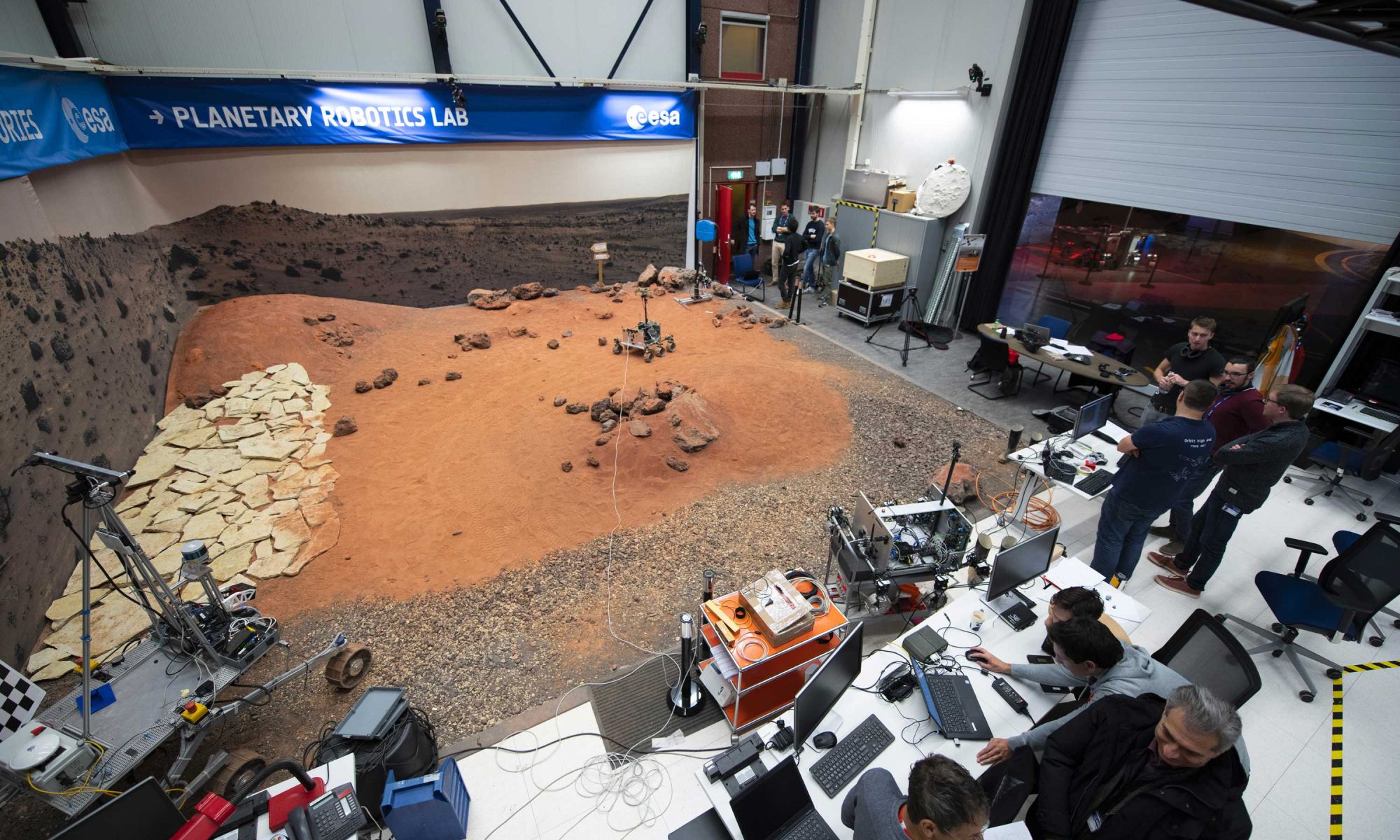
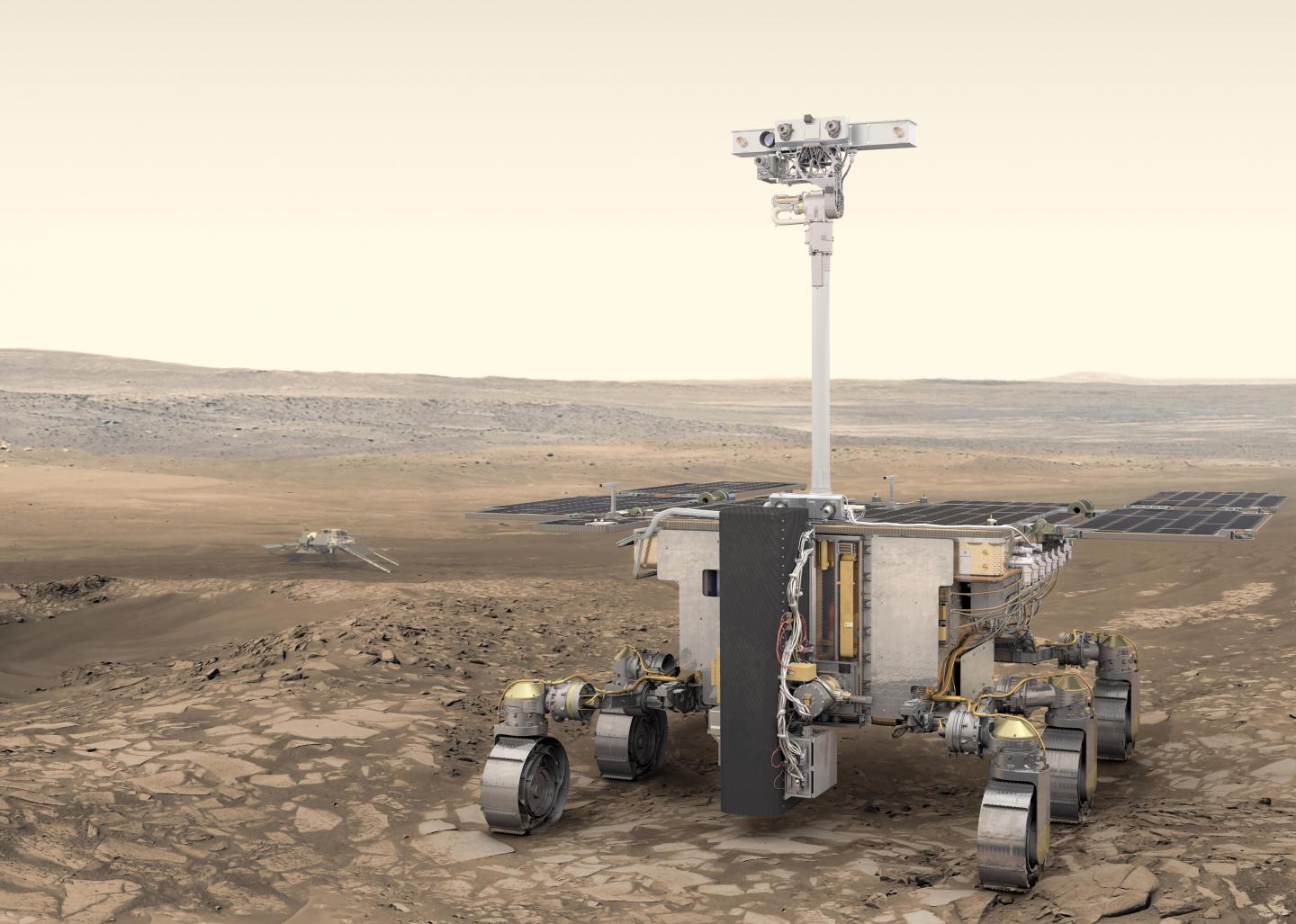
Russia’s attack on Ukraine has delayed its launch, but the ESA’s Rosalind Franklin rover is heading toward completion. It was originally scheduled to launch in 2018, but technical delays prevented it. Now, after dropping Russia from the project because of their invasion, the ESA says it won’t launch before 2028.
But when it does launch and then land on Mars, it will do something no other rover has done: drill down two meters into Mars and collect samples.
Continue reading “How the ESA’s Rosalind Franklin Rover Will Drill for Samples on Mars”