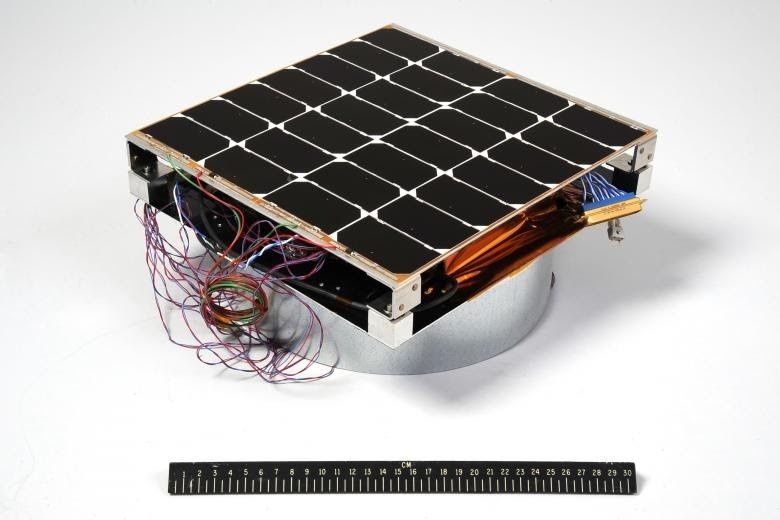
SpaceX has drawn plenty of praise and criticism with the creation of Starlink, a constellation that will one-day provide broadband internet access to the entire world. To date, the company has launched over 800 satellites and (as of this summer) is producing them at a rate of about 120 a month. There are even plans to have a constellation of 42,000 satellites in orbit before the decade is out.
However, there have been some problems along the way as well. Aside from the usual concerns about light pollution and Radio Frequency Interference (RFI), there is also the rate of failure these satellites have experienced. Specifically, about 3% of its satellites have proven to be unresponsive and are no longer maneuvering in orbit – which could prove hazardous to other satellites and spacecraft in orbit.
Continue reading “About 3% of Starlinks Have Failed So Far”