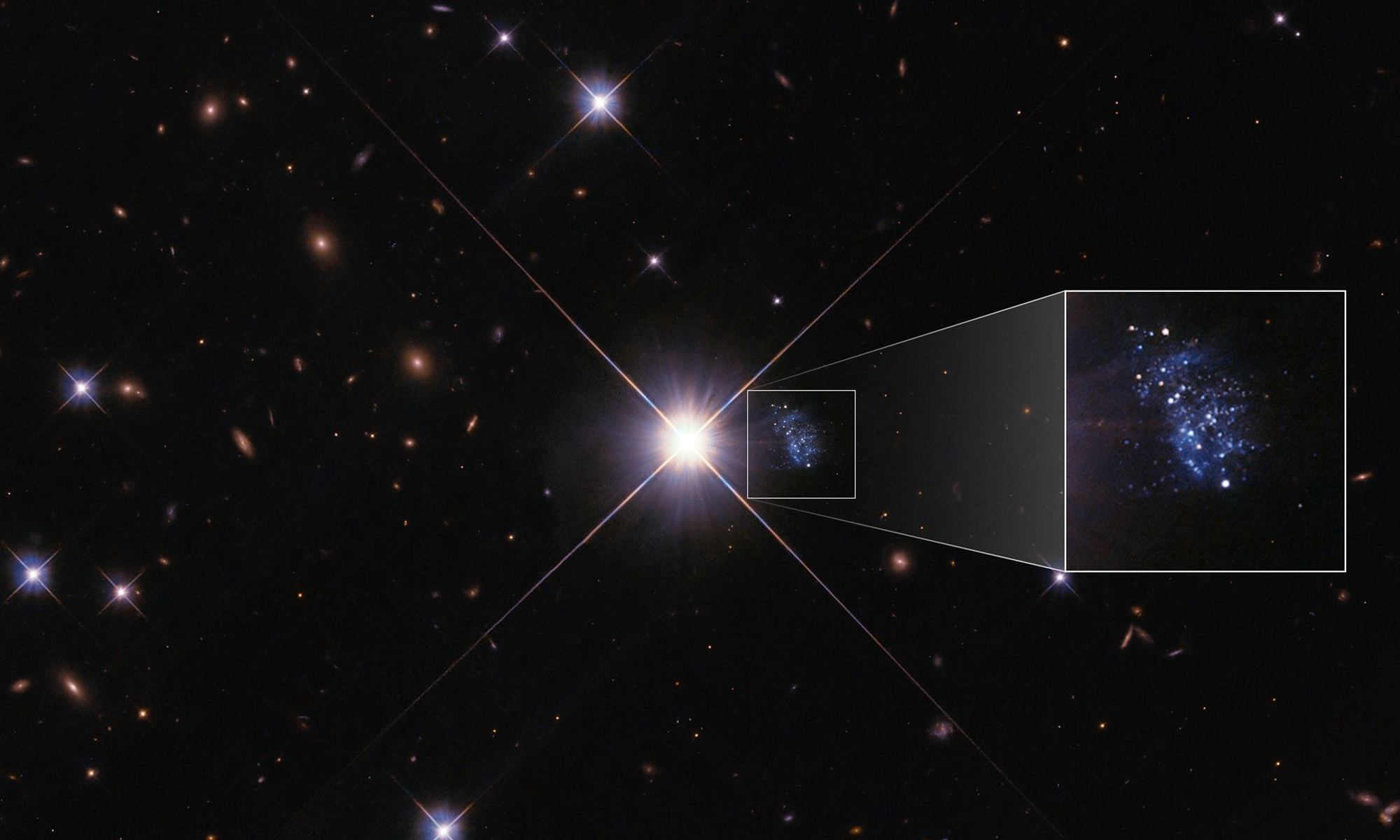
One of the biggest puzzles in astronomy, and one of the hardest ones to solve, concerns the formation and evolution of galaxies. What did the first ones look like? How have they grown so massive?
A tiny galaxy only 20 million light-years away might be a piece of the puzzle.
Continue reading “A Star was Blocking a Galaxy, but Now it’s Moved Enough That Astronomers can Finally Examine What it Was Hiding”