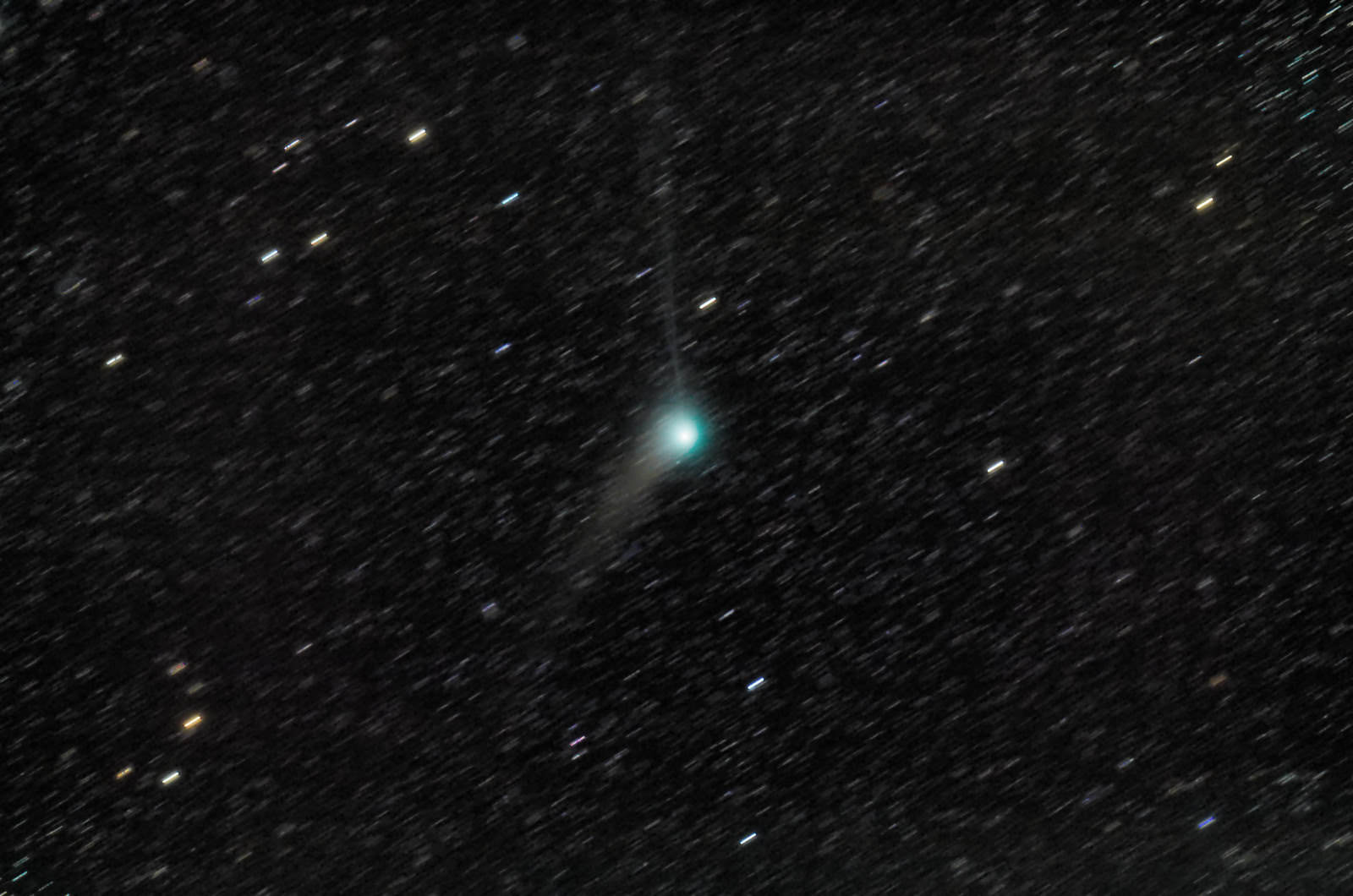
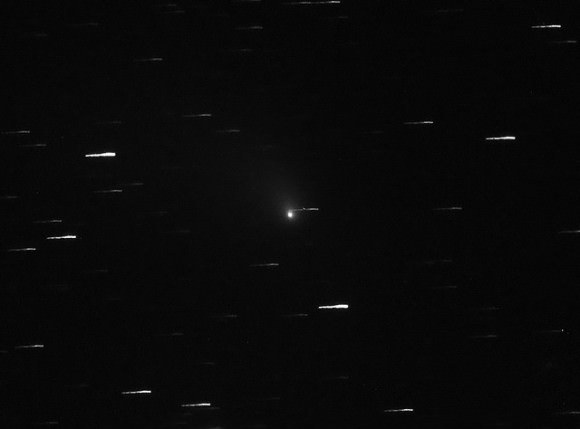
Comet C/2012 K1 PanSTARRS, one of the most dependable comets of 2014, may put on its encore performance over the coming weeks for southern hemisphere observers.
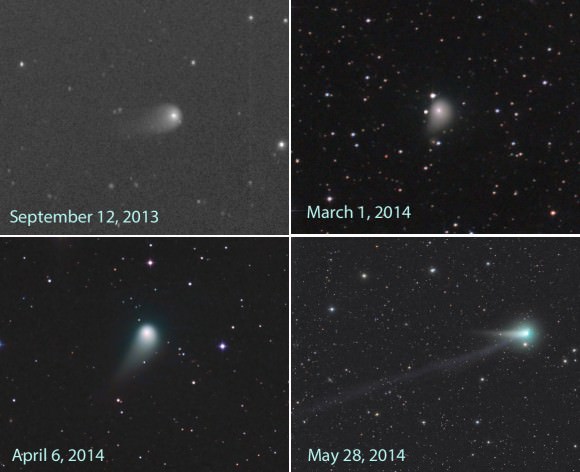
First, the story thus far. Discovered as a +19th magnitude smudge along the borders of the constellations Ophiuchus and Hercules in mid-May 2012 courtesy of the Panoramic Survey Telescope And Rapid Response System (PanSTARRS) based atop Haleakala on the Hawaiian island of Maui, astronomers soon realized that comet C/2012 K1 PanSTARRS would be something special.
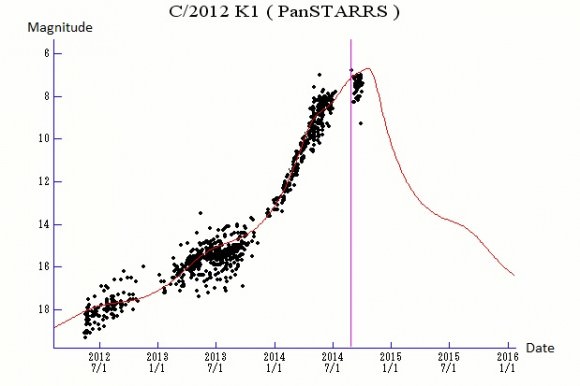
The comet broke +10th magnitude to become a visible binocular object in early 2014, and wowed northern hemisphere observers as it vaulted across the constellations of Boötes and Ursa Major this past spring.
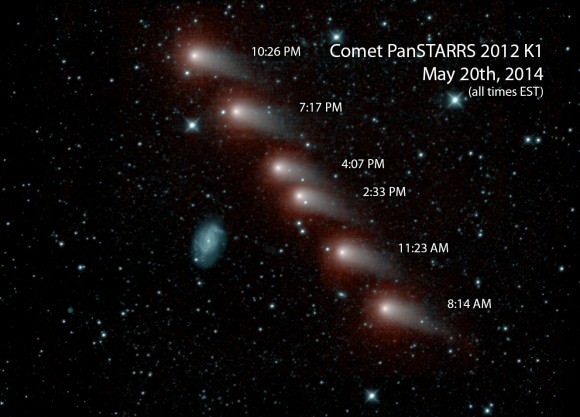

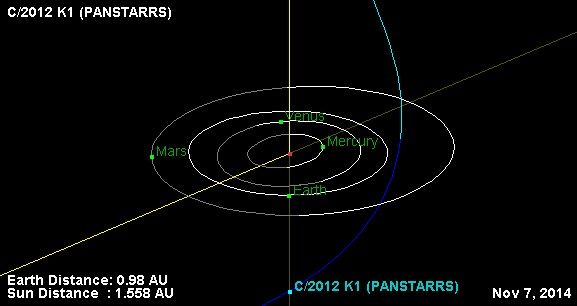
The comet is approaching the inner solar system on a retrograde, highly-inclined orbit tilted 142 degrees relative the ecliptic. This bizarre orbit also assures that the comet will actually reach opposition twice in 2014 as seen from our earthly vantage point: once on April 15th, and another opposition coming right up on November 7th.
As was the case with comet Hale-Bopp way back in 1997, had C/2012 K1 PanSTARRS arrived six months earlier or later, we would’ve been in for a truly spectacular show, as the comet reached perihelion on August 27th, 2014, only 0.05 A.U.s (4.6 million miles or 7.7 million kilometres) outside the orbit of the Earth! But such a spectacle was not to be… back in ’97, Hale-Bopp’s enormous size — featuring a nucleus estimated 40 to 60 kilometres across — made for a grand show regardless… fast forward to 2014, and the tinier nucleus of K1 PanSTARRS has been relegated to binocular status only.
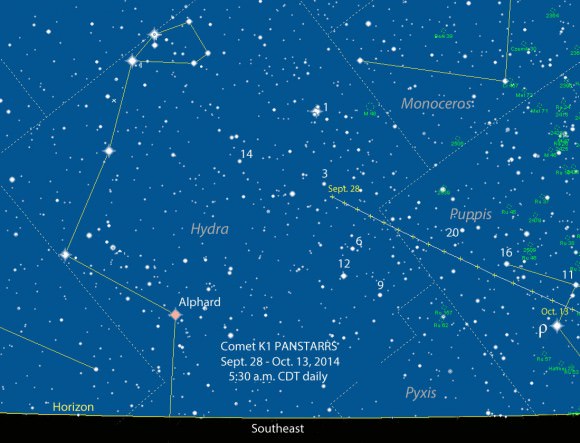
From here on out, K1 PanSTARRS is headed south “with a bullet” and into memory for most northern hemisphere observers. We spied the comet this morning low to the south near +3rd magnitude Nu Puppis in the pre-dawn sky with our trusty 15×45 binocs from Yuma, Arizona, for what will probably be our last time. This also means that the time to catch a last glimpse of K1 PanSTARRS for northern hemisphere viewers is now. This week sees the comet transiting just 20 degrees above the southern horizon at 3:00 to 4:00 AM local for observers based from latitude 30 degrees north as it crosses the constellation Puppis. The bright star Sirius nearly shares the same position as the comet in right ascension this week, and K1 PanSTARRS sits about 24 degrees south of the Dog Star.
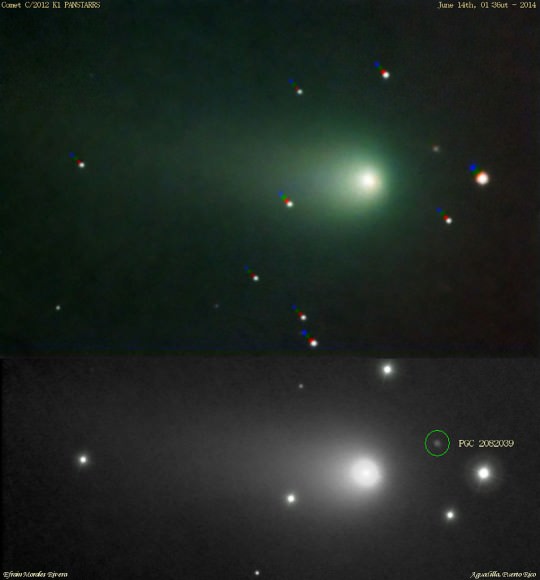

Halloween sees the comet even lower, crossing the southern meridian at only 13 degrees elevation as seen from latitude 30 degrees north. Draw a straight line from Sirius to the south celestial pole around this date to find the comet just 5 degrees to the north of Canopus.
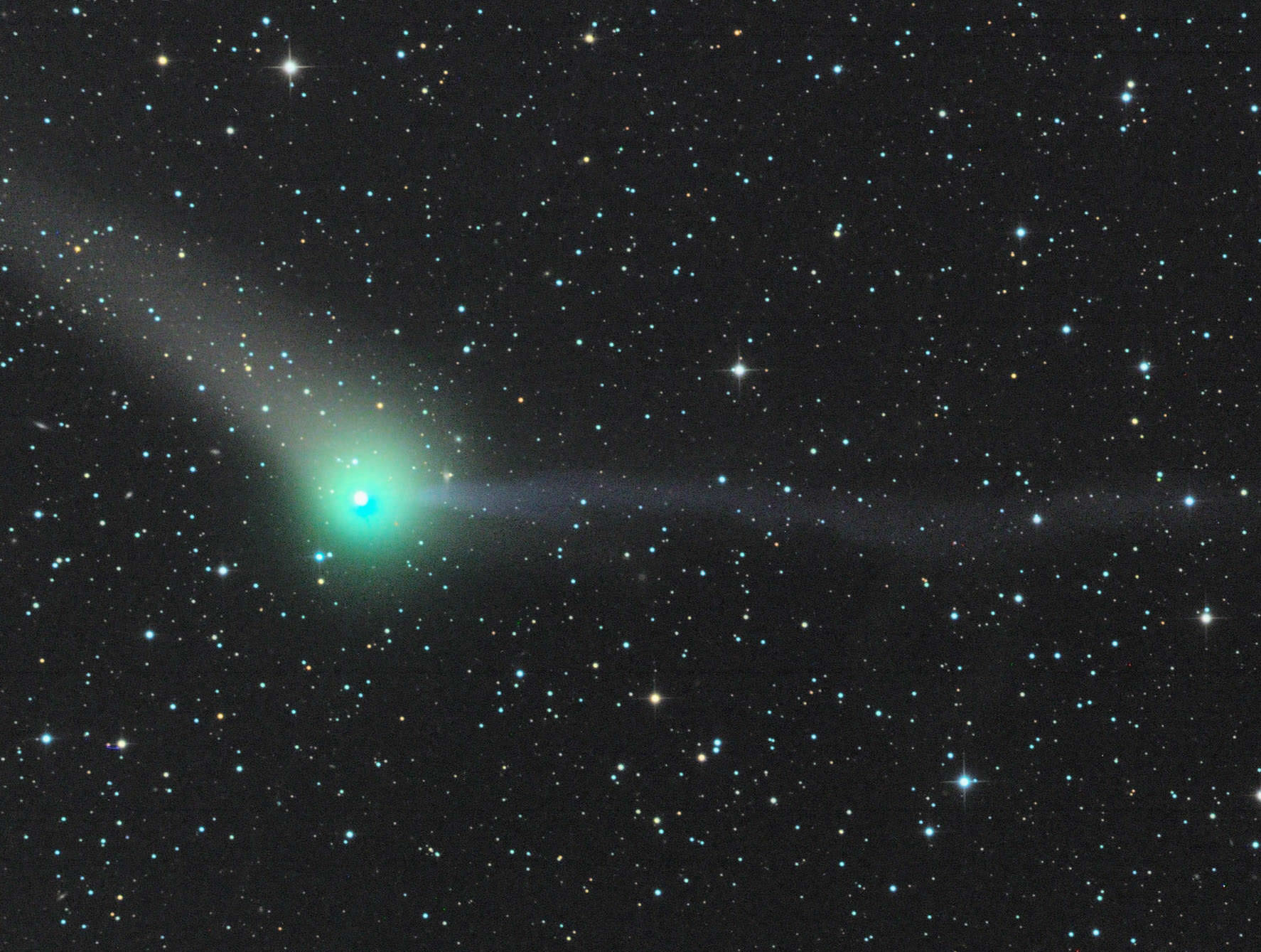
But the show is just beginning for southern hemisphere residents. Observing from the town of Bright Australia, Robert Kaufmann recently noted in a posting on the Yahoo Groups Comet Observer’s message board that the comet currently exhibits a 4’ wide coma shining at about magnitude +7.3 with an elevation of 28 degrees above the horizon on October 25th.
And if the comet holds steady in brightness, it may break the visual threshold and become a naked eye object as seen from a dark sky site in early November.
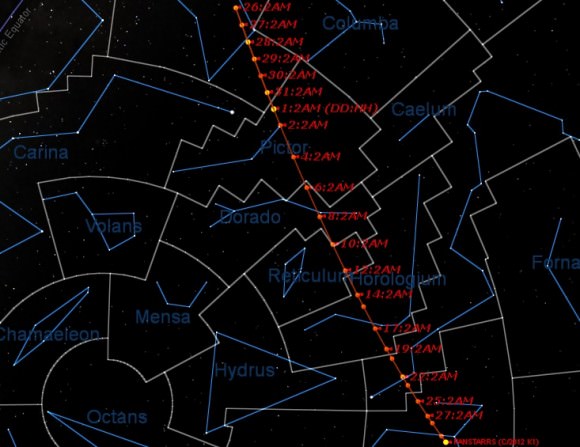
The comet will be literally “hauling tail” across the constellation Dorado as it nears its second opposition of the year on November 7th, moving about 1.5 degrees a day – 3 times the apparent diameter of the Full Moon – on closest approach.
Currently, the comet has been observed to have an estimated magnitude holding steady at+7 and is predicted to peak at perhaps magnitude +6 early next month. And while it would’ve been great had it arrived 6 months earlier or later, the aforementioned high retrograde inclination of its orbit assured that K1 PanSTARRS was a top performer for both hemispheres in 2014.
Perihelion passage occurred two months ago, but to paraphrase a famous Monty Python skit, Comet K1 PanSTARRS is “not dead yet.” Here are some key observing dates coming right up as the comet gains prominence in the southern hemisphere sky:
(Note that close passages of less than one degree near stars +4th magnitude or brighter only are mentioned).
Oct 31st: Passes closest to Earth, at 0.953 A.U.s distant.
Nov 1st: Crosses into the constellation Pictor.
Nov 2nd: Passes near the +3.8 magnitude star Beta Pictoris.
Nov 6th: Crosses into the constellation Dorado.
Nov 6th: Full Moon occurs, marking the beginning of an unfavorable week for comet hunting.
Nov 7th: The second opposition of the comet for 2014 occurs at 3:00 UT.
Nov 8th: Passes near the +3.3 magnitude star Alpha Doradus.
Nov 11th: Crosses into the constellation Reticulum.
Nov 13th: Crosses into the constellation Horologium.
Nov 14th: Passes 34 degrees from the South Celestial Pole.
Nov 20th: Crosses into the constellation Eridanus.
Nov 22nd: New Moon occurs, marking a week long span optimal for comet-hunting.
Nov 25th: Crosses into the constellation Phoenix.
Dec 6th: Full Moon occurs.
Dec 12th: Passes near the +2.8 magnitude star Alpha Phoenicis (Ankaa).
Dec 18th: Crosses into the constellation Sculptor.
Dec 22nd: New Moon occurs.
Looking at 2015, K1 PanSTARRS will probably fall back below +10th magnitude by late January. The comet will then head back out into the depths of the outer solar system, its multi-million year orbit only slightly altered by its inner solar system passage down into the ~700,000 year range. What will Earth be like on that far off date? Will human eyes greet the comet once again, and will anyone remember its appearance way back in the mists of time in 2014? All thoughts to ponder as we bid fair well to Comet C/2012 K1 PanSTARRS, a fine binocular comet indeed.