A new study shows that Mars may very well be volcanically active. Nobody’s seen direct evidence of volcanism; no eruptions or magma or anything like that. Rather, the proof is in the water.
Continue reading “There’s Evidence that Mars is Still Volcanically Active”Without the Impact that Formed the Moon, We Might Not Have Life on Earth

The Earth wasn’t formed containing the necessary chemicals for life to begin. One well-supported theory, called the “late veneer theory”, suggests that the volatile chemicals needed for life arrived long after the Earth formed, brought here by meteorites. But a new study challenges the late veneer theory.
Evidence shows that the Moon was created when a Mars-sized planet named Theia collided with the Earth. The impact created a debris ring out of which the Moon formed. Now, this new study says that same impact may have delivered the necessary chemicals for life to the young Earth.
Saturn’s Rings are Only 10 to 100 Million Years Old
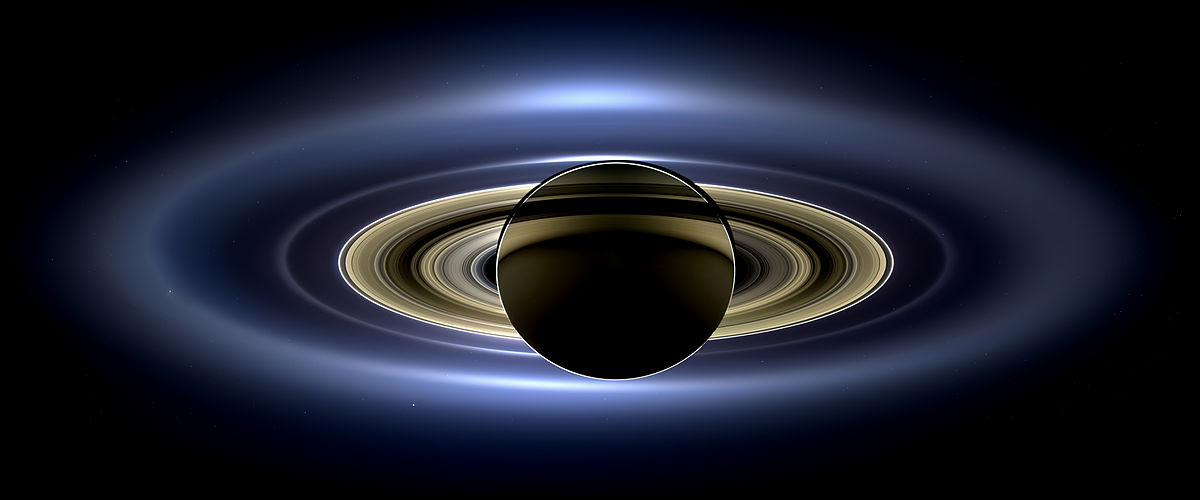

Can you imagine the Solar System without Saturn’s rings? Can you envision Earth at the time the dinosaurs roamed the planet? According to a new paper, the two may have coincided.
Data from the Cassini mission shows that Saturn’s rings may be only 10 to 100 million years old. They may not have been there during the reign of the dinosaurs, and may in fact be a fairly modern development in our Solar System.
Continue reading “Saturn’s Rings are Only 10 to 100 Million Years Old”CERN is Planning to Build a Much Larger Particle Collider. Much, Much, Larger.
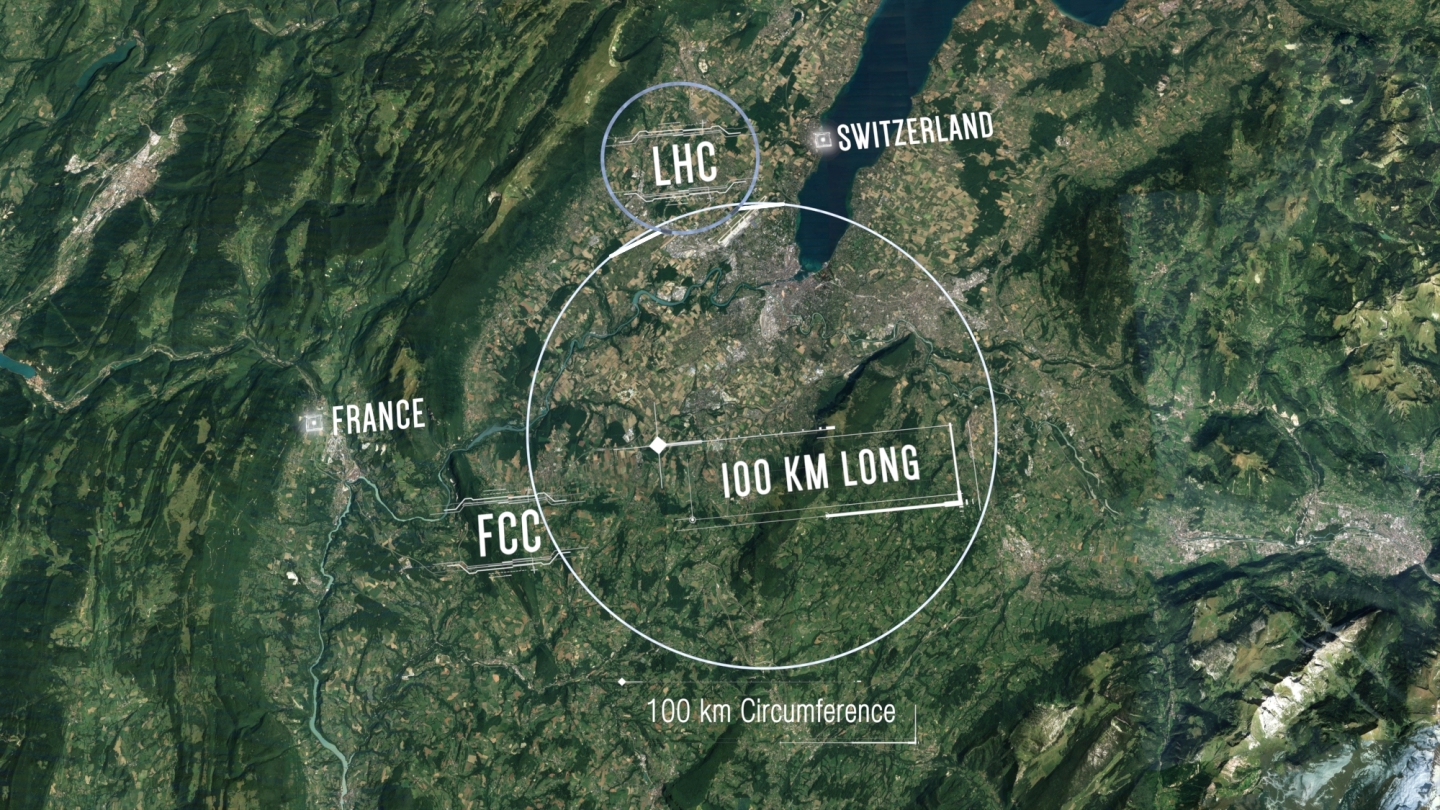
CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research, wants to build a particle collider that will dwarf the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). The LHC has made important discoveries, and planned upgrades to its power ensures it will keep working on physics problems into the future. But eventually, it won’t be enough to unlock the secrets of physics. Eventually, we’ll need something larger and more powerful.
Enter the Future Circular Collider (FCC.) The FCC will exceed the LHC in power by an order of magnitude. On January 15th, the FCC collaboration released its Conceptual Design Report (CDR) that lays out the options for CERN’s Future Circular Collider.
Continue reading “CERN is Planning to Build a Much Larger Particle Collider. Much, Much, Larger.”A New Technique to Figure Out How Old Stars Are

Our understanding of the universe, and of the Milky Way, is built on an edifice of individual pieces of knowledge, all related to each other. But each of those pieces is only so accurate. The more accurate we can make one of the pieces of knowledge, the more accurate our understanding of the whole thing is.
The age of stars is one such piece. For years, astronomers have used a method of determining the age of stars that has a 10% to 20% margin of error. Now, a team of scientists from Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University has developed a new technique to determine the age of stars with a margin of error of only 3% to 5%.
Continue reading “A New Technique to Figure Out How Old Stars Are”Giant Streak Structure Found in Venus’ Cloudtops
A team of researchers in Japan has discovered a gigantic streak structure in the cloud tops of Venus. The discovery is based on observations of Venus by the Japanese spacecraft Akatsuki. The findings were published in January 9th in the journal Nature Communications.
Venus is unlike any other planet in the Solar System. The entire planet is shrouded in thick clouds of sulfuric acid between altitudes of 45 km to 70 km. This thick shroud has prevented scientists from studying Earth’s so-called “sister planet” in detail. But Japanese researchers are making progress.
Continue reading “Giant Streak Structure Found in Venus’ Cloudtops”Extreme Bacteria on the Space Station are Evolving to Handle the Harsh Conditions, not to Make Astronauts Sick
For years, scientists have been conducting studies aboard the International Space Station (ISS) to determine the effects of living in space on humans and micro-organisms. In addition to the high levels of radiation, there are also worries that long-term exposure to microgravity could cause genetic mutations. Understanding these, and coming up with counter-measures, is essential if humanity is to become a truly space-faring species.
Interestingly enough, a team of researchers from Northwestern University recently conducted a study with bacteria that was kept aboard the ISS. Contrary to what many suspected, the bacteria did not mutate into a drug-resistant super strain, but instead mutated to adapt to its environment. These results could be vital when it comes to understanding how living beings will adapt to the stressful environment of space.
Continue reading “Extreme Bacteria on the Space Station are Evolving to Handle the Harsh Conditions, not to Make Astronauts Sick”Bad News. Planets Orbiting Red Dwarfs Might not have the Raw Materials for Life

New research from the Hubble Space Telescope and the ESO’s Very Large Telescope is dampening some of the enthusiasm in the search for life. Observations by both ‘scopes suggest that the raw materials necessary for life may be rare in solar systems centered around red dwarfs.
And if the raw materials aren’t there, it may mean that many of the exoplanets we’ve found in the habitable zones of other stars just aren’t habitable after-all.
Continue reading “Bad News. Planets Orbiting Red Dwarfs Might not have the Raw Materials for Life”New Research Reveals How Galaxies Stay Hot and Bothered

It’s relatively easy for galaxies to make stars. Start out with a bunch of random blobs of gas and dust. Typically those blobs will be pretty warm. To turn them into stars, you have to cool them off. By dumping all their heat in the form of radiation, they can compress. Dump more heat, compress more. Repeat for a million years or so.
Eventually pieces of the gas cloud shrink and shrink, compressing themselves into a tight little knots. If the densities inside those knots get high enough, they trigger nuclear fusion and voila: stars are born.
Continue reading “New Research Reveals How Galaxies Stay Hot and Bothered”
You’re Looking at an Actual Image of a White Dwarf Feeding on Material from a Larger Red Giant, 650 Light Years from Earth.
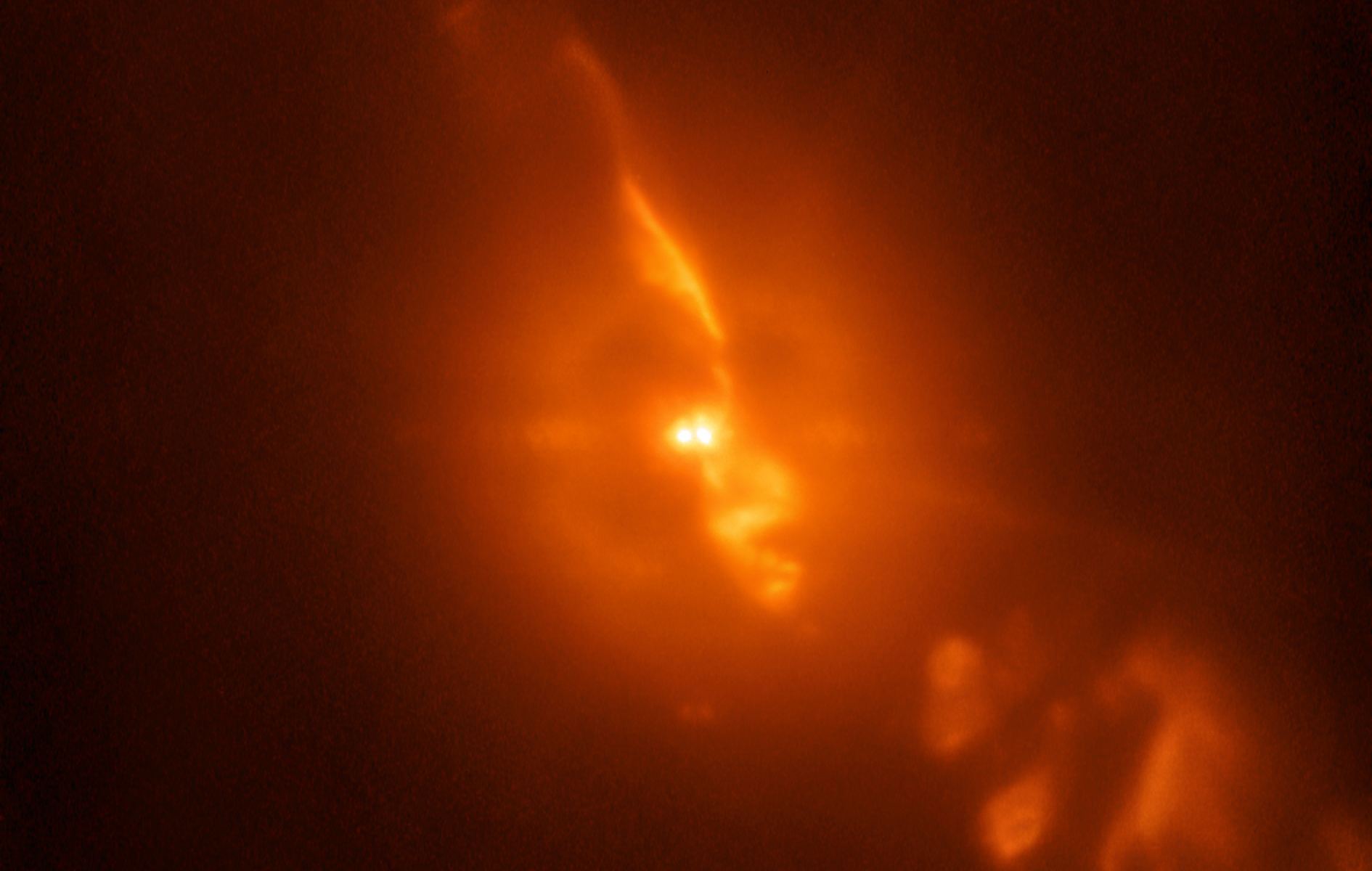

The SPHERE planet-hunting instrument on the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope captured this image of a white dwarf feeding on its companion star, a type of Red Giant called a Mira variable. Most stars exist in binary systems, and they spend an eternity serenely orbiting their common center of gravity. But something almost sinister is going on between these two.
Astronomers at the ESO have been observing the pair for years and have uncovered what they call a “peculiar story.” The Red Giant is a Mira variable, meaning it’s near the end of its life, and it’s pulsing up to 1,000 times as bright as our Sun. Each time it pulses, its gaseous envelope expands, and the smaller White Dwarf strips material from the Red Giant.