Astronomy is poised for another leap. In the next several years, major ground-based telescopes will come online, including the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT,) the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT,) the Giant Magellan Telescope (GMT,) and the Vera Rubin Observatory. The combined power of these telescopes will help drive discovery in the next couple of decades.
But something threatens to undermine astronomical observing in the coming years: Starlink and other internet satellite constellations.
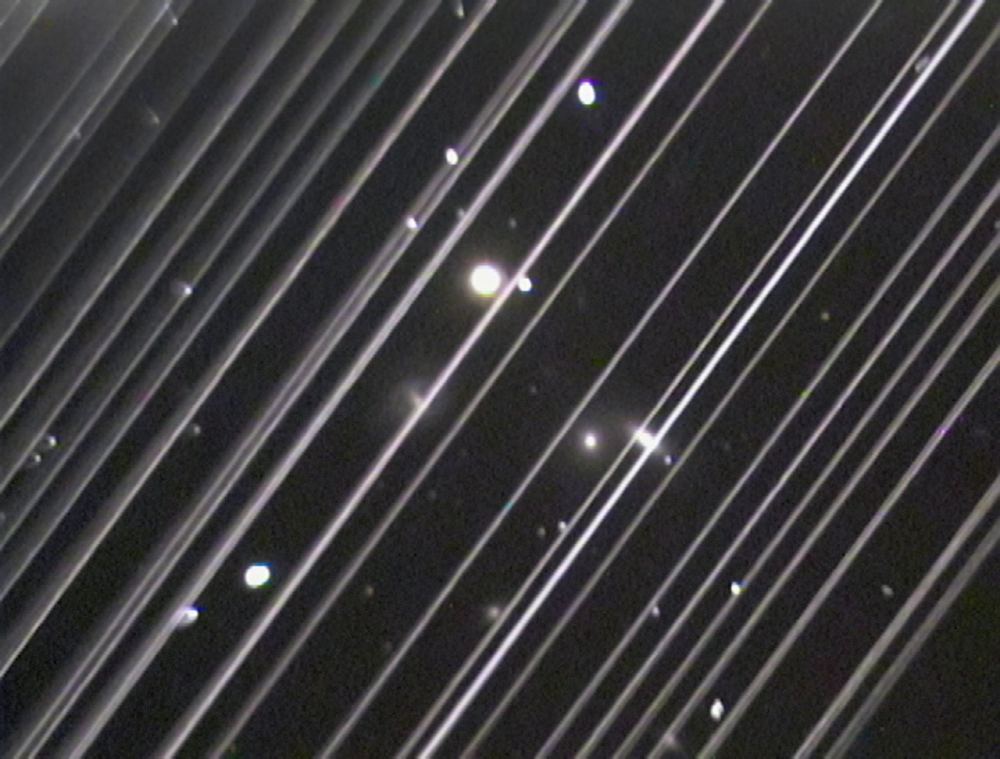
Now a group of astronomers have shown that even the Hubble can’t escape the satellite problem.
Continue reading “Hubble’s Orbit Has Dropped So Far that Starlink Satellites are Photobombing its Images”