Now that several decades have passed since the launch of Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 in 1977, we look back on that time with a hazy sense of history and what the event meant for humanity’s ongoing odyssey. While the Voyager spacecraft were sober scientific missions, they also carried with them a hint of the deeper yearnings that lie inside humanity’s heart: the Golden Records.
Continue reading “What Would a Modern “Golden Record” Include?”Fly Slowly Through Enceladus' Plumes to Detect Life
Enceladus is blasting water into space from the jets at its southern pole. This makes it the ideal place to send a dedicated mission, flying the spacecraft through the plumes with life-detection instruments s. A new study suggests that a spacecraft must proceed carefully through the plumes, keeping its speed below 4.2 km/second (2,236 miles per hour). Using a specialized, custom-built aerosol impact spectrometer at these speeds will allow fragile amino acids to be captured by the spacecraft’s sample collector. Any faster, they’ll shatter, providing inclusive results.
Continue reading “Fly Slowly Through Enceladus' Plumes to Detect Life”The Second Most Energetic Cosmic Ray Ever Found

“Oh My God,” someone must have said in 1991 when researchers detected the most energetic cosmic ray ever to strike Earth. Those three words were adopted as the name for the phenomenon: the Oh-My-God particle. Where did it come from?
Continue reading “The Second Most Energetic Cosmic Ray Ever Found”What Can Slime Mold Teach Us About the Universe?
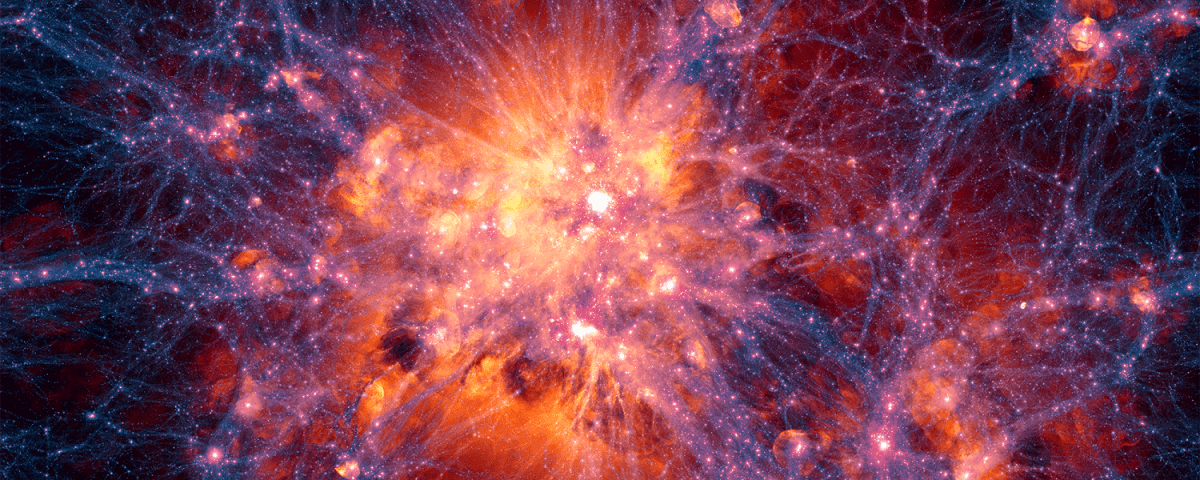
What can slime molds tell us about the large-scale structure of the Universe and the evolution of galaxies? These things might seem incongruous, yet both are part of nature, and Earthly slime molds seem to have something to tell us about the Universe itself. Vast filaments of gas threading their way through the Universe have a lot in common with slime molds and their tubular networks.
Continue reading “What Can Slime Mold Teach Us About the Universe?”TESS Finds Eight More Super-Earths

NASA’s Kepler spacecraft has discovered most of the confirmed exoplanets that we know of. But its successor, TESS (Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite), is catching up. New research announces the validation of eight more TESS candidates, and they’re all Super-Earths.
Continue reading “TESS Finds Eight More Super-Earths”Old Data from Kepler Turns Up A System with Seven Planets
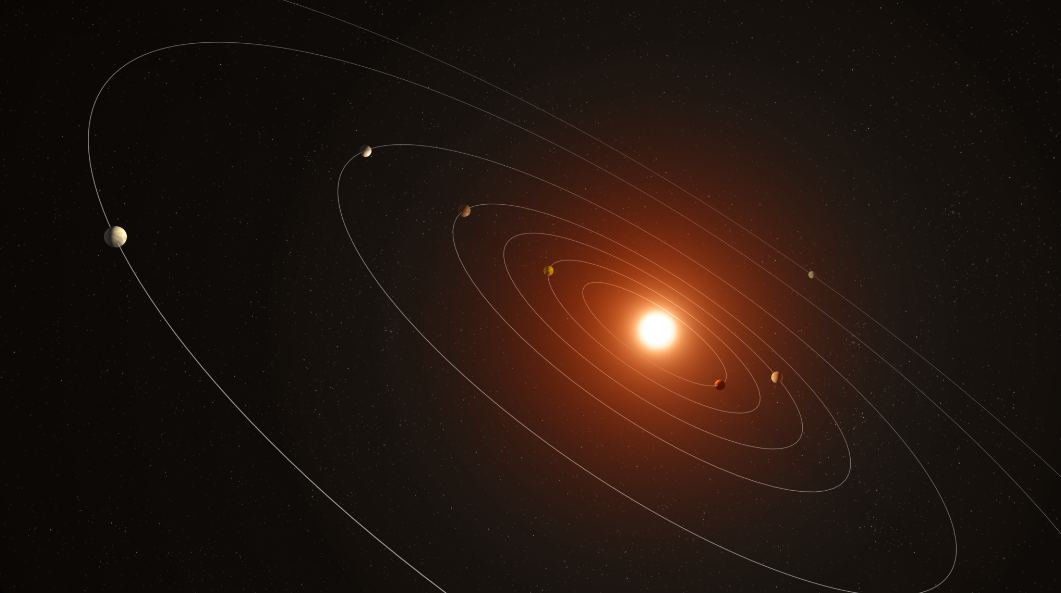

NASA’s Kepler mission ended in 2018 after more than nine years of fruitful planet-hunting. The space telescope discovered thousands of planets, many of which bear its name. But it also generated an enormous amount of data that exoplanet scientists are still analyzing.
Now, a team of researchers has shed new light on a seven-planet system in Kepler’s ocean of data.
Continue reading “Old Data from Kepler Turns Up A System with Seven Planets”A Huge New Gaia Data Release: More Stars, Gravitational Lenses and Asteroids

The ESA’s Gaia mission is releasing a new tranche of astronomical data. The mission has released three regular, massive hauls of data since it launched in 2013, named Gaia DR1, DR2, and DR3. The ESA is calling this one a ‘focused product release,’ and while it’s smaller than the previous three releases, it’s still impactful.
Continue reading “A Huge New Gaia Data Release: More Stars, Gravitational Lenses and Asteroids”Seeing the Moment Planets Start to Form
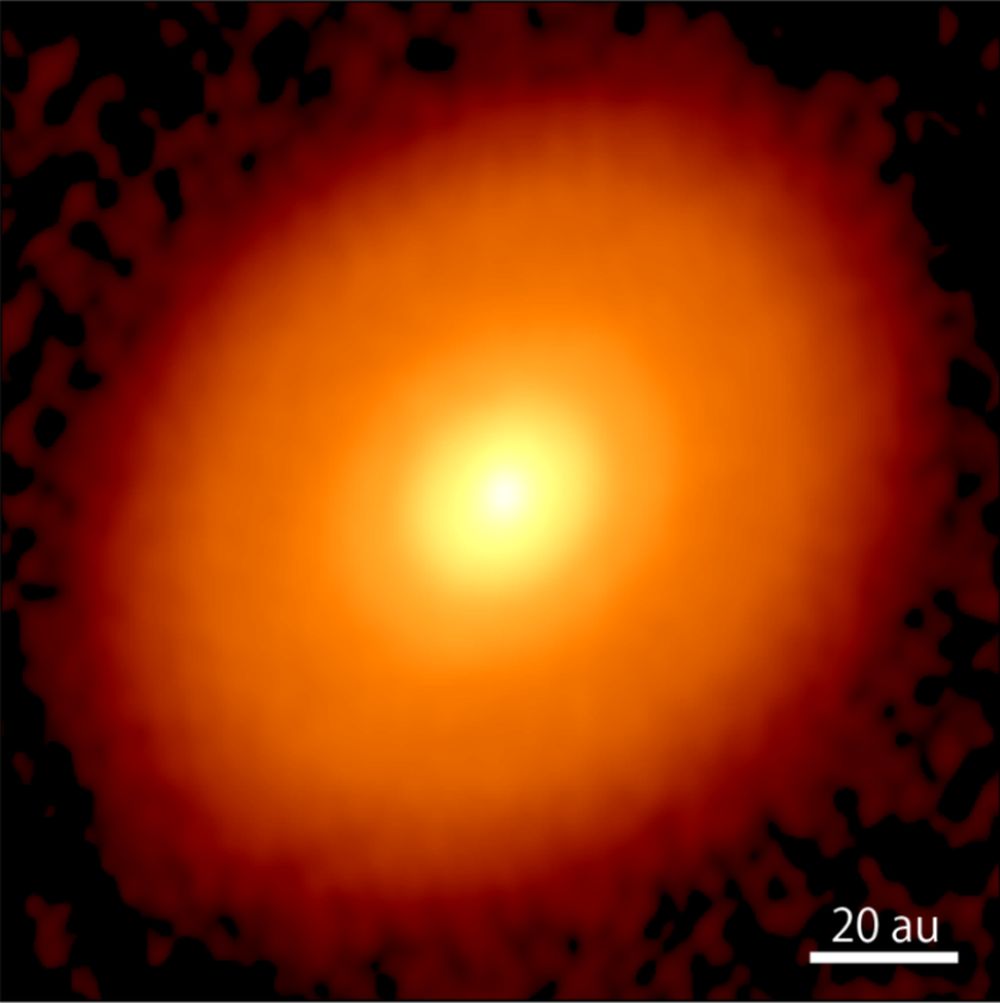
Nature makes few duplicates, and planets are as distinct from one another as snowflakes are. But planets all start out in the same circumstances: the whirling disks of material surrounding young stars. ALMA’s made great progress imaging these disks and the telltale gaps excavated by young, still-forming planets.
But new images from ALMA (Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array) show a star and disk so young that there are no telltale gaps in the disk. Is this the moment that planets start to form?
Continue reading “Seeing the Moment Planets Start to Form”How Do Lava Worlds Become Earth-Like, Living Planets?

Earth was once entirely molten. Planetary scientists call this phase in a planet’s evolution a magma ocean, and Earth may have had more than one magma ocean phase. Earth cooled and, over 4.5 billion years, became the vibrant, life-supporting world it is today.
Can the same thing happen to exo-lava worlds? Can studying them shed light on Earth’s transition?
Continue reading “How Do Lava Worlds Become Earth-Like, Living Planets?”Even Tiny Amounts of DNA on Mars Will Be Detectable

The Search for Life is focused on the search for biosignatures. Planetary life leaves a chemical fingerprint on a planet’s atmosphere, and scientists are trying to work out which chemicals in what combinations and amounts are a surefire indicator of life. Martian methane is one they’re puzzling over right now.
But new evidence suggests that super-tiny amounts of DNA can be detected in Martian rocks if it’s there. And though it requires physical samples rather than remote sensing, it’s still an intriguing development.
Continue reading “Even Tiny Amounts of DNA on Mars Will Be Detectable”

