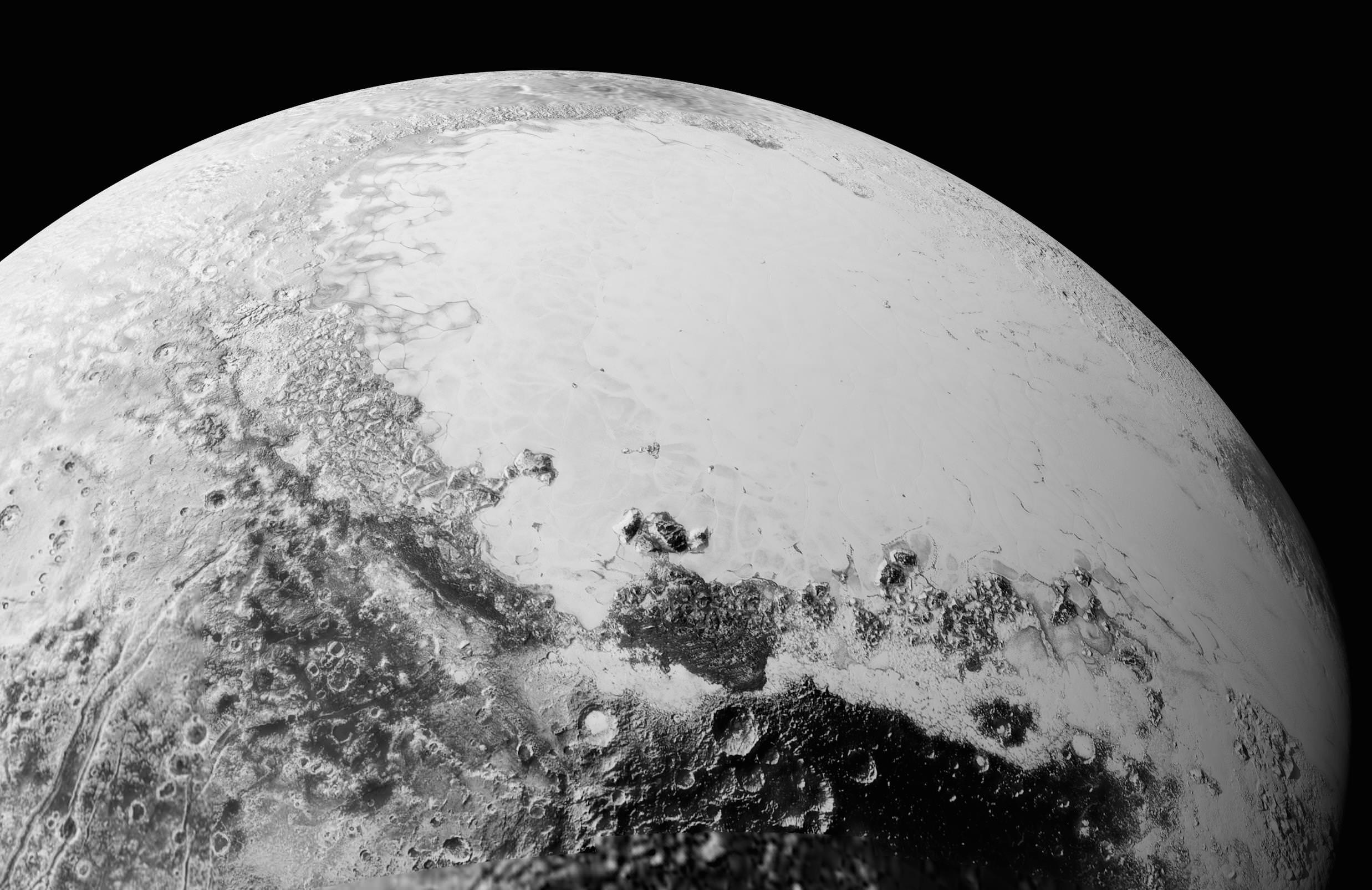

“It gives a breathtaking view of how diverse the geology is and also how diverse the seasonal volatile transport must be across the surface.”
“It’s just absolutely magical and breathtaking. There is a lot going on there.”
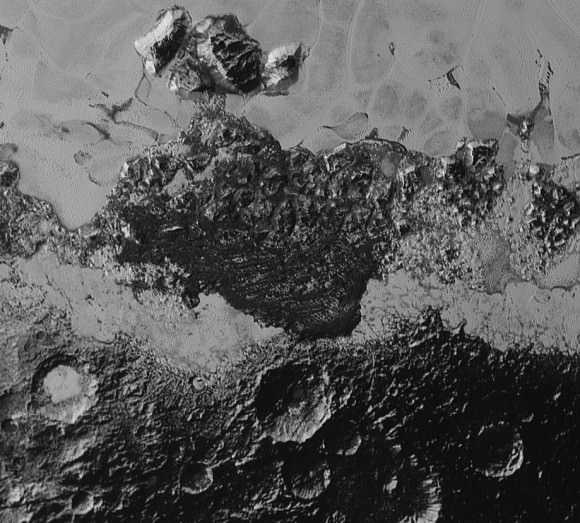
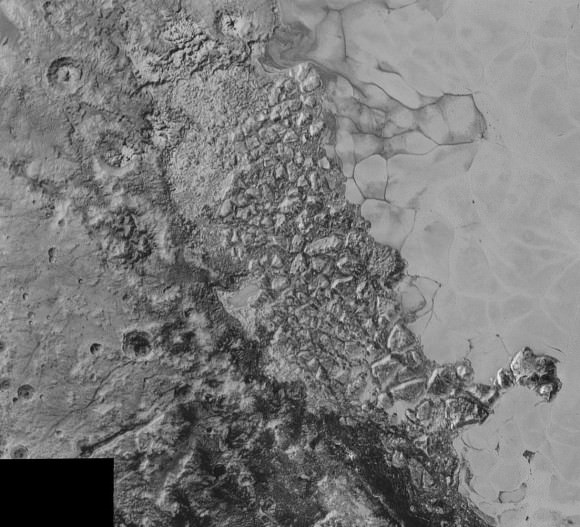
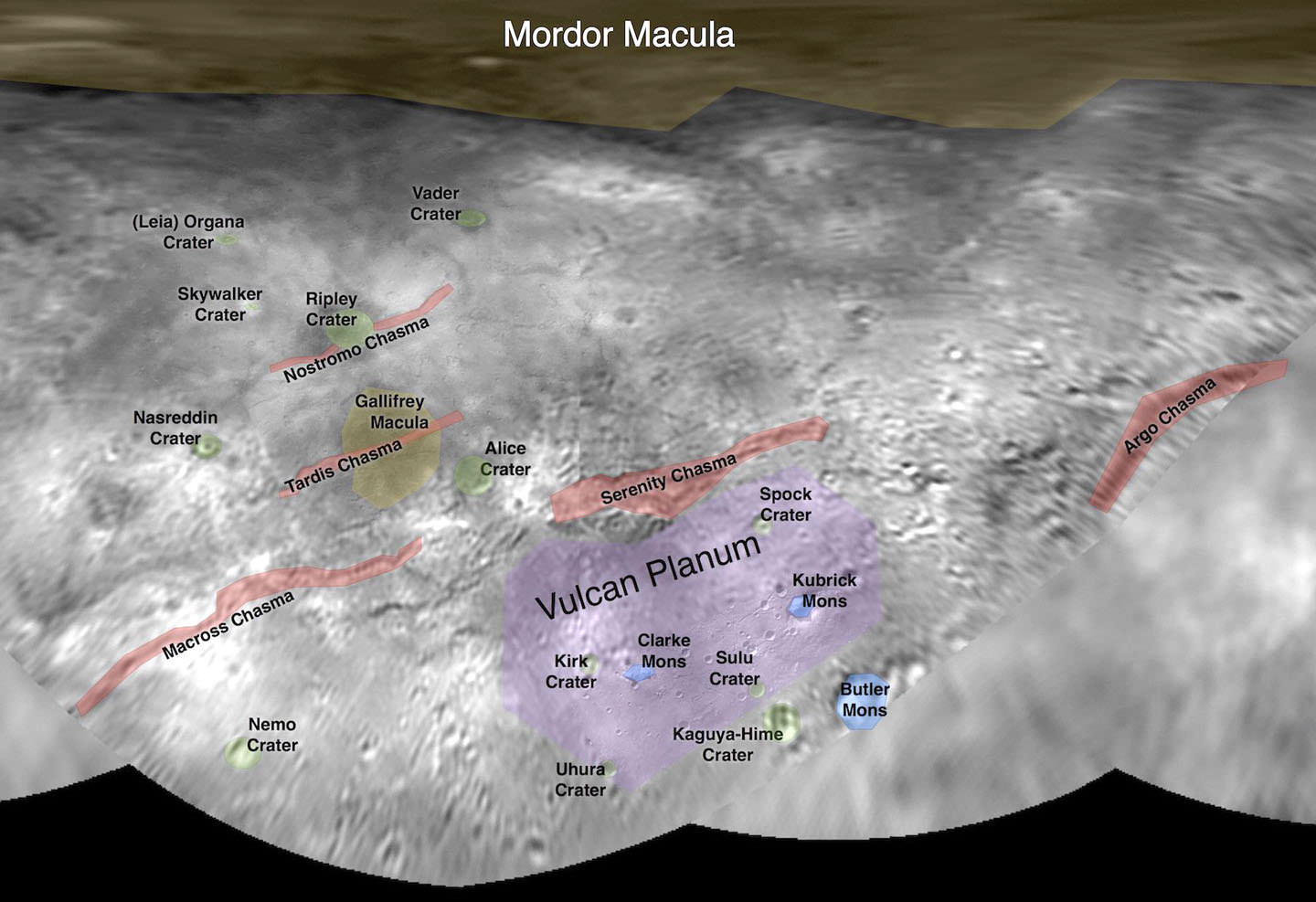
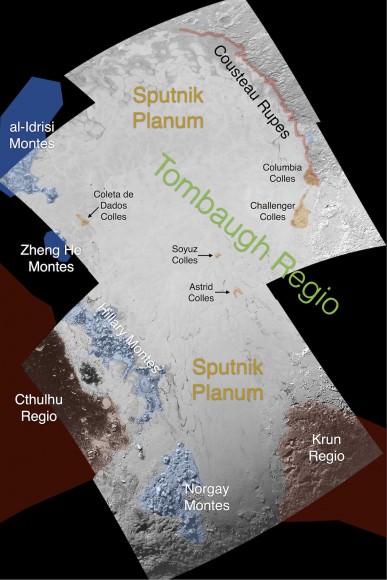
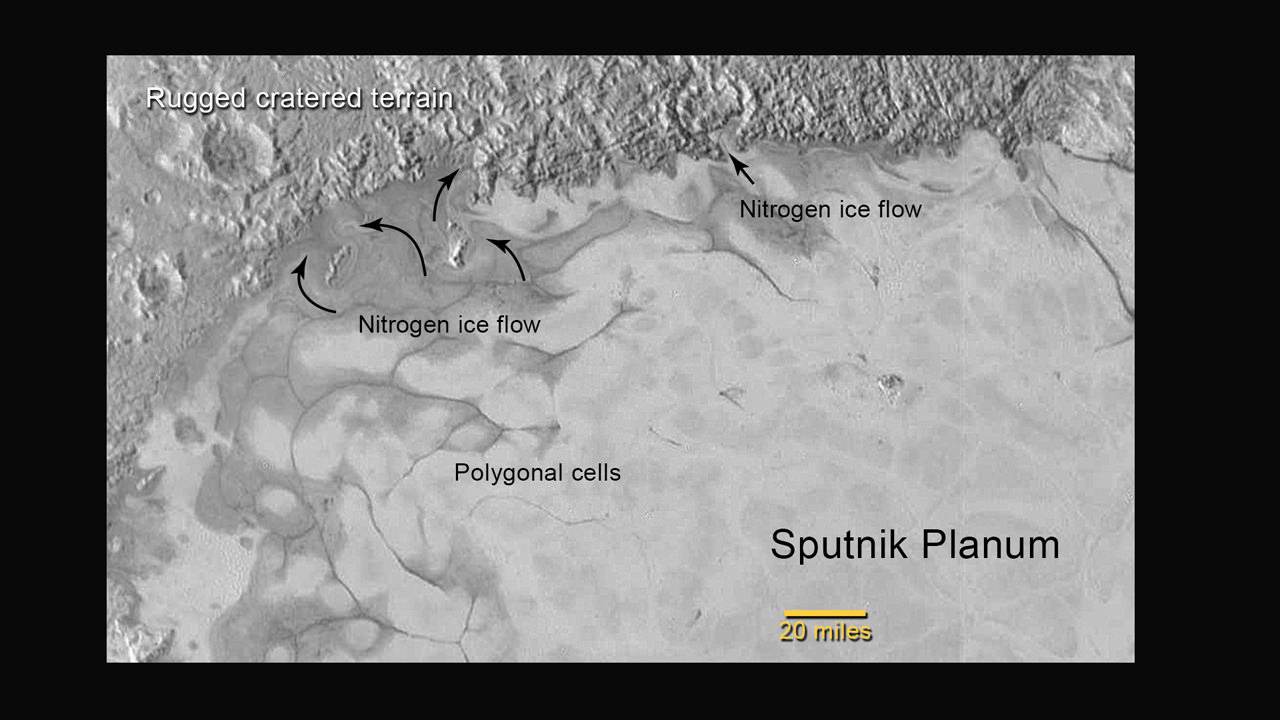
“The big bright area on the left side of the heart shaped feature is informally called Sputnik Planum after the first spacecraft – Sputnik. Surrounding the Texas sized plain are steep mountain ranges that are as tall as the Rockies in Colorado.”
What are Pluto’s plains and mountains comprised of?
“We know that the mountain ranges are not made of the same stuff as the planum, or plains. The plains are made of nitrogen. But nitrogen is too soft a material to build mountains out of, even in Pluto’s weak gravity.”
“So the mountains must be made of something else stronger. Rock and water ice are the two most likely possibilities. But they are most likely water ice, the lighter stuff. Because the rock has almost certainly sunk to the center of Pluto and the ice has floated to the top and formed the mantle and perhaps the crust of Pluto.”
“So we think the volatiles like the nitrogen, methane and carbon monoxide you see there and that shifts around with the seasons and interacts with the atmosphere – is just a veneer. It’s just a coating on the surface. And in some places its very thin and looks like it is breaking up on the margins. In other places it may be quite thick, maybe even kilometers thick.”
“We’ll see when we have more data!” exclaimed Stern.
“The data downlink will take over a year to get all the data to the ground [on Earth].”
“Over 50 gigabits of science data from the Pluto system needs to be sent back. The Pluto flyby took place on the 50th anniversary of NASA’s first flyby of Mars by Mariner IV. New Horizons dataset amounted to several thousand times more data collected compared to what Mariner IV sent back during its first flyby of Mars,” Stern elaborated.
“The surface of Pluto is every bit as complex as that of Mars,” says Jeff Moore, leader of the New Horizons Geology, Geophysics and Imaging (GGI) team at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California. “The randomly jumbled mountains might be huge blocks of hard water ice floating within a vast, denser, softer deposit of frozen nitrogen within the region informally named Sputnik Planum.”
How much data has been returned so far varies by instrument.
“The average across all the entire science payload is only about 5 or 6 percent so far,” Stern explained.
“All the flyby data from the two plasma instruments – PEPSI and SWAP – and the Student Dust Counter instrument is back on the ground, because they were small datasets.”
“But less than 3% of the ALICE UV spectrometer data is back so far. And for the other imaging instruments its similar.”
“So it’s going to take about another year to send all the data back!”

Stern informed that the team has submitted a paper to the journal Science and plans a large series of technical scientific presentations at upcoming meetings, including the Division of Planetary Sciences Meeting in Washington in November.
And New Horizons is in excellent shape to get those 50 gigabits of data back to the eagerly waiting researchers since all the spacecraft systems are operating normally.
“The spacecraft is doing very well,” said Alice Bowman, New Horizons Mission Operations Manager of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), during the Weekly Space Hangout.
“It’s very healthy and we are getting back gobs of data – causing a flurry of emails among the science team.”
“It’s been a good ride and we had a good flyby of Jupiter too [along the way].”
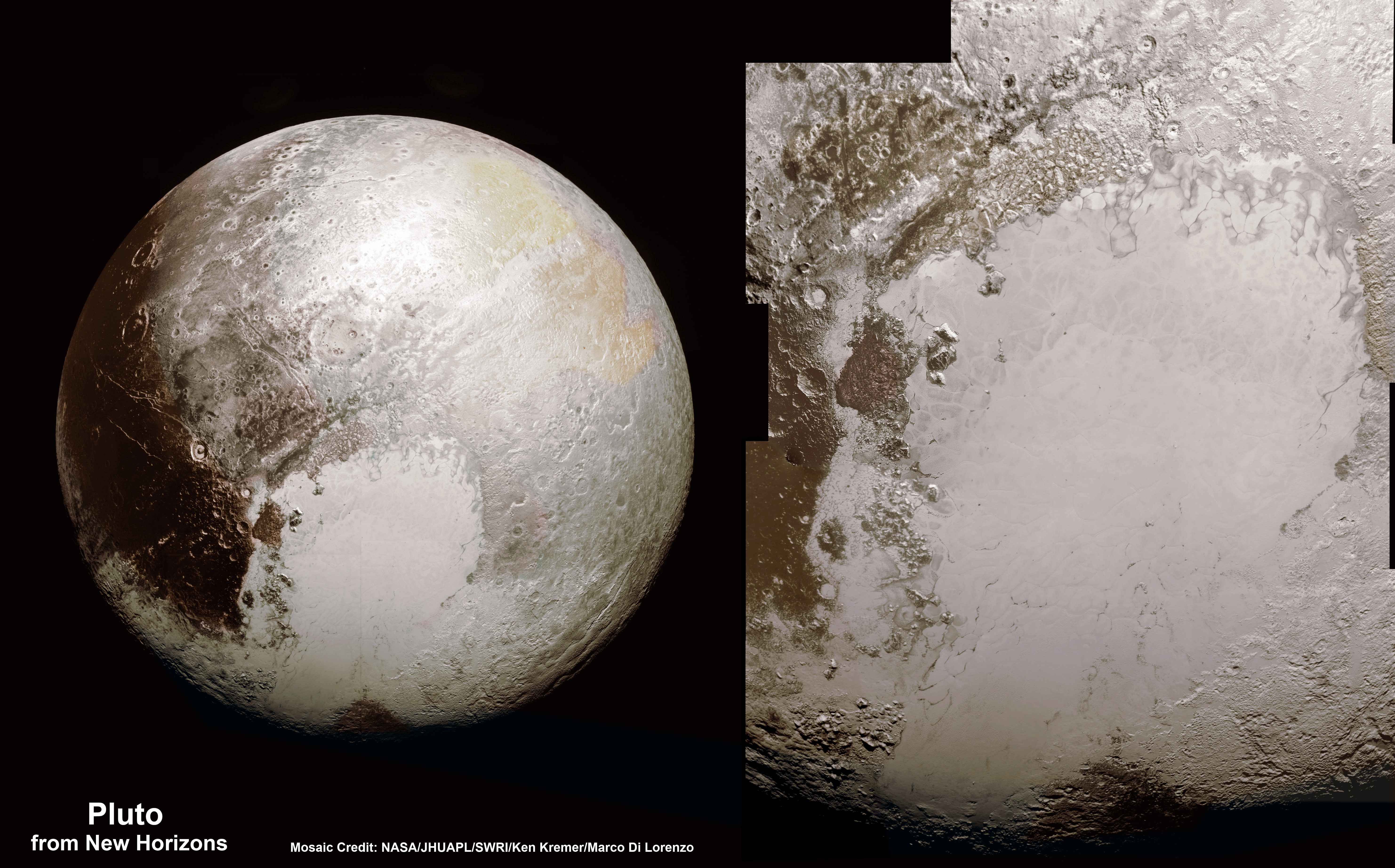

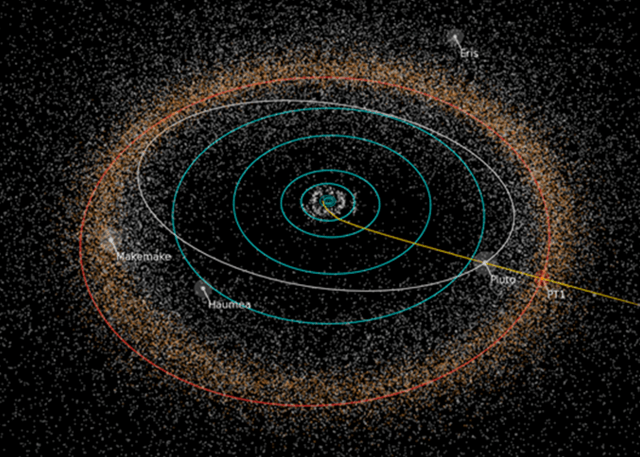
New Horizons also discovered that Pluto is the largest known body beyond Neptune – and thus reigns as the “King of the Kuiper Belt!”
As of today, Sept. 14, New Horizons is 2 months past the Pluto flyby and already over 73 million kilometers ( over 45 million miles) beyond Pluto and continuing its journey into the Kuiper Belt, the third realm of worlds in our solar system.
The science team plans to target New Horizons to fly by another much smaller Kuiper Belt Object (KBO) in 2019 after recently selecting the object dubbed PT1, for Potential Target 1, based on images taken by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope.
“Since the flyby, we have been planning for the extended mission which we will propose to NASA next year,” Stern explained. NASA will then decide whether to approve and fund the new KBO mission proposal.
“We expect to do an engine burn for that [new KBO target] next month [in October]. The KBO flyby will take place about a billion miles beyond Pluto at about 44 AU.”
The actual flyby distance of New Horizons from the KBO is yet to be determined. Stern thinks it could perhaps be much closer, but all those details still need to be worked out.

Watch for Ken’s continuing coverage of the Pluto flyby. He was onsite reporting live on the flyby and media briefings for Universe Today from the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), in Laurel, Md.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
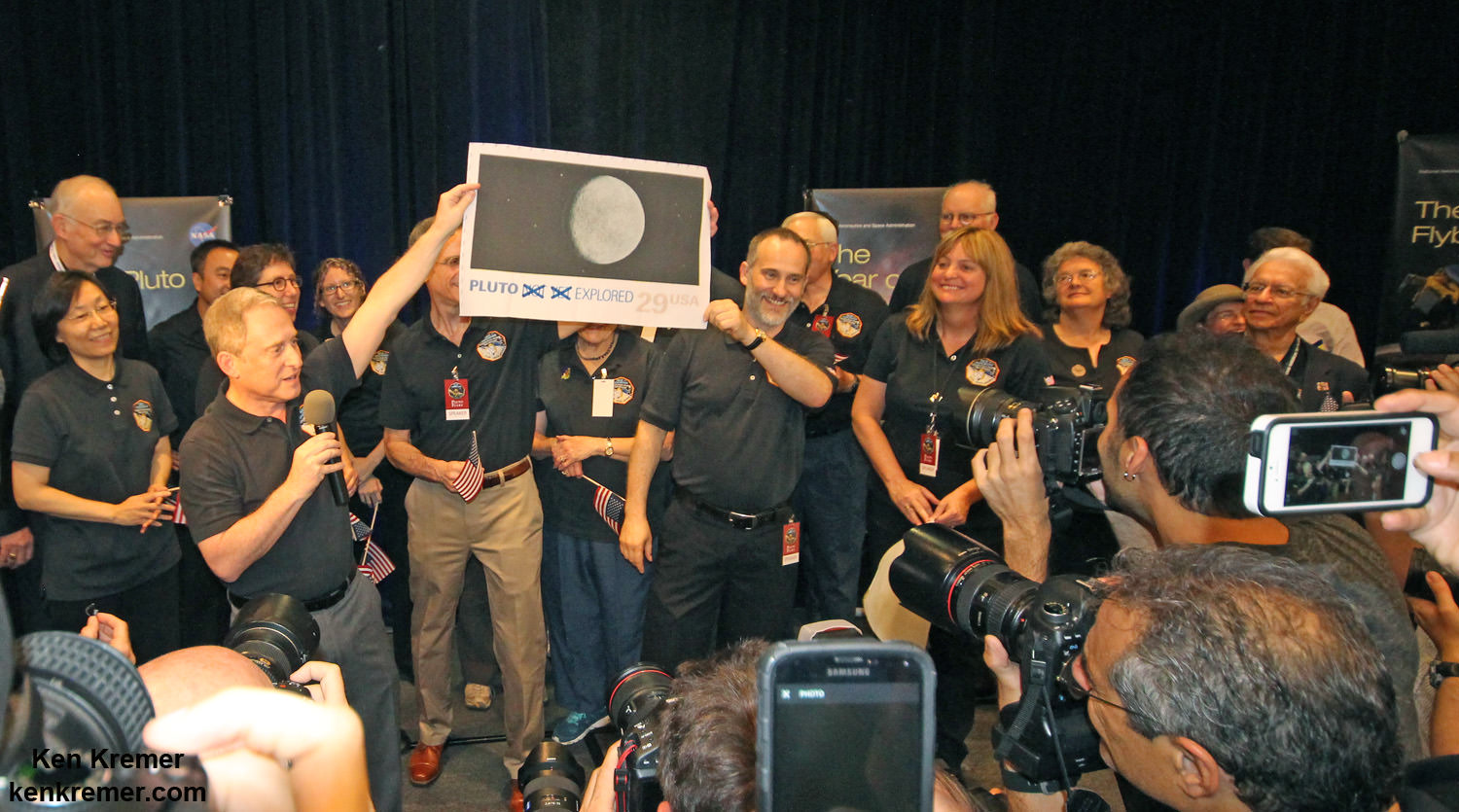

The New Horizons mission team celebrates successful flyby of Pluto in the moments after closest approach at 7:49 a.m. EDT on July 14, 2015. New Horizons Principal Investigator Alan Stern of Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO., left, Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) Director Ralph Semmel, center, and New Horizons Co-Investigator Will Grundy Lowell Observatory hold an enlarged print of an U.S. stamp with their suggested update after Pluto became the final planet in our solar system to be explored by an American space probe (crossing out the words ‘not yet’) – at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Credit: Ken Kremer/kenkremer.com