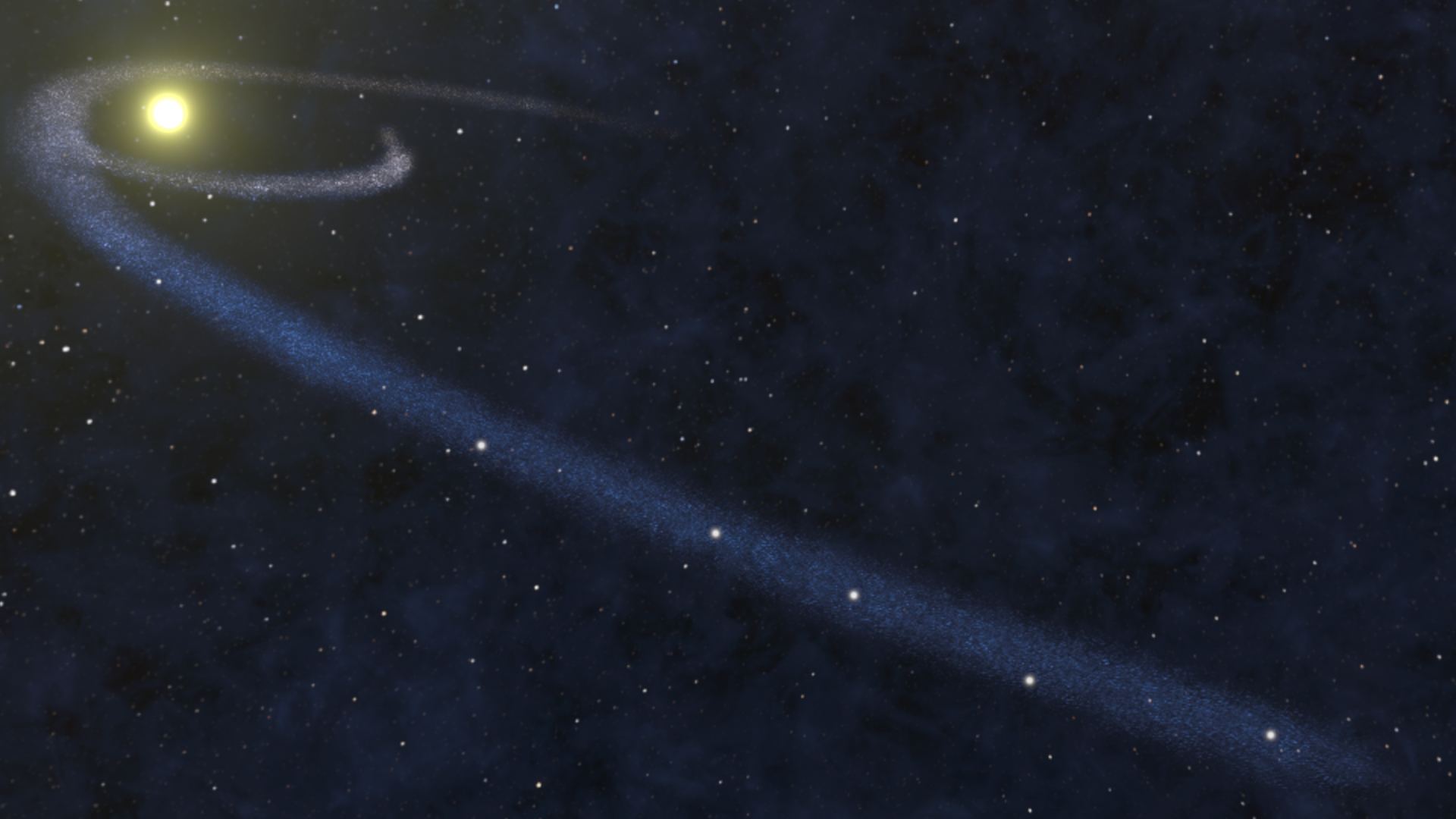
Where is all the missing matter? That question has plagued astronomers for decades, because the Universe looks emptier than it should, given current theories about its makeup. Most of the Universe (70%) appears to be composed of Dark Energy, the mysterious force which is causing the Universe’s rate of expansion to increase. Another 25% of the Universe is Dark Matter, an unknown substance which cannot be seen, but has been theorized to explain the otherwise inexplicable gravitational forces which govern the formation of galaxies. That leaves Baryonic Matter – all the normal ‘stuff’ like you, me, the trees, the planets, and the stars – to make up just 5% of the Universe. But when astronomers look out into the sky, there doesn’t even seem to be enough normal matter to make up 5%. Some of the normal matter is missing!
Continue reading “A New Technique to Find Cold Gas Streams That Might Make up the Missing (Normal) Matter in the Universe”Astronomers are Starting to Understand the Quasar Lifecycle

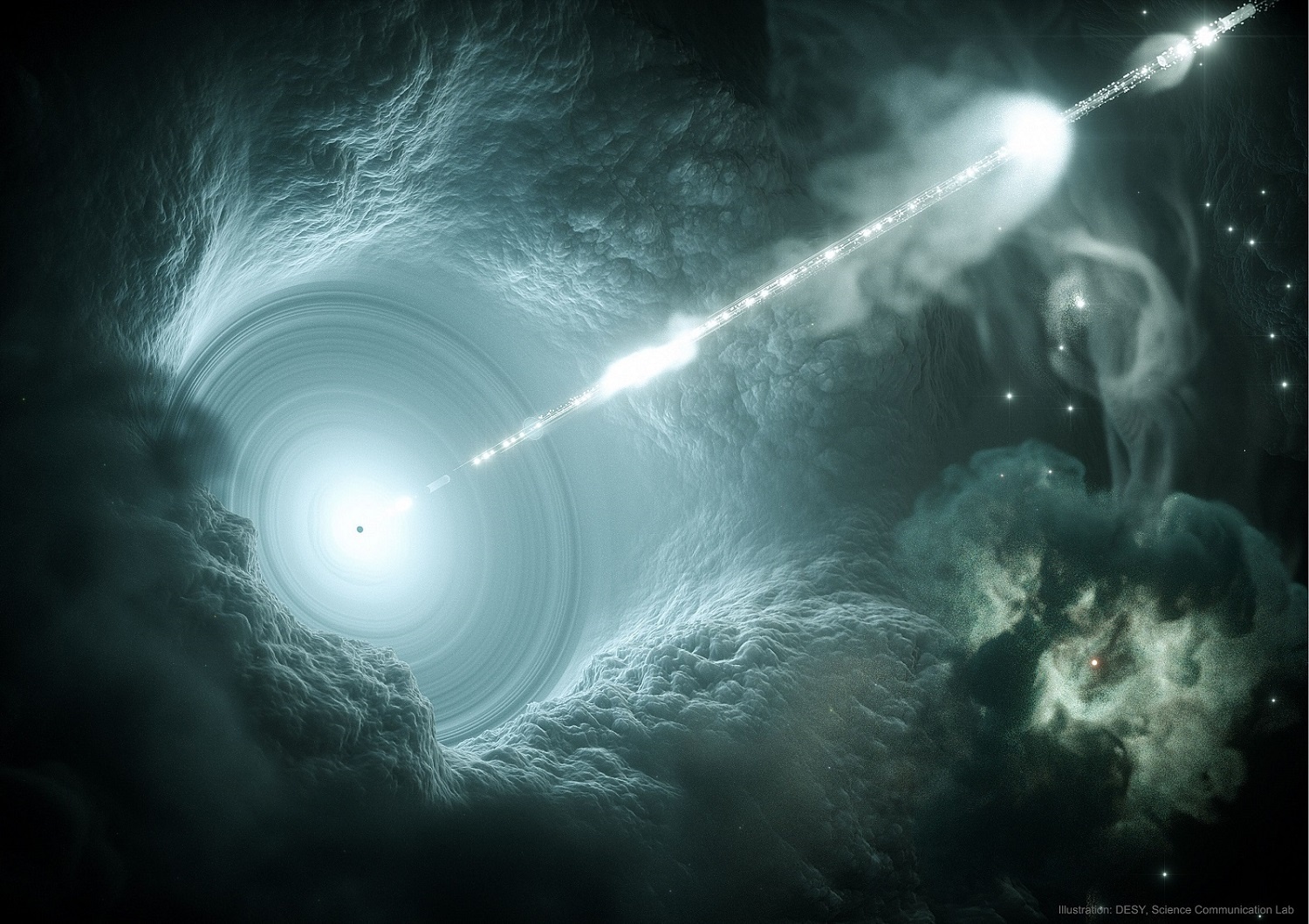
Supermassive black holes have a complicated lifecycle. Sometimes they’re “on”, blasting out tremendous amounts of energy, and sometimes they’re “off’, where they sleep like dragons in their caves. By comparing the proportion of high-energy to low-energy waves emitted by quasars, astronomers are beginning to pin down how many black holes are sleeping, and when they’re likely to wake back up.
Continue reading “Astronomers are Starting to Understand the Quasar Lifecycle”A Galaxy is Making New Stars Faster Than its Black Hole Can Starve Them for Fuel

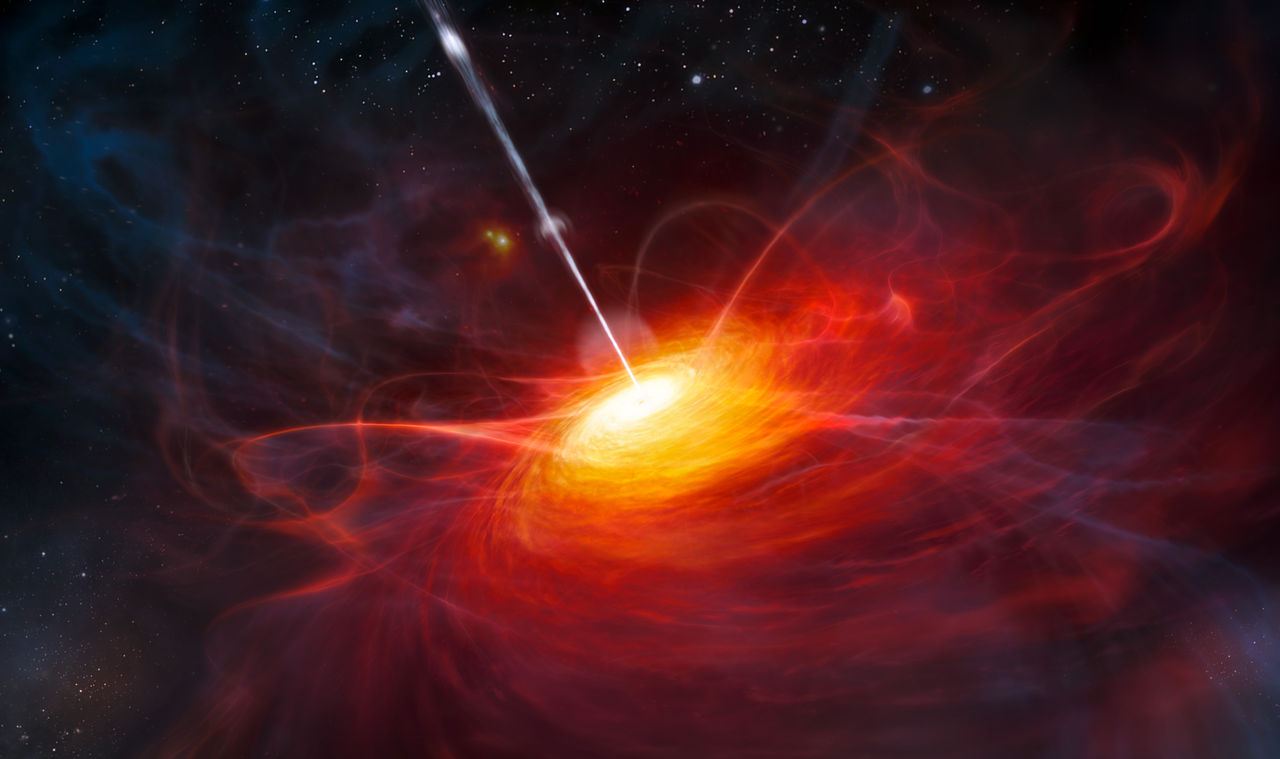
A monster lurks at the heart of many galaxies – even our own Milky Way. This monster possesses the mass of millions or billions of Suns. Immense gravity shrouds it within a dark cocoon of space and time – a supermassive black hole. But while hidden in darkness and difficult to observe, black holes can also shine brighter than an entire galaxy. When feeding, these sleeping monsters awaken transforming into a quasar – one of the Universe’s most luminous objects. The energy a quasar radiates into space is so powerful, it can interfere with star formation for thousands of light years across their host galaxies. But one galaxy appears to be winning a struggle against its awoken blazing monster and in a recent paper published in the Astrophysical Journal, astronomers are trying to determine how this galaxy survives.
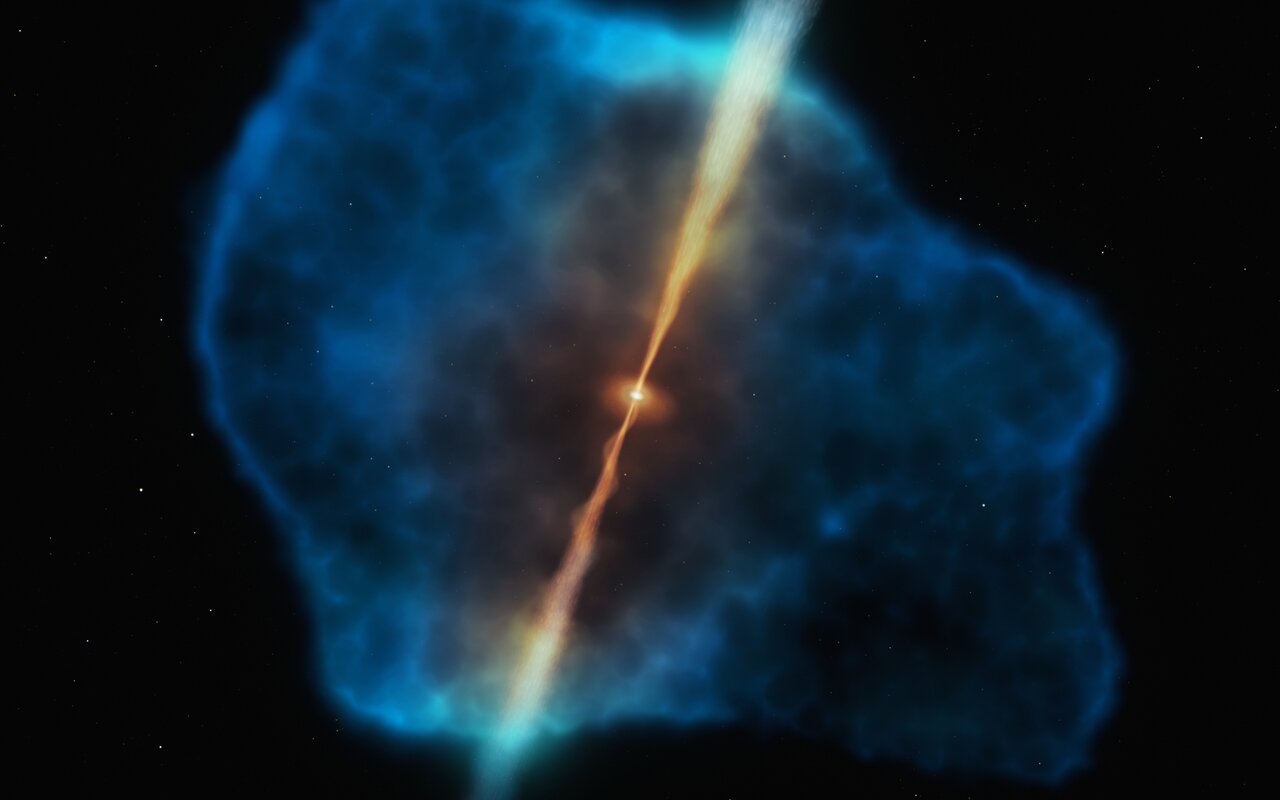
New jets seen blasting out of the center of a galaxy
Giant black holes can launch jets that extend for tens of thousand of light-years, blasting clean out of their host galaxies. These jets can last for tens of millions of years. Recently astronomers have spotted the first-ever jet in the process of forming, creating a cavity in the span of only twenty years.
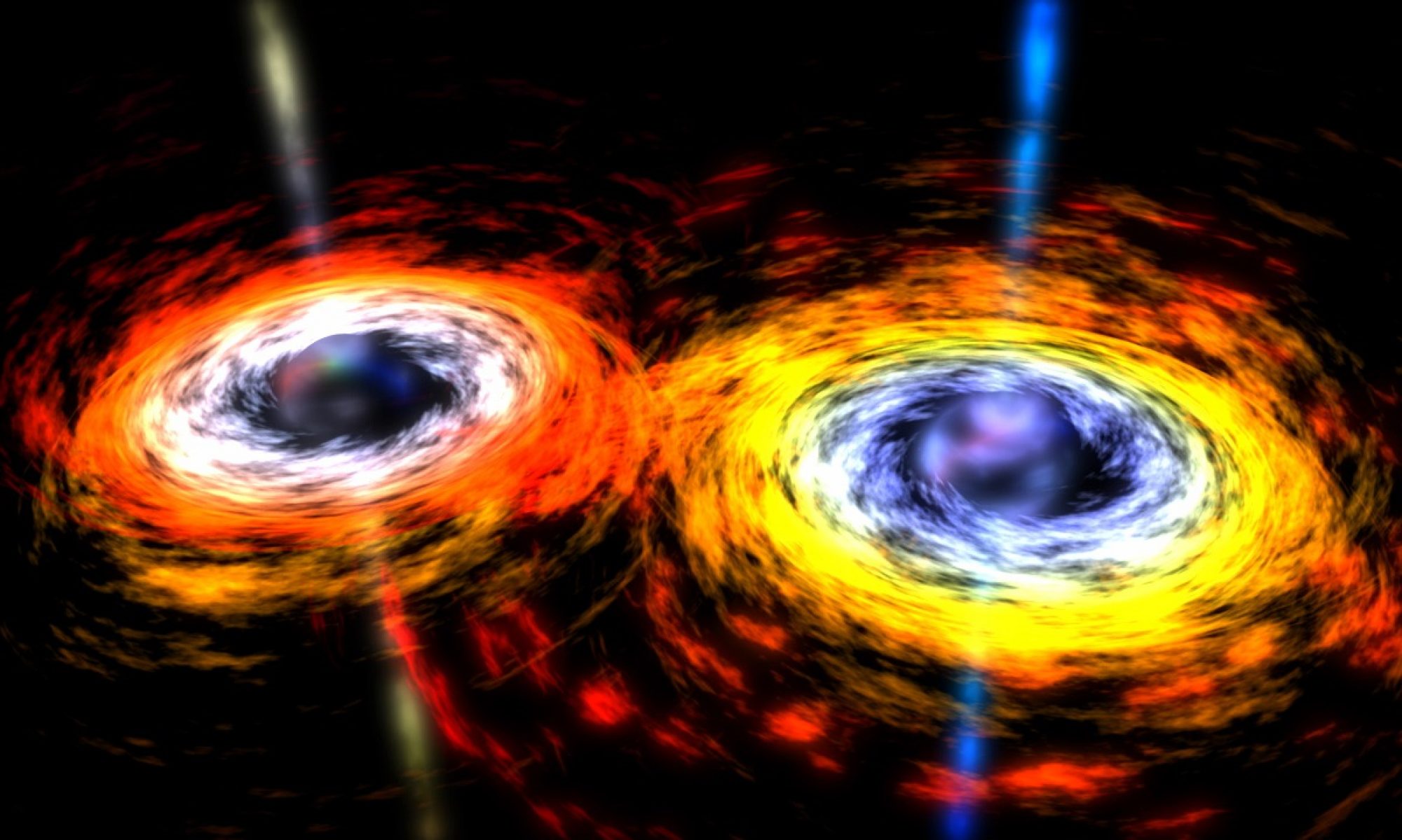
Continue reading “New jets seen blasting out of the center of a galaxy”Some Quasars Actually Contain Two Supermassive Black Holes in the Process of Merging
Quasars are some of the most powerful objects in the Universe. They were first discovered in the 1950s as bright radio sources coming from almost point-like objects. They were given the name quasi-stellar radio sources, or quasars for short. We now know that they are powered by supermassive black holes at the center of distant galaxies.
Continue reading “Some Quasars Actually Contain Two Supermassive Black Holes in the Process of Merging”Quasars can twinkle?
It turns out you can teach an old dog new tricks. With a recent upgrade to a 50-year-old radio telescope, astronomers have spotted nearly a dozen of a rare class of quasars, ones capable of flickering in less than an hour.
Continue reading “Quasars can twinkle?”Quasars are the Biggest Particle Accelerators in the Universe

We puny humans think we can accelerate particles? Look how proud we are of the Large Hadron Collider. But any particle accelerator we build will pale in comparison to Quasars, nature’s champion accelerators.
Those things are beasts.
Read more


