Image Caption: This image of comet ISON (C/2012 S1) ) from NASA’s Deep Impact spacecraft clearly shows the coma and nucleus on Jan. 17/18, 2013 beyond the orbit of Jupiter. See the dramatic new movie sequence below. It combines all 146 80-second clear filter exposures for a total integration time of 11680 seconds (about 3.25 hours). Individual frames were shifted to align the comet at the center before coadding. By keeping the comet centered and adding all of the images together, the stars effectively get smeared so the long streaks are the trails of background stars. Some have called it the “Comet of the Century.” Credit: NASA
NASA’s legendary Deep Impact comet smashing spacecraft has just scored another major coup – Imaging the newly discovered Comet ISON. The comet could possibly become one of the brightest comets ever late this year as it passes through the inner Solar System and swings around the Sun for the very first time in history – loaded with pristine, volatile material just raring to burst violently forth from the eerie surface, and is therefore extremely interesting to scientists. See the Movie below
“Comet ISON was just imaged by Deep Impact out by Jupiter on Jan. 17 and 18,” said Dr. Jim Green, Director of NASA Planetary Sciences at NASA HQ, in an exclusive interview with Universe Today on the campus of Princeton University. “We will try to look at ISON with the Curiosity rover as it flies past Mars, and with other NASA assets in space [along the way]. It should be spectacular!”
“We are all, ops team and science team, thrilled that we were able to make these observations when the comet was still more than 5 AU from the sun,” said Deep Impact Principal Investigator Prof. Michael A’Hearn of the University of Maryland, in an exclusive interview with Universe Today.
ISON could potentially become the next “Great Comet”, according to NASA. Deep Impact is the first spacecraft to observe ISON.
“We are continuing to observe ISON – it is observable from Deep Impact into mid-March 2013,” A’Hearn told me.
ISON will be the 4th comet observed by Deep Impact. On July 4, 2005 the spacecraft conducted a close flyby of Comet Tempel 1 and delivered a comet smashing impactor that made headlines worldwide. Next, it flew near Hartley 2 in Nov. 2010. In January 2012, the spacecraft performed a long distance imaging campaign on comet C/2009 P1 (Garradd). And it has enough fuel remaining for an Asteroid encounter slated for 2020 !
“NASA’s assets at Mars should be able to observe ISON because it will fly really, really close to Mars!” Green said with a big smile – and me too, as he showed me a sneak preview of the brand new Deep Impact movie.
“ISON observations are in the cue for Curiosity from Mars surface and from orbit with NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) – and we’ll see how it works out. It should be pretty spectacular. We will absolutely try with Curiosity’s high resolution Mastcam 100 camera.”
“LRO (NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter) also has a good shot at ISON.”
“Because of the possibility of observations of for example ISON, with probes like Deep Impact is why we want to keep NASA’s [older] assets viable.”
146 visible light images snapped by Deep Impact just days ago on Jan. 17 and 18, have been compiled into a dramatic video showing ISON speeding through interplanetary space back dropped by distant star fields – see above and below. The new images were taken by the probes Medium-Resolution Imager (MRI) over a 36-hour period from a distance of 493 million miles (793 million kilometers).
“A composite image, combining all of the Jan 17/18 data – after cleaning up the cosmic rays and improving the S/N (signal to noise ratio) clearly shows the comet has a coma and tail,” said Tony Farnham, a Deep Impact research scientist at the University of Maryland, to Universe Today.
Video Caption: This series of images of comet C/2012 S1 (ISON) was taken by the Medium-Resolution Imager (MRI) of NASA’s Deep Impact spacecraft over a 36-hour period on Jan. 17 and 18, 2013. At the time, the spacecraft was 493 million miles (793 million kilometers) from the comet. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UMD
ISON is a conglomeration of ice and dust and a long period, sun-grazing comet.
“It is coming in from the Solar System’s Oort cloud at the edge of the Solar System”, said Green, and was likely disturbed out of its established orbit by a passing star or other gravitational effects stemming from the Milky Way galaxy. “It will pass within 2.2 solar radii during perihelion and the Sun will either blast it apart or it will survive.”
Despite still being in the outer Solar System and a long distance from the Sun, ISON is already quite “variable” said A’Hearn, and it’s actively spewing material and ‘outgassing”.
The tail extending from the nucleus was already more than 40,000 miles (64,400 kilometers) long on Jan. 18. It’s a science mystery as to why and the Deep Impact team aims to try and determine why.
In addition to imaging, Deep Impact will also begin collecting long range spectral observations in the next week or so to help answer key questions.
“In mid-February, the solar elongation will allow IR (infrared) spectra for a few weeks,” A’Hearn elaborated.
“The 6-7% variability that we observed in the first day of observing shows that there is variable ‘outgassing’, presumably modulated by rotation of the nucleus. We hope to pin down the rotational period with the continuing images.”
“The interesting question is what drives the outgassing!”
Since ISON is still a very great distance away at more than 5 AU, data collection will not be an easy task. The comet is 5.1 AU from the Sun and 5.3 AU from Deep Impact. And the mission could also be imperiled by looming slashes to NASA’s budget if the Federal sequester actually happens in March.
“Getting spectra will be a real challenge because, at these large heliocentric and geocentric distances, the comet is really faint. However, maybe we can test whether CO2 is driving the outgassing,” Ahearn explained.
“Since we have the only facility capable of measuring CO2, it will be important to observe again in our second window in July-August, but that depends on NASA finding a little more money for us.”
“We, both the ops team and the science team, are funded only for the observations through March,” A’Hearn stated.
Although observing predictions for the brightness of comets are sometimes notoriously wrong and they can fade away precipitously, there is some well founded hope that ISON could put on a spectacular sky show for observers in both the northern and southern hemispheres.
The comet will continue to expand in size and grow in brightness as it journeys inward.
“ISON might be pretty spectacular,” said Green. “If things work out it might become bright enough to see during the day and be brighter than the Moon. The tail might be 90 degrees.”
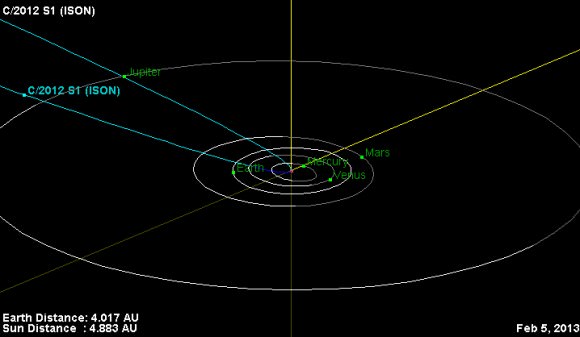
Image caption: This is the orbital trajectory of comet C/2012 S1 (ISON). The comet is currently located just inside the orbit of Jupiter. In November 2013, ISON will pass less than 1.1 million miles (1.8 million kilometers) from the sun’s surface. The fierce heating it experiences during this close approach to the sun could turn the comet into a bright naked-eye object. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The best times to observe the comets head and growing tail will be from Nov. 2013 to Jan. 2014, if it survives its closest approach to the Sun, known as perihelion, on Nov. 28, 2013 and doesn’t break apart.
There’s no need to worry about doomsday predictions from conspiracy theorists. At its closest approach next Christmas season on Dec. 26, 2013, ISON will pass by Earth at a safe distance of some 40 million miles.
A pair of Russian astronomers only recently discovered the comet on Sept. 21, 2012, using the International Scientific Optical Network’s 16-inch (40-centimeter) telescope near Kislovodsk.
The study of comets has very important implications for understanding the evolution of not just the Solar System but also the origin of life on Earth. Comets delivered a significant portion of the early Earth’s water as well as a range of both simple and complex organic molecules – the building blocks of life.
Image caption. Deep Impact images Comet Tempel 1 alive with light after colliding with the impactor spacecraft on July 4, 2005. CREDIT: NASA/JPL-Caltech/UMD


![HRI_937_1[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/02/HRI_937_11-580x580.jpg)