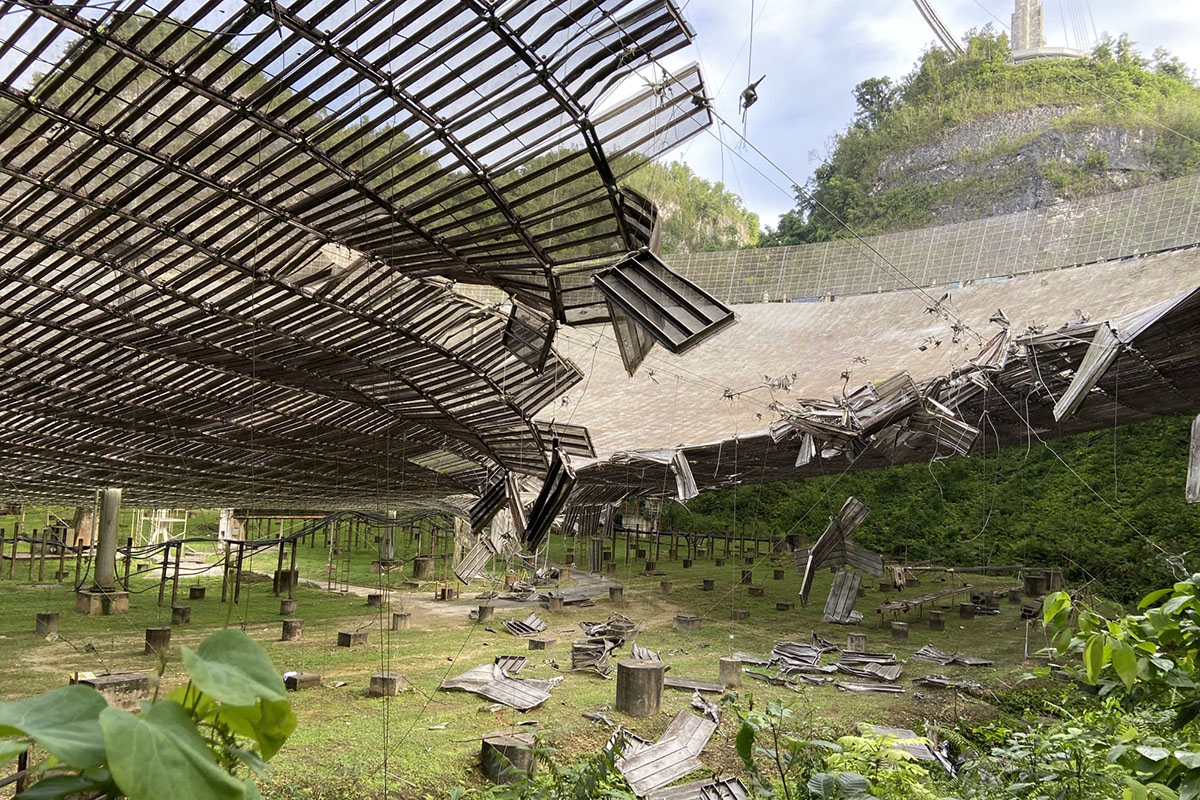
Another main cable that supports the Arecibo Observatory broke last week, falling onto the reflector dish and causing more damage. This is the second time a cable has snapped on the iconic radio observatory in just three months.
The new damage is an unfortunate and devastating setback for the observatory, just as repairs from the first accident were about to begin.
Continue reading “A Second Cable has Failed at Arecibo, Causing Even More Damage to the Radio Observatory”