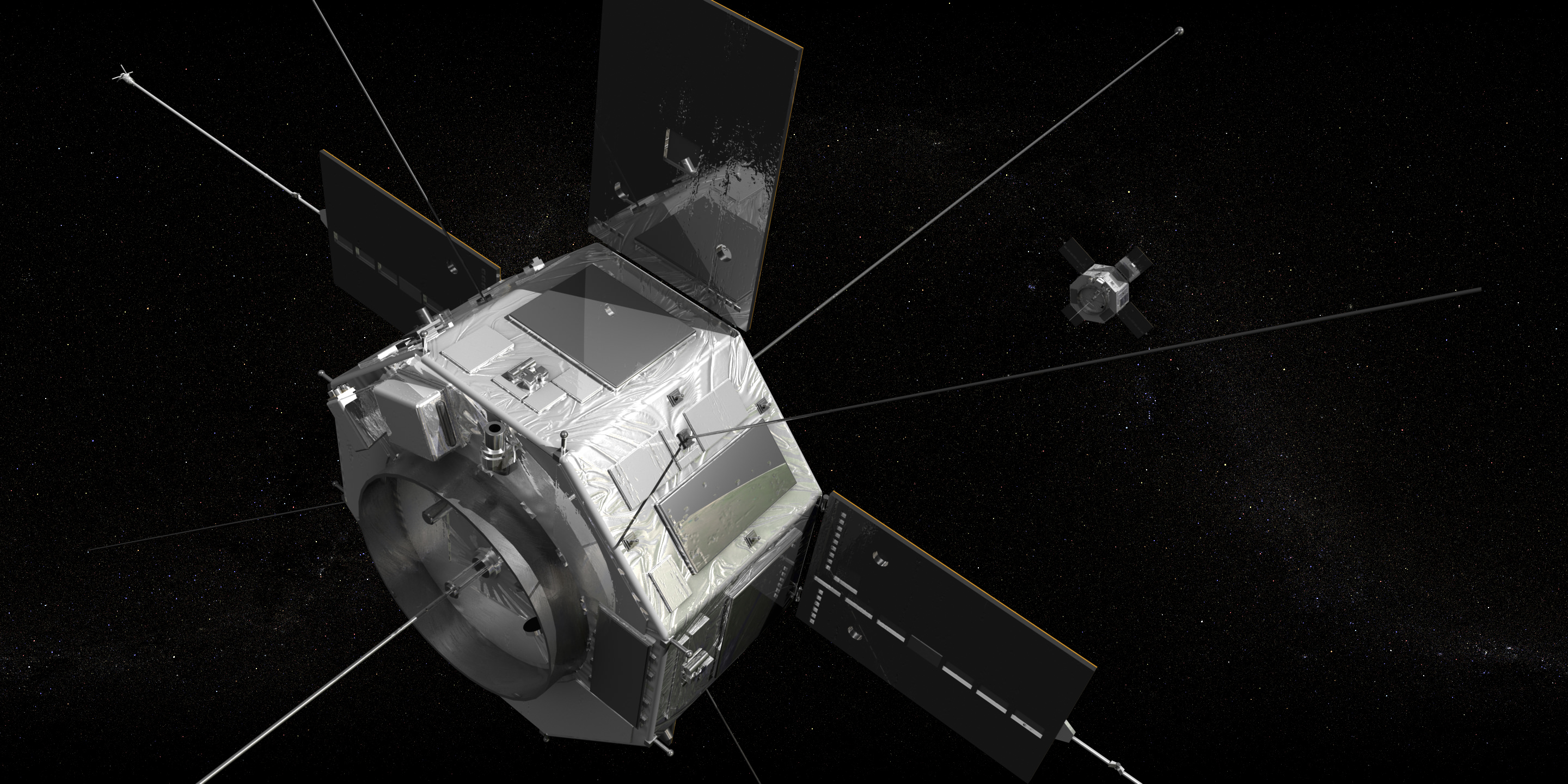
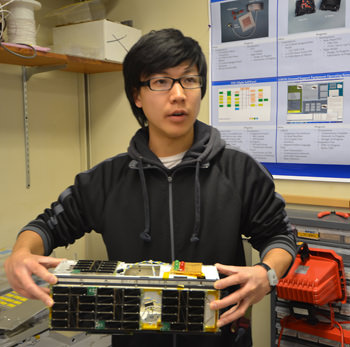
Caption: Jerry Kim, a former student and systems engineer, holds the CINEMA nanosatellite before it was packaged up and sent to NASA in January 2012. Credit: Robert Sanders.
We all will be biting our nails on August 5th as Curiosity makes its perilous descent to the surface of Mars. We have put all our eggs in the biggest, heaviest, most expensive basket, with one of the the most complex science packages and landing procedures. But there is another mission that launches this Friday that likes to keep things small, simple, cheap and accessible!
Scheduled to launch Friday, Aug. 3 from Space Launch Complex-3 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, at 12:27 a.m. PDT CINEMA (CubeSat for Ions, Neutrals, Electrons, & MAgnetic fields) is only one of 11 tiny cubesat satellites that are hitching a lift on an Atlas V rocket alongside the main payload, classified satellite
NROL-36.
ESA included seven Cubesats in the payload for Vega’s maiden flight back in February, but this will be the first time for NASA. Cubesats are modular, cheap, nanosatellites, measuring 10 cm per side, with a maximum mass of 1 kg. CINEMA is comprised of three such cubes, forming a shoebox-sized package weighing 3.15 kg and was developed by students at the University of California, Berkeley, Kyung Hee University in Korea, Imperial College London, Inter-American University of Puerto Rico, and University of Puerto Rico, Mayaguez.
CINEMA is designed to obtain images of the electrical ring current that encircles the Earth and which, during large magnetic storms can knock out our power grids. It carries the STEIN (Suprathermal Electrons, Ions, and Neutrons) Sensor, which will produce an image of the high-energy charged particles in Earth’s atmosphere, mostly ionized hydrogen and oxygen, by detecting energetic neutral atoms (ENAs) As ionized particles spiral around magnetic field lines surrounding Earth, they occasionally hit a neutral particle and grab an electron, transforming into ENAs that travel in a straight line. These can reveal the energy and location of the charged particles from which they came. CINEMA will be joined next year by three identical satellites, two launched by Korea and another by NASA, together they will monitor the 3-dimensional structure of the ring current. Also on board is the MAGIC (MAGnetometer from Imperial College) instrument, provided by Imperial College London, to measure changes in Earth’s magnetic field caused by magnetic storms.
CINEMA is only one of five university-built CubeSats aboard the Atlas V rocket. As they can be bought for only around $1,000 and can then fitted with sensors, transmitters, cameras etc, being able to include multiple satellites in a single launch keeps costs down. Universities can use cubesats to give students hands-on experience of designing, planning, building, running and monitoring a real scientific space mission.
CINEMA principal investigator Robert Lin, professor emeritus of physics and former director of UC Berkeley’s Space Sciences Laboratory, explained some of the pros and cons of cubesats. “There is more risk with these projects, because we use off-the-shelf products, 90 percent of the work is done by students, and the parts are not radiation-hard,” he said. “But it is cheaper and has the latest hardware. I will be very impressed if it lasts more than a year in orbit.”
Additionally, being small means that these satellites pose no threat as space junk either, burning up harmlessly in Earth’s atmosphere when they reach the end of their lifespan.
Find out more about CINEMA at the UC Berkley News Center