Greetings, fellow SkyWatchers! Even if you missed the peak of the Perseid meteor shower, there will still be plenty of “strays” to sparkle this week’s dark nights. For astronomy without a telescope, be sure to check out all the planetary alignments – and tell your friends! When you’re ready to learn more about what to view and when this week, then meet me in the back yard…
Monday, August 13 – Celestial scenery alert! If you’re out before dawn this morning, look for the very close pairing of Venus and the slender crescent Moon. For viewers in the north-eastern Asia area, this is an occultation event, so be sure to check resources for times and locations in your area! How about some more eye candy? Then check out the splendid alignment of Saturn, Mars and Spica just after sky dark. Look for the blue/white star to the west, accompanied by red Mars to the east and yellow Saturn even higher to the east. The trio will be roughly separated by the same distance from each other and the colors will be a welcome sight. Be sure to alert your family and friends to all the celestial action that doesn’t require a telescope today!
Tonight, begin with just your eyes as you gaze about four fingerwidths above the top of the Sagittarius “teapot dome” for an open window on the stars and mighty M24 (Right Ascension: 18 : 18.4 – Declination: -18 : 25)…
This huge, hazy patch of stars is in reality an area of space known as “Baade’s Window” – an area free of obscuring gas and dust. Cataloged by Messier in 1764 as object 24, even small binoculars will reveal the incredible vista of the “Sagittarius Star Cloud.” Although it’s actually not a cluster, but rather a clean view of an area of our own galaxy’s spiral arm, that will not lessen the impact when viewed through a telescope. Spanning a degree and a half of sky, it is one of the few areas in which even a novice can easily perceive areas of dark dust.
For larger telescopes, look for the dim, open cluster NGC 6603 (Right Ascension: 18 : 18.4 – Declination: -18 : 25) in the northeastern position of the Window. There are two very notable dark nebulae, B92 and B93, located in the northern segment as well. Near teardrop shaped B92 and its single central star, you should spot open cluster Collinder 469 and also Markarian 38 south of B93. You’ll find B86 near Gamma Sagittarii . At the southern edge of the star cloud, look for emission nebula IC 1283-1284, along with the reflection nebulae NGC 6589 (Right Ascension: 18 : 16.9 – Declination: -19 : 46) and NGC 6590 (Right Ascension: 18 : 17.0 – Declination: -19 : 53) and open cluster NGC 6595 (Right Ascension: 18 : 17.0 – Declination: -19 : 53). Still up for more? Then head west to see if you can find 12th-magnitude planetary nebula NGC 6567 (Right Ascension: 18 : 13.7 – Declination: -19 : 05).
Even if you don’t accept these challenges, you can still enjoy looking at a 560 light-year swatch of stars from one of the Milky Way’s loving arms! (If you’re out late, look for Mira… It was discovered by Fabricius on this date in 1596.)
Tuesday, August 14 – Celestial scenery alert! Be out just after sunset to catch a splendid stellar and planetary conjunction. To the west you’ll see bright Spica. Just above it, Mars. And just above that? Saturn! The trio are all separated by just a few degrees, so be sure to stop and enjoy!
Your first challenge for tonight will be to venture about three fingerwidths northeast of Lambda Sagittarii to visit a well-known but little visited galactic cluster – M25 (Right Ascension: 18 : 31.6 – Declination: -19 : 15).
First discovered by Cheseaux and then cataloged by Messier, it was observed and recorded by William Herschel, Johann Elert Bode, Admiral Smythe and T. W. Webb…but never added to the NGC catalog of John Herschel! Thanks to J.L.E. Dreyer, it did make the second Index Catalog as IC 4725.
Seen with even the slightest optical aid, this 5th magnitude cluster contains two G-type giants as well as a Delta Cephei-type variable with the designation of U, which changes about one magnitude in a period of less than a week. It’s very old for an open cluster, perhaps near 90 million years, and the light you see tonight left the cluster over 2000 years ago. While binoculars will see around a double handful of bright stars overlaying fainter members, telescopes will reveal more and more as aperture increases. At one time it was believed to have only about 30 members, but this was later revised to 86. But recent studies by Archinal and Hynes indicate it may have as many as 601 member stars!
Wednesday, August 15 – Celestial scenery alert! Get up before dawn to spot Mercury low on the eastern horizon, a very tiny crescent Moon to its west/southwest and brilliant Venus ruling above it all! To add to the mix, you’ll see the pairing of the Gemini Twins – Castor and Pollux – just about a handspan above Mercury and luminous Procyon about the same distance due south. If you missed your opportunity to view Spica, Mars and Saturn on Monday, don’t worry. The colorful trio is still around tonight just after sky dark to the west, but now you can see that Mars has moved slightly to the south. Ain’t celestial mechanics grand?!
Tonight we’ll head back to Scorpius to have a look at three pristine open clusters. Begin your starhop at the colorful southern Zeta pair and head north less than one degree for NGC 6231 (Right Ascension: 16 : 54.0 – Declination: -41 : 48).
Wonderfully bright in binoculars and well resolved to the telescope, this tight open cluster was first discovered by Hodierna before 1654. De Cheseaux cataloged it as object 9, Lacaille as II.13, Dunlop as 499, Melotte as 153, and Collinder as 315. No matter what catalog number you chose to put in your notes, you’ll find the 3.2 million year young cluster shining as the “Northern Jewelbox!” For high power fans, look for the brightest star in this group – it’s van den Bos 1833, a splendid binary.
About another degree north is loose open cluster Collinder 316, with its stars scattered widely across the sky. Caught on its eastern edge is another cluster known as Trumpler 24, a site where new variables might be found. This entire region is encased in a 90 arc minute faint emission nebula called IC 4628 (Right Ascension: 16 : 57.0 – Declination: -40 : 20) – making this low power journey through southern Scorpius a red hot summer treat!
Thursday, August 16 – If you did not get a chance to look at the Northern Jewelbox region in Scorpius, return again and sweep the area tonight. For those with larger telescopes, we’re going to hop about a degree and a half south of twin Nu for NGC 6242 (Right Ascension: 16 : 55.6 – Declination: -39 : 30).
Discovered by Lacaille and cataloged as I.4, it is also known as Dunlop 520, Melotte 155 and Collinder 317. At roughly magnitude 6, this open cluster is within binocular range, but truly needs a telescope to appreciate its fainter stars. While NGC 6242 might seem like nothing more than a pretty little cluster with a bright double star, it contains an x-ray binary which is a “runaway” black hole. It is surmised that it formed near the galactic center and was vaulted into an eccentric orbit when the progenitor star exploded. Its kinetic energy is much like a neutron star or a millisecond pulsar, and it was the first black hole confirmed to be in motion.
Now head a little more than a degree east-southeast for NGC 6268 (Right Ascension: 17 : 02.4 – Declination: -39 : 44). At a rough magnitude of 9, this small open cluster can be easily observed in smaller scopes and resolved in larger ones. The cluster itself is somewhat lopsided, with more of its members concentrated on the western half of its borders. While it, too, might not seem particularly interesting, this young cluster is highly evolved and contains some magnetic, chemically peculiar stars and Be class, or metal-weak, members.
Friday, August 17 – Today in 1966 Pioneer 7 was launched. It was the second in a series of satellites sent to monitor the solar wind, and study cosmic rays, interplanetary space, and magnetic fields. If you’re out early, be sure to take a look for the close pairing of Mars and Saturn and Spica. If you’ve had the opportunity to view them over the last few days, you can see how quickly Mars has moved! Instead of being in a line, the trio now… well… triangulates!
Tonight it’s New Moon! Let’s return to previous study star Lambda Scorpii and hop three fingerwidths northeast… We’re re-hunting the “Butterfly!”
Easily seen in binoculars and tremendous in the telescope, this brilliant magnitude 4 open cluster was first discovered by Hodierna before 1654 and independently discovered by de Cheseaux as his object 1, before being cataloged by Messier as M6 (Right Ascension: 17 : 40.1 – Declination: -32 : 13). Containing around 80 stars, the light you see tonight left its home in space around the year 473 A.D. It is believed to be around 95 million years old and contains a single yellow supergiant – the variable BM Scorpii. While most of M6?s stars are hot, blue main sequence, the unique shape of this cluster gives it not only visual appeal, but wonderful color contrast as well!
Now let’s head towards more unusual open clusters – this time in Cygnus. Starting with Gamma Cygni, locate a loose cluster involving Gamma, Do (Dolidze) 43. Now shift two degrees southwest to pick up Do 42 as well. Don’t confuse Do 42 with nearby M29 though, for the two look very similar. For fans of the “Double Cluster” in Perseus, you’ll like the next pairing! Shift another half degree southwest along the body of Cygnus to pick out Do 40 and Do 41. This pretty pair can be placed in the same low power field. By moving another half degree due west, you’ll find highly populated Do 39 and that, too, is a double treat. The brighter clump of stars in the same low power field is IC 4996 (Right Ascension: 20 : 16.5 – Declination: +37 : 38).
Now for two bright open clusters. The first, Ruprecht 173 is about a degree northwest of Epsilon Cygni. You’ll truly appreciate this heavily populated star cluster! The next is as easy as identifying the constellation of Lyra. Just southeast of bright Vega is a wonderful double for binoculars, Delta 1 and 2 – the easternmost most two stars in the lyre. This bright pair is part of an open cluster known as Stephenson 1.
Saturday, August 18 – On this day in 1868, Norman Lockyer was very busy as he was the first to see helium absorption lines in the Sun’s spectrum. Tonight we’ll take a walk from helium rich Lambda Scorpii about three fingerwidths east-northeast to an even more prominent area of stars that was known to Ptolemy as far back as 130 AD.
Astronomers throughout the ages have spent time with this cluster: Hodierna as Ha II.2; Halley in 1678 as number 29, Derham in 1733 as number 16, De Cheseaux as number 10, Lacaille as II.14; Bode as 41; once for William Herschel and again for John as h 3710; Dreyer as NGC 6475… But we know it best as Messier Object 7 (Right Ascension: 17 : 53.9 – Declination: -34 : 49).
Set against the backdrop of the Milky Way, even the smallest of binoculars will enjoy this bright open cluster while telescopes can resolve its 80 members. Roughly 800 light-years away, it contains many different spectral types in various stages of evolution, giving the cluster an apparent age of about 260 million years. Full of binaries and close doubles, an extreme test of tonight’s lighting conditions would be to see if you can spot the 11th magnitude globular cluster NGC 6453 (Right Ascension: 17 : 50.9 – Declination: -34 : 36) to the northwest!
And for last, the densely populated open cluster M11 (Right Ascension: 18 : 51.1 – Declination: -06 : 16). The “Wild Duck” cluster soars about a fist’s width northeast of M16. Dominated by a single 8th magnitude star, this conically-shaped 3,000 member assembly of stardust easily resolves into innumerable stars with any significant amount of magnification. Through intermediate aperture, this 6000 light-year distant, 250 million year old cluster takes on a new form as several hundred 13th and 14th magnitude members begin to spill outside its V-shaped bounds! Discovered by Gottfried Kirch of Berlin observatory in 1681, the cluster was first noted as stellar by William Derham in the first third of the 18th century. Charles Messier added it to his catalog May 30, 1764.
Sunday, August 19 – Born today in 1646, let’s have a look at John Flamsteed. He was an English astronomer with a passion for what he did. Despite a rather difficult childhood and no formal education, he went on to become the First Observer at the Royal Observatory and his catalog of 3000 stars was perhaps the most accurate yet published. Flamsteed star numbers are still in use. Also born on this day was Orville Wright, in 1871, and in 1891, Milton Humason, a colleague of Edwin Hubble at Mts. Wilson and Palomar. The latter was instrumental in measuring the faint spectra of galaxies, which in turn provided evidence for the expansion of the Universe.
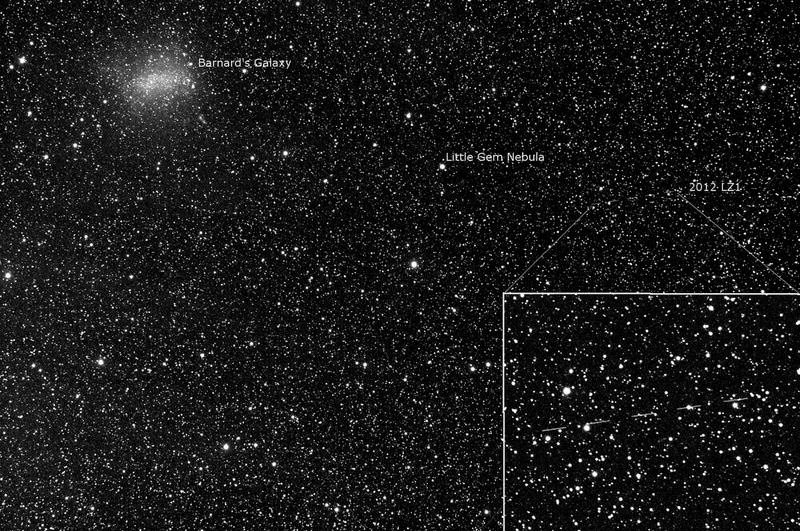
This would be a great time for us to have a look at one of the summer’s most curious galaxies – NGC 6822 (Right Ascension: 19 : 44.9 – Declination: -14 : 48). This study is a telescopic challenge even for skilled observers. Set your sights roughly 2 degrees northeast of easy double 54 Sagittarii, and have a look at this distant dwarf galaxy bound to our own Milky Way by invisible gravitational attraction…
Named after its discoverer (E. E. Barnard – 1884), “Barnard’s Galaxy” is a not-so-nearby member of our local galaxy group. Discovered with a 6? refractor, this 1.7 million light-year distant galaxy is not easily found, but can be seen with very dark sky conditions and at the lowest possible power. Due to large apparent size, and overall faintness (magnitude 9), low power is essential in larger telescopes to give a better sense of the galaxy’s frontier. Observers using large scopes will see faint regions of glowing gas (HII regions) and unresolved concentrations of bright stars. To distinguish them, try a nebula filter to enhance the HII and downplay the star fields. Barnard’s Galaxy appears like a very faint open cluster overlaid with a sheen of nebulosity, but the practiced eye using the above technique will clearly see that the “shine” behind the stars is extragalactic in nature.
Now look less than a degree north-northwest to turn up pale blue-green NGC 6818 (Right Ascension: 19 : 44.0 – Declination: -14 : 09) – the “Little Gem” planetary. Easily found in any size scope, this bright and condensed nebula reveals its annular nature in larger scopes but hints at it in scopes as small as 6?. Use a super wide field long-focus eyepiece to frame them both!
Until next week? Wishing you clear skies!