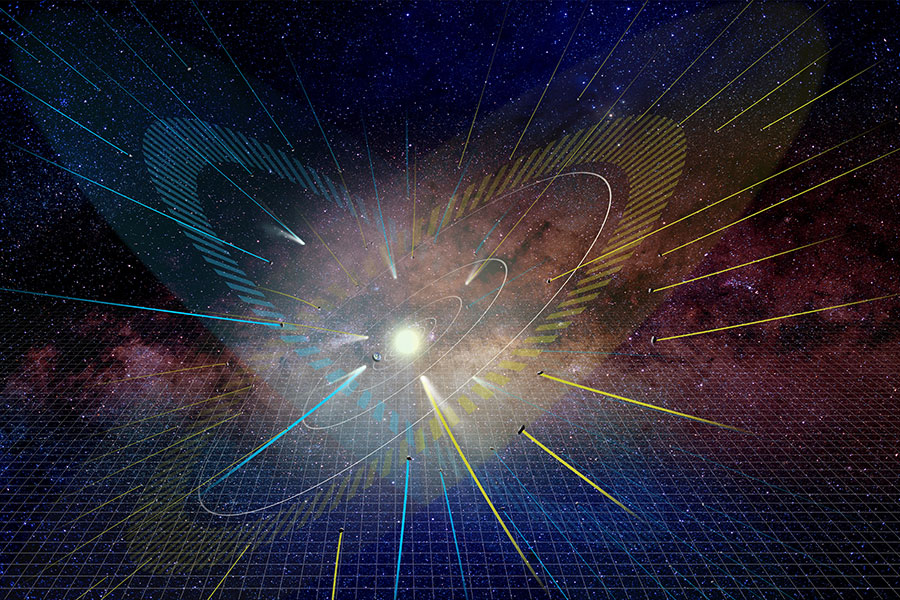
200 light-years away from Earth, there’s a K-type main-sequence star named TOI (TESS Object of Interest) 178. When Adrian Leleu, an astrophysicist at the Center for Space and Habitability of the University of Bern, observed it, it appeared to have two planets orbiting it at roughly the same distance. But that turned out to be incorrect. In fact, six exoplanets orbit the smallish star.
And five of those six are locked into an unexpected orbital configuration.
Continue reading “Exoplanetary System Found With 6 Worlds in Orbital Resonance”