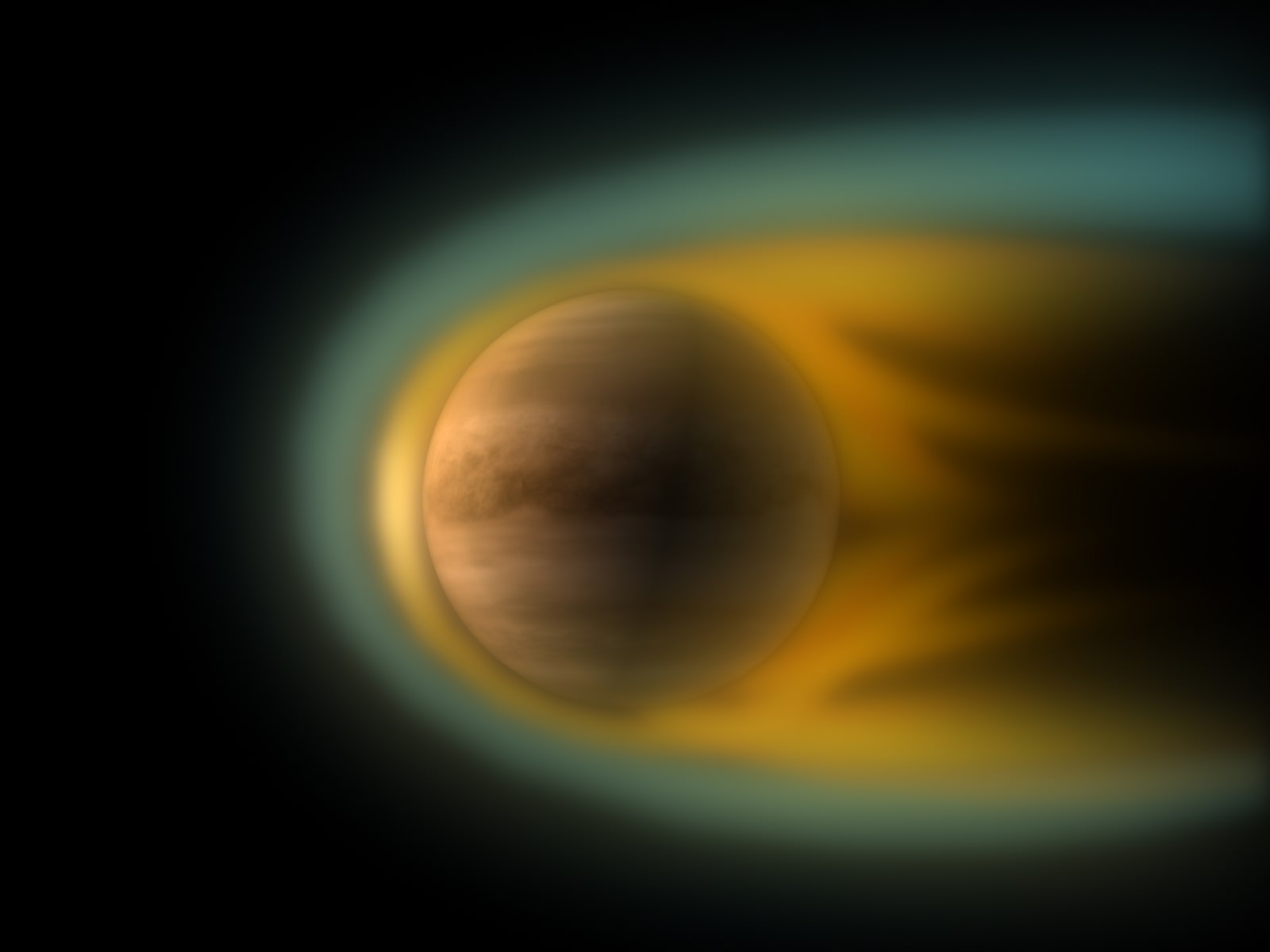
Named for the ancient goddess of fertility, the planet Venus could not be more hostile to life as we know it. Aside from being the hottest planet in the Solar System, Venus has also an atmosphere that is 92 times denser than Earth’s, and regularly experiences sulfuric acid rain. But as we’ve learned from multiple surveys, Venus was once a much milder climate and even had vast oceans on its surface.
For astronomers and geologists alike, the burning question is, how much of its water did Venus hold onto during this massive transition? According to research presented by Moa Persson of the Swedish Institute of Space Physics (IRF), Venus actually retained most of its water over the past 4 billion years. Contrary to what researchers previously thought, Venus lost only a small amount of its water to a runaway Greenhouse Effect.
Continue reading “Venus Held Onto its Water Surprisingly Well During its History”