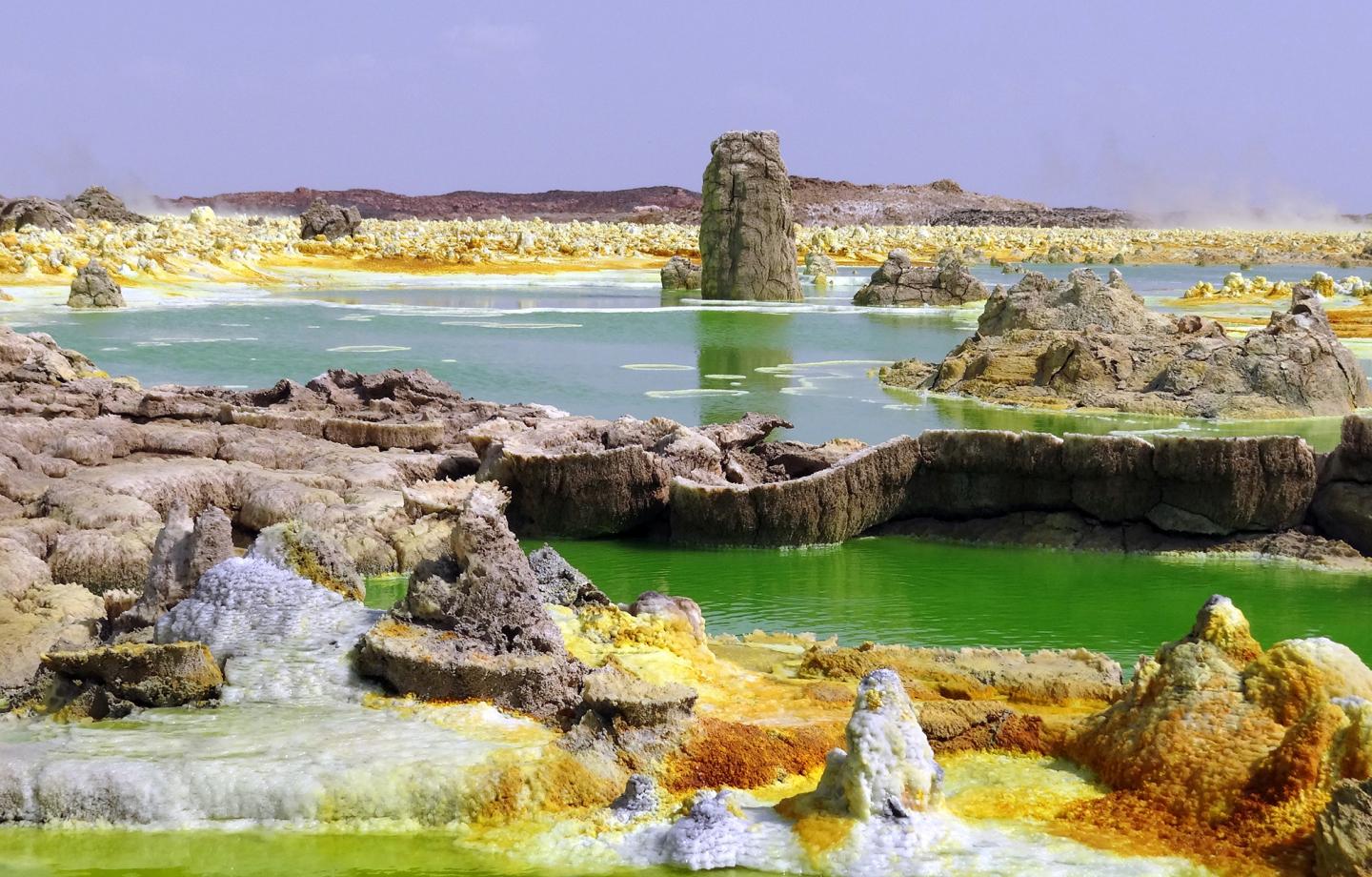
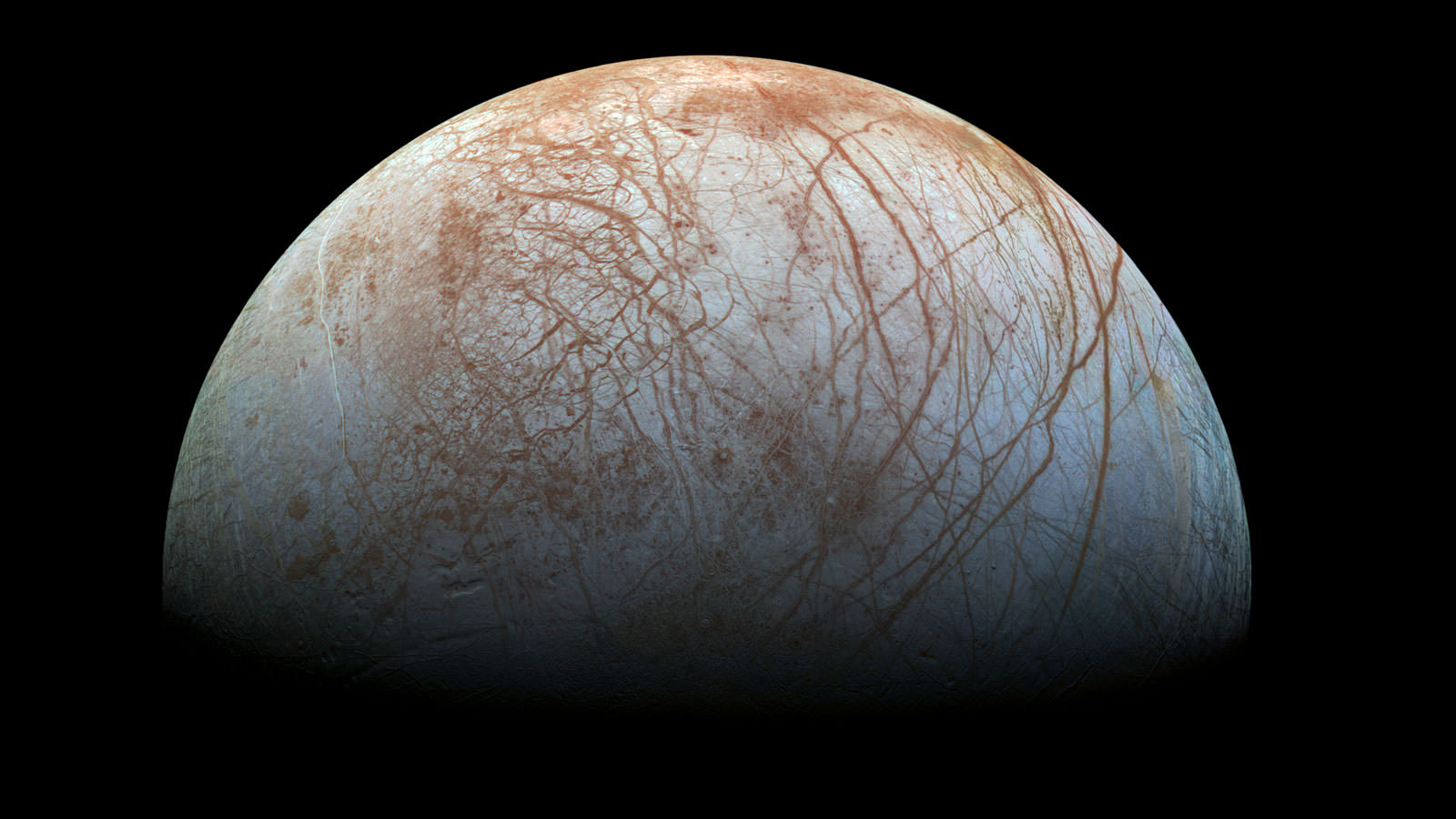
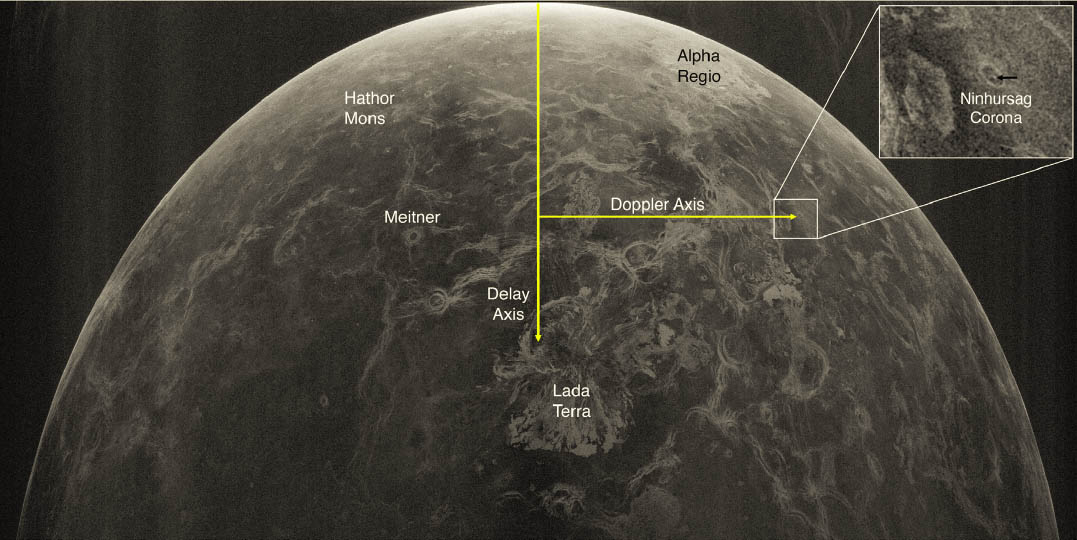
In recent years research into extremophiles has captured the interest of astrobiologists. The discovery of lifeforms in some of Earth’s most extreme environments has helped shape our thinking about extraterrestrial life. Life on other worlds may not need the kind of temperate, balanced environment that most life on Earth is adapted to.
Continue reading “Finally! Scientists Find a Place on Earth with Liquid Water But No Life”Finally! Scientists Find a Place on Earth with Liquid Water But No Life