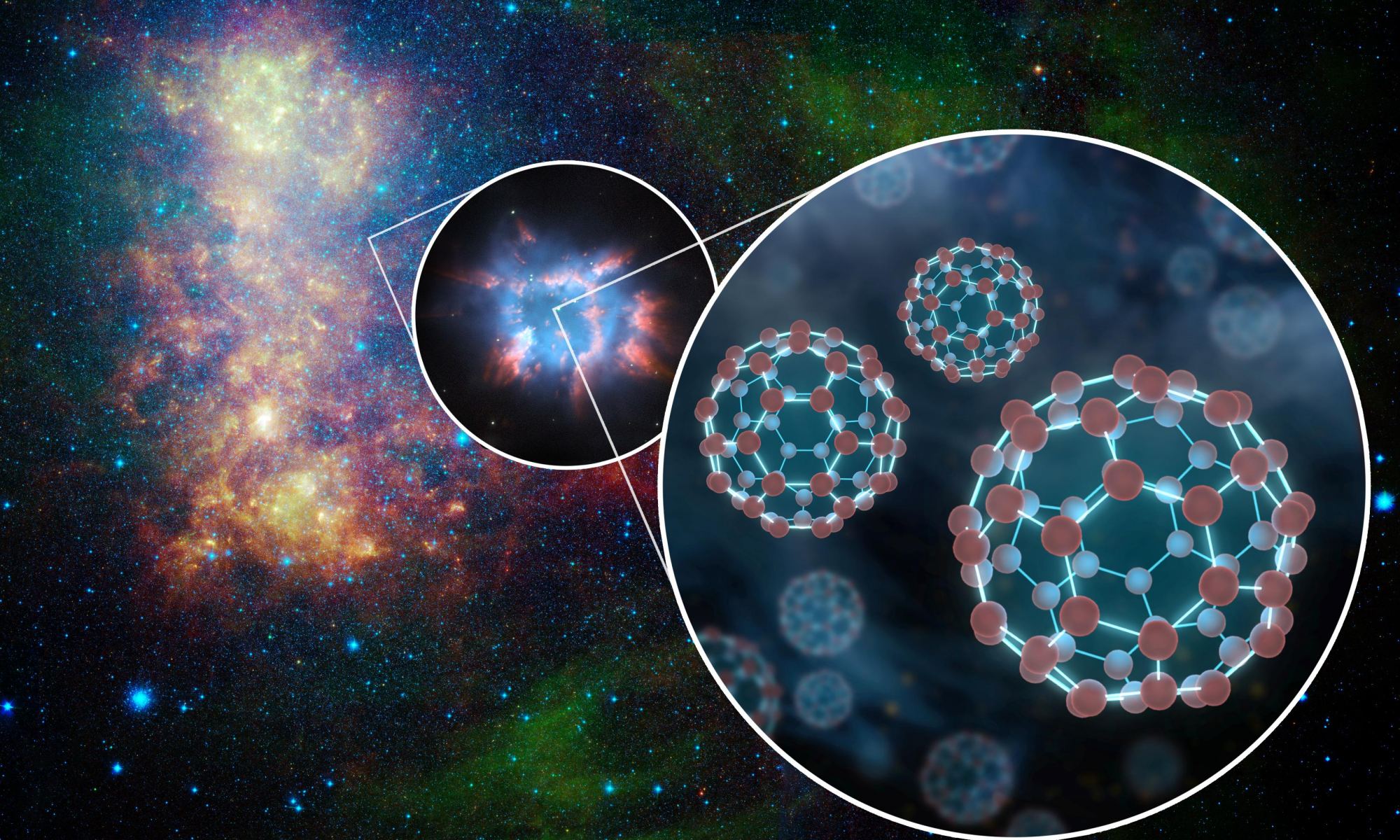
Scientists working with the Hubble Space Telescope have found a very complex molecule out there in space. Called Buckyballs, after renowned thinker Buckminster Fuller, they are a molecular arrangement of 60 carbon atoms (C60) in the rough shape of a soccer ball. Though it’s not the first time these exotic molecules have been spotted in space, it is the first time that Buckyball ions have been found.
Continue reading “Hubble Finds Buckyballs in Space”Hubble Finds Buckyballs in Space