In July of 2015, Russian billionaire Yuri Milner announced the creation of Breakthrough Listen, a decade-long project that would conduct the largest survey to date for signs of extra-terrestrial communications (ETI). As part of his non-profit organization, Breakthrough Initiatives, this survey would rely on the latest in instrumentation and software to observe the 1,000,000 closest stars and 100 closest galaxies.
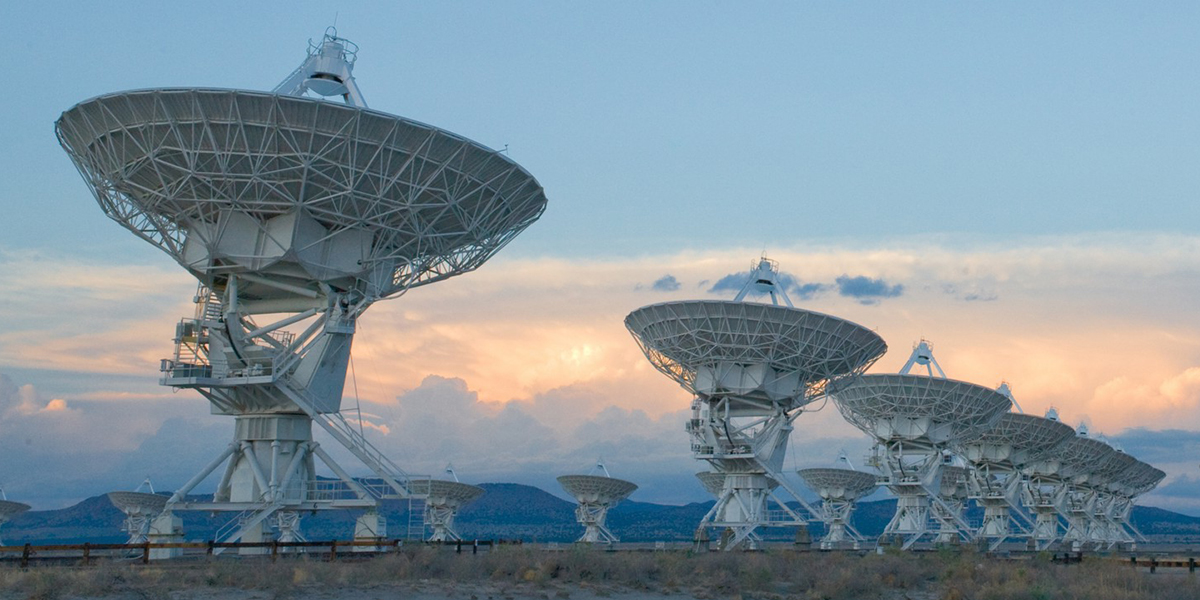
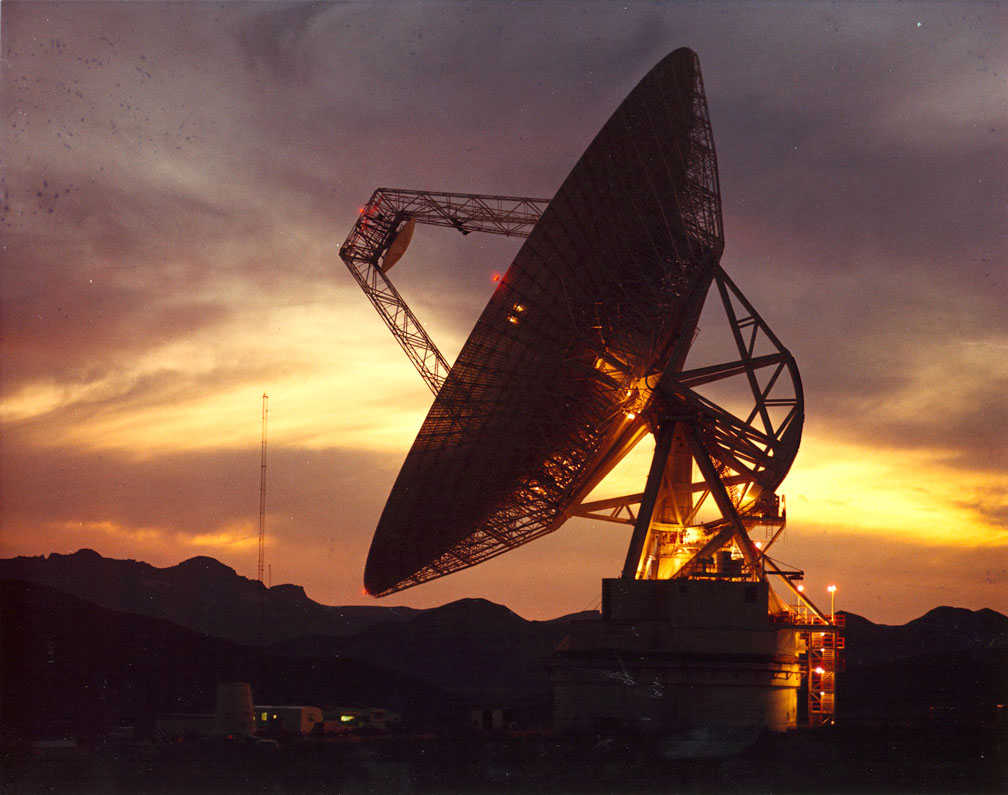
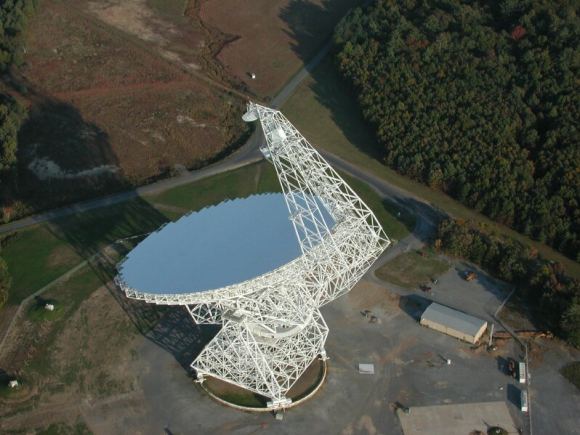
Using the Green Bank Radio Telescope in West Virginia, the Listen science team at UC Berkeley has been observing distant stars for over a year now. And less than a week ago, they observed 15 Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) coming from a dwarf galaxy located three billion light-years away. According to a study that described their findings, this was the first time that repeating FRBs have been seen coming from this source at these frequencies.
The team’s study, titled “FRB 121102: Detection at 4 – 8 GHz band with Breakthrough Listen backend at Green Bank“, was recently published in The Astronomers Telegraph. Led by Dr. Vishal Gajjar – a postdoctoral researcher at the University of California, Berkeley – the team conducted a detailed survey of FRB 121102. This repeating FRB source is located in a dwarf galaxy in Auriga constellation, some 3 billion light-years from Earth.

To clarify, FRBs are brief, bright pulses of radio waves that are periodically detected coming from distant galaxies. This strange astronomical phenomena was first detected in 2007 by Duncan Lorimer and David Narkovic using the Parkes Telescope in Australia. To honor their discovery, FRBs are sometimes referred to as “Lorimer Bursts”. Many FRB sources have been confirmed since then, some of which were found repeating.
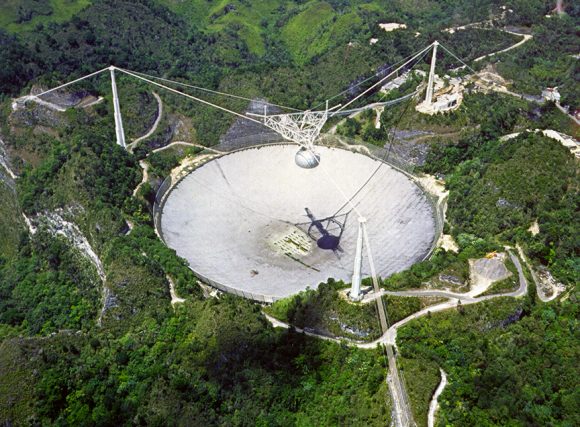
The source known as FRB 121101 was discovered back on November 2nd, 2012, by astronomers using the Arecibo radio telescope. At the time, it was the first FRB to be discovered; and by 2015, it became the first FRB to be seen repeating. This effectively ruled out the possibility that repeating FRBs were caused by catastrophic events, which had previously been theorized.
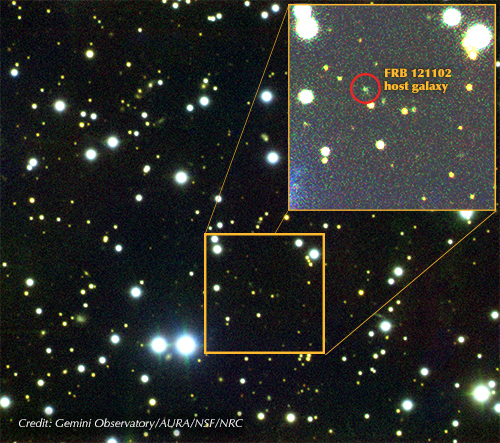
And in 2016, FRB 121102 was the first FRB to have its location pinpointed to such a degree that its host galaxy could be identified. As such, the Listen science team at UC Berkeley was sure to add FRB 121102 to their list of targets. And in the early hours of Saturday, August 26th, Dr. Vishal Gajjar – a postdoctoral researcher at UC Berkeley – observed FRB 121102 using the Green Bank Radio Telescope (GBRT) in West Virginia.
Using the Digital Backend instrument on the GBRT, Dr. Gajjar and the Listen team observed FRB 121102 for five hours. From this, they accumulating 400 terabytes of data in the entire 4 to 8 GHz frequency band which they then analyzed for signs of short pulses over a broad range of frequencies. What they found was evidence of 15 new pulses coming from FRB 121102, which confirmed that it was in a newly active state.

In addition, their observations revealed that the brightest of these 15 emissions occurred at around 7 GHz. This was higher than any repeating FRBs seen to date, which indicated for the first time that they can occur at frequencies higher than previously thought. Last, but not least, the high-resolution data the Listen team collected is expected to yield valuable insights into FRBs for years to come.
This was made possible thanks to the Digital Backend instrument on the GBRT, which is able to record several GHz of bandwidth simultaneously and split the information into billions of individuals channels. This enables scientists to study the proprieties and the frequency spectrum of FRBs with greater precision, and should lead to new theories about the causes of these radio emissions.
So even if these particular signals should prove to not be an indication of extra-terrestrial intelligence, Listen is still pushing the boundaries of what is possible with radio astronomy. And given that Breakthrough Listen is less than two years into its proposed ten-year survey, we can expect many more sources to be observed and studied in the coming years. If there’s evidence of ETI to be found, we’re sure to find out about it sooner or later!
And be sure to check out this video of the Green Bank Telescope and the surveys it allows for, courtesy of Berkeley SETI:
Further Reading: Breakthrough Initiatives