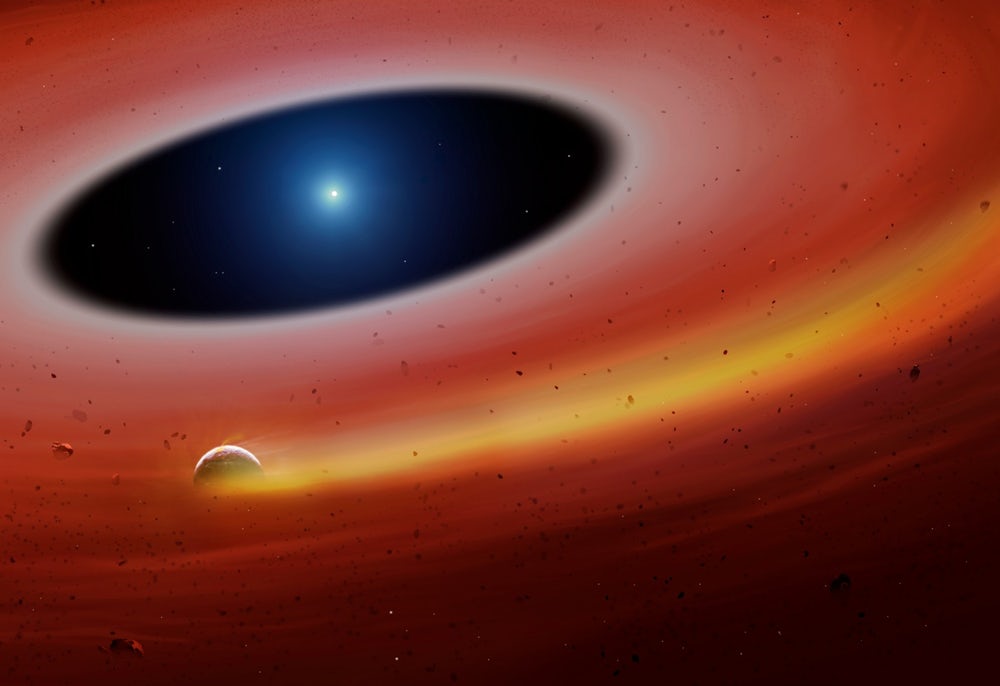
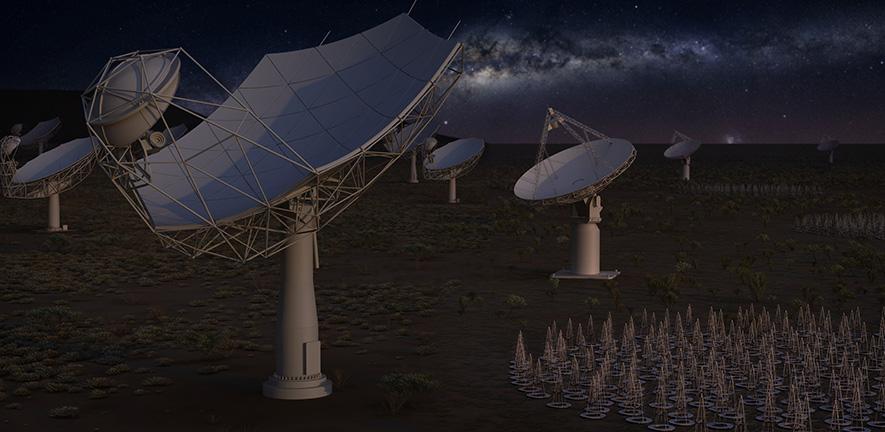
When astronomers talk about an optical telescope, they often mention the size of its mirror. That’s because the larger your mirror, the sharper your view of the heavens can be. It’s known as resolving power, and it is due to a property of light known as diffraction. When light passes through an opening, such as the opening of the telescope, it will tend to spread out or diffract. The smaller the opening, the more the light spreads making your image more blurry. This is why larger telescopes can capture a sharper image than smaller ones.
Continue reading “How Interferometry Works, and Why it’s so Powerful for Astronomy”How Interferometry Works, and Why it’s so Powerful for Astronomy