A black hole as a source of energy?
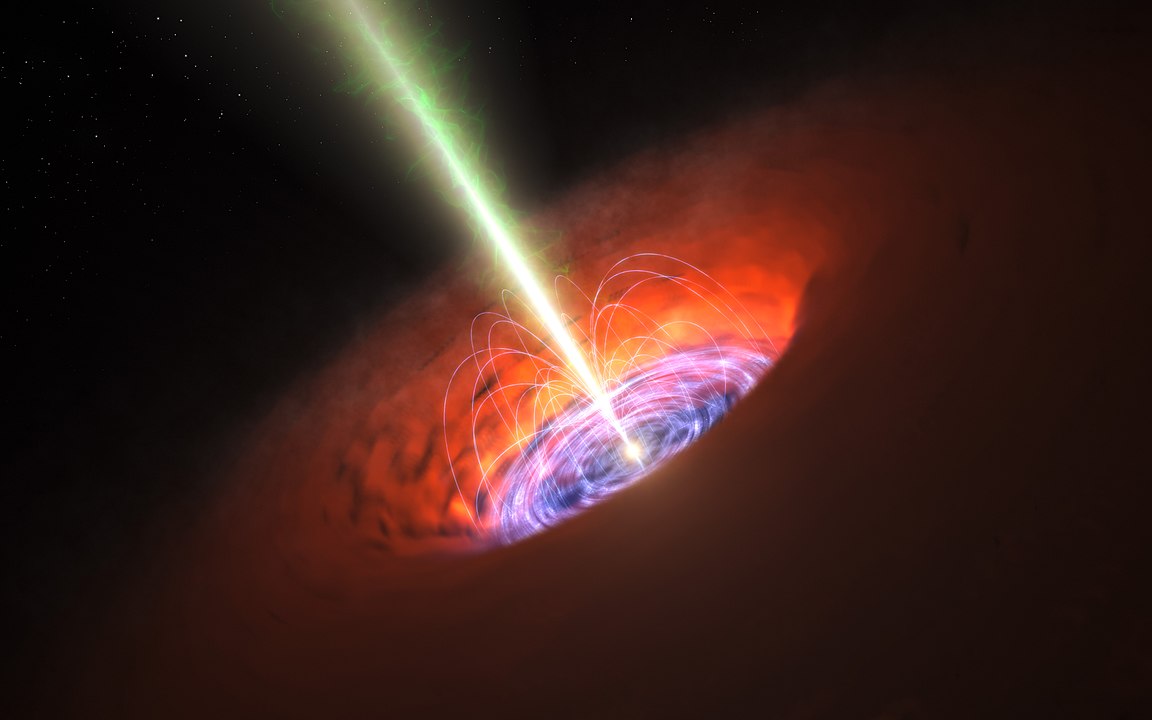
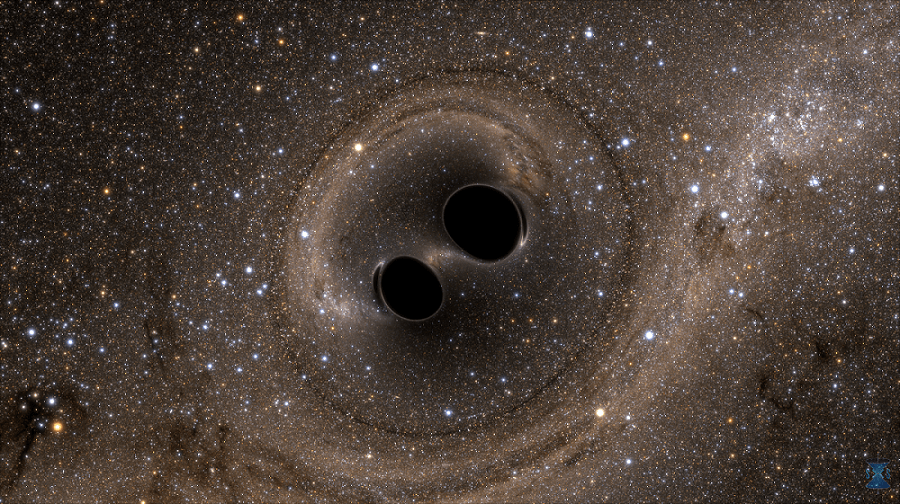
We know black holes as powerful singularities, regions in space time where gravity is so overwhelming that nothing—not even light itself—can escape.
About 50 years ago, British physicist Roger Penrose proposed that black holes could be a source of energy. Now, researchers at the University of Glasgow in Scotland have demonstrated that it may be possible.
Continue reading “How an Advanced Civilization Could Exploit a Black Hole for Nearly Limitless Energy”