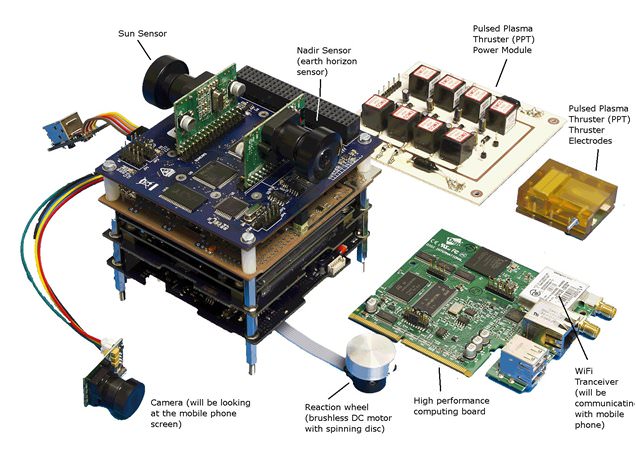
The STRaND-1 Smartphone Nanosatellite. Credit: Surry Satellite Technology
The first “Alien” movie was promoted with the celebrated tagline, “In space, no one can hear you scream.” But a group of students want to find out if this is really true, and they’re asking the public for help. Students from the University of Cambridge in the UK will be loading human screams onto a smartphone that will be launched into space in December 2012 on a nanosatellite. The screams will be played at maximum volume while the smartphone is in low Earth orbit, and at the same time as the phone will record the playback to test if it’s possible to capture the sound of screaming in space. They want the best screams possible, and so are inviting the public to submit their screams via video. There will also be public voting on the screams to determine which screams will go to space.
You know you’ve always wanted to do this…..
“Obviously, we’re not expecting to get much back, there may be some buzzing, but this is more about getting young people interested in satellites and acoustics, perhaps encouraging them to consider future study in science or engineering” said Edward Cunningham, a physics undergraduate at Churchill College and one of the members of the Cambridge University Space Flight group (CUSF).
What is actually being tested is verifying the capabilities of a smartphone to control a satellite in space. UK space company Surrey Satellite Technology and their STRaND (Surrey Training Research and Nanosatellite Demonstration) team ran a Facebook competition to find apps to go into orbit – and CUSF’s screaming app was one of the winners. STRaND-1 project is touted as the “World’s first SmartPhone Nanosatellite.”
Here’s a video showing the satellite:
The phone will run on Android’s open-source operating system, and a computer, built at the Surrey Space Centre, will test the vital statistics of the phone once in space. When all the tests are complete, the plan is to switch off the micro-computer and the smartphone will be used to operate parts of the satellite. At its lowest, the phone will orbit 400km above the Earth, roughly the same as the International Space Station.
“Modern smartphones are pretty amazing,” said Shaun Kenyon, the project manager at Surrey Satellite Technology. “We want to see if the phone works up there, and if it does, we want to see if the phone can control a satellite.”
To submit your scream, create a YouTube video and send it in at www.screaminspace.com.
Each video must be at most ten seconds long, and there will be ten winning screams which can be voted for by the public on the project’s website. Screams must be entered before midnight (UTC) on Sunday November 4, 2012. The winning videos will be announced later and loaded onto the phone for launch, which is scheduled before the end of this year.
Other winners in the STRaND-1 project were iTesa, which will record the magnitude of the magnetic field around the phone during orbit, a STRAND Data app will show satellite telemetry on the smartphone’s display which can be imaged by an additional camera on-board, and Postcards from Space and 360, a joint effort with an app that will take images using the smartphone’s camera and use the technology onboard the spacecraft to establish STRaND-1’s position.
Source: University of Cambridge
, Surrey Satellite