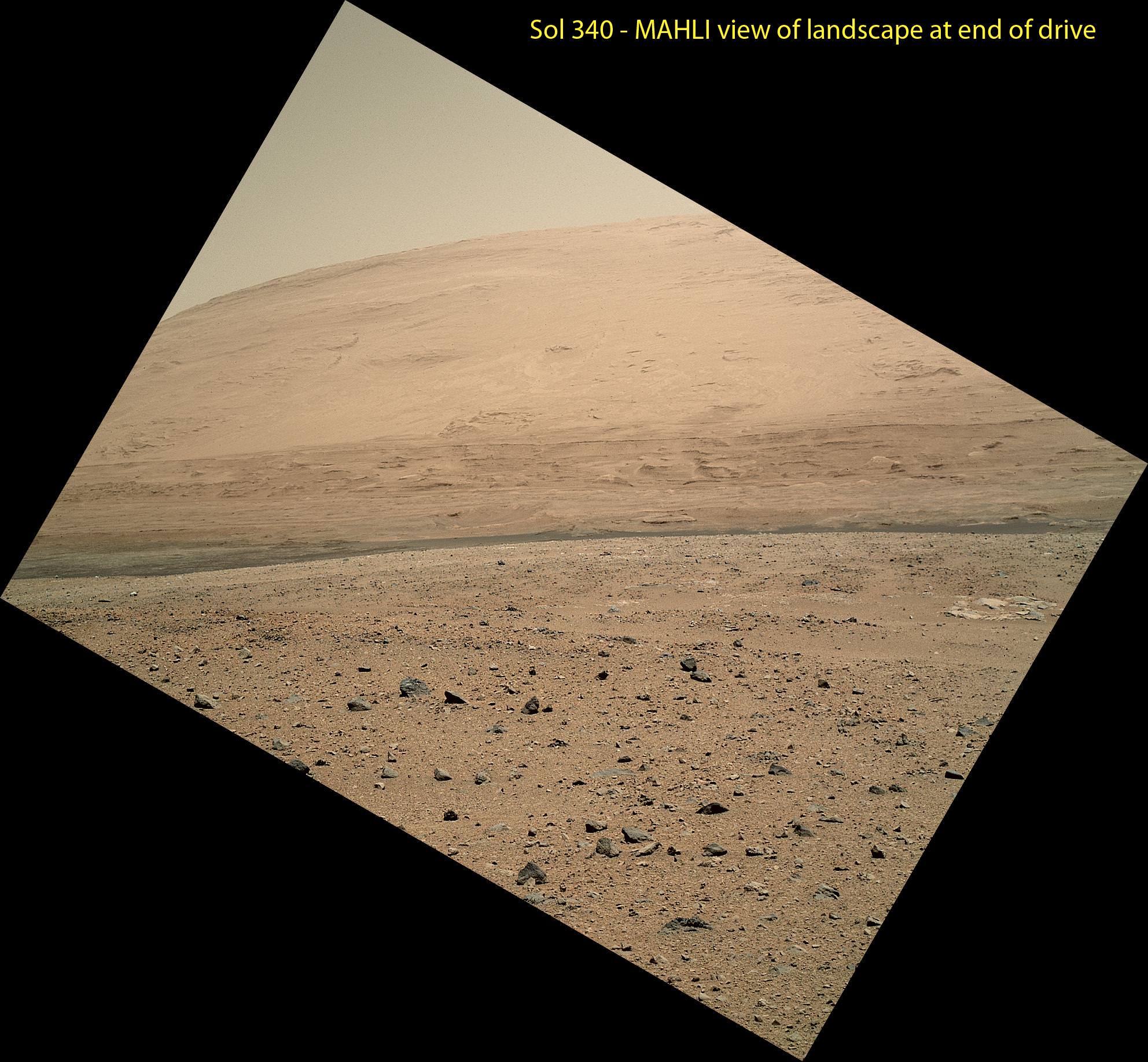
This scene was taken on Sol 340 shortly after Curiosity finished her longest drive yet
The 329.1-foot (100.3-meter) drive was twice as long as any previous sol’s drive by Curiosity. The view is toward the south, including a portion of Mount Sharp and a band of dark dunes in front of the mountain. The Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera on NASA’s Curiosity rover is carried at an angle when the rover’s arm is stowed for driving. Still, the camera is able to record views of the terrain Curiosity is crossing in Gale Crater, and rotating the image 150 degrees provides this right-side-up scene. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
See updated Traverse Map below[/caption]
NASA’s car-sized Curiosity rover is now blazing across the Red Planet’s surface and moving at a record setting pace towards a towering Martian mountain loaded with mineral caches that could potentially support a habitable environment.
On Sunday, July 21 (or Sol 340), Curiosity drove the length of a football field – 109.7 yards (100.3 meters) – a span that’s twice as far as she had ever driven before since the dramatic touch down on Mars nearly a year ago.
The previous record for a one-day drive was about half a football field – 54 yards (49 meters) – and achieved on Sol 50 (Sept. 26, 2012), roughly seven weeks after the pulse pounding landing inside Gale Crater on Aug. 6, 2012.
The 6 wheeled robot was able to move so far because on the prior drive she wound up atop a rise offering an uncommonly good view of the surrounding landscape and the road ahead across the crater floor towards Mount Sharp – the ultimate driving goal.

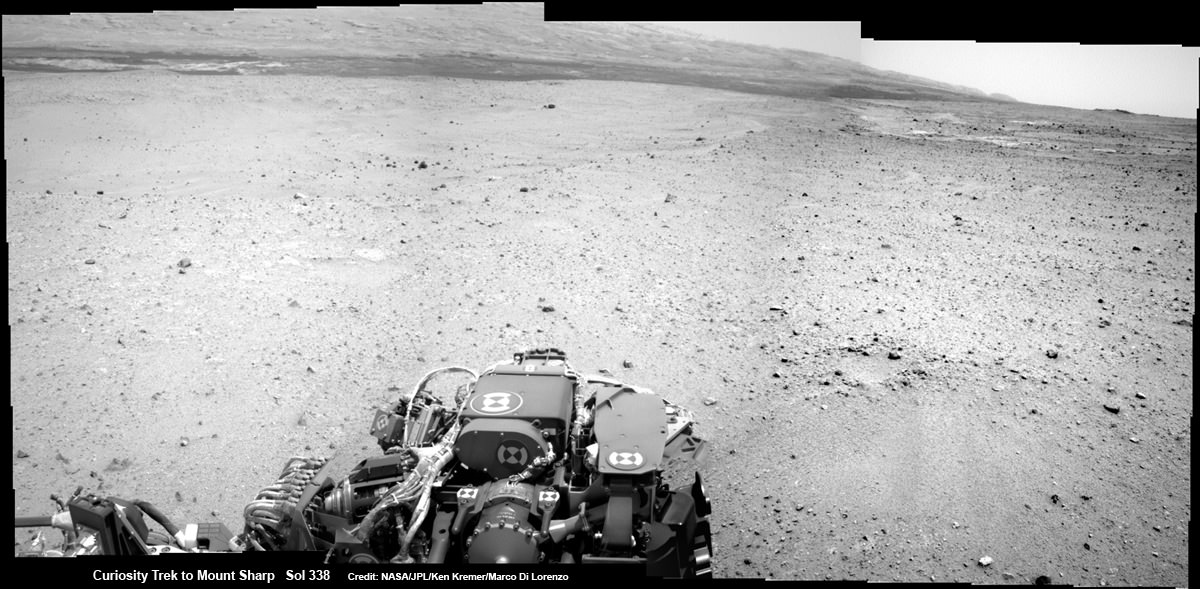
Curiosity captured this panoramic view of the path ahead to the base of Mount Sharp and potentially dangerous sand dunes after a recent drive on July 19, 2013. She must safely cross over the dark dune field to climb and reach the lower sedimentary layers of Mount Sharp.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer-(kenkremer.com)/Marco Di Lorenzo
“What enabled us to drive so far on Sol 340 was starting at a high point and also having Mastcam images giving us the size of rocks so we could be sure they were not hazards,” said rover planner Paolo Bellutta of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif, in a NASA statement.
“We could see for quite a distance, but there was an area straight ahead that was not clearly visible, so we had to find a path around that area.”
Following another lengthy drive of 68.2 yards (62.4 meters) on Wednesday, July 23 (Sol 342), the mission’s total driving distance so far stands at 0.81 mile (1.23 kilometers).
Mount Sharp lies about 5 miles (8 kilometers) distant – as the Martian crow flies.
On July 4, Curiosity embarked on the epic trek to Mount Sharp after completing more than seven months of science investigations and historic interplanetary drilling and sample analysis at an area known as Glenelg and Yellowknife Bay. There she discovered a habitable environment with the chemical ingredients that could sustain Martian microbes- thereby already accomplishing the primary goal of NASA’s flagship mission to Mars.
A combination of increased experience by the engineers directing the mega rover as well as intermediate software upgrades also play key roles in speeding Curiosity towards 3.4 mile (5.5 km) high Mount Sharp.
A huge leap in roving across Mars is in the works soon using new driving software called autonomous navigation, or autonav, that will hasten the overland journey.
“We have put some new software – called autonav, or autonomous navigation – on the vehicle right after the conjunction period back in March 2013,” said Jim Erickson, Curiosity Project Manager, in exclusive interview with Universe Today. Erickson is from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, Calif.
“This will increase our ability to drive.”
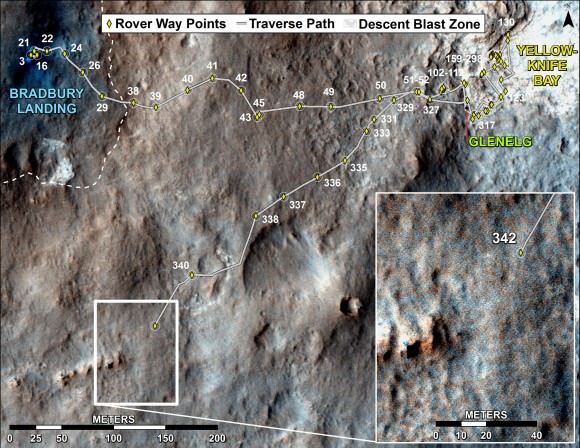
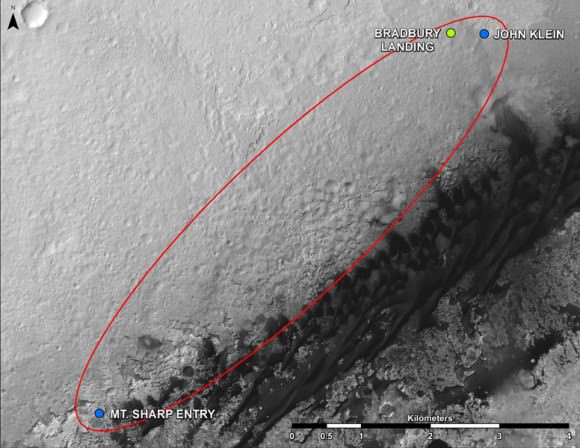
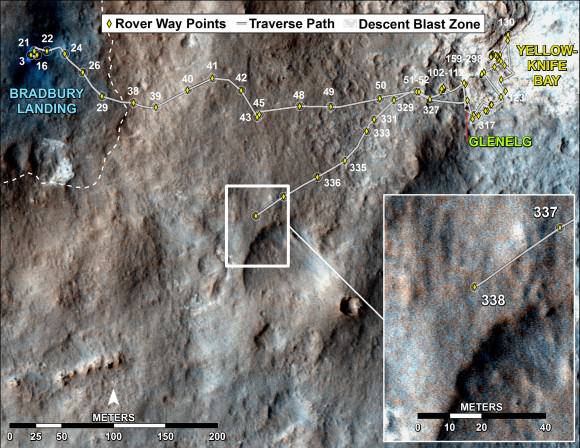
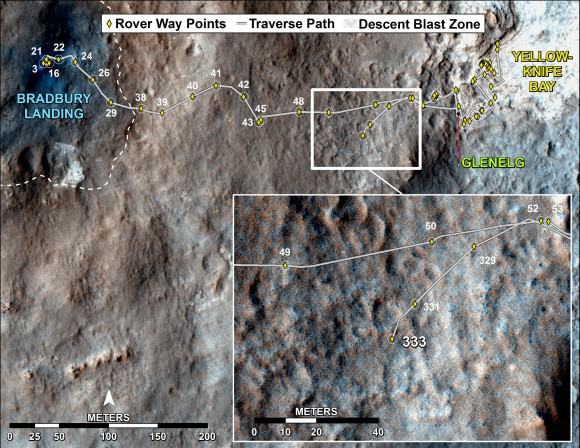
This map shows the route driven by NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity through the 342 Martian day, or sol, of the rover’s mission on Mars (July 21, 2013). Numbering of the dots along the line indicate the sol number of each drive. North is up. The scale bar is 200 meters (656 feet). From Sol 340 to Sol 342, Curiosity had driven a straight line distance of about 191.9 feet (58.49 meters). The base image from the map is from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment Camera (HiRISE) in NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona
Implementing the new driving software will make Curiosity smarter as well as more capable, productive and independent than ever before.
“With autonav the rover will have the ability to understand how far it’s driving, whether its slipping or not, and it improves safety,” Erickson told me.
The rover’s route is on a southwestward heading towards the ancient sedimentary layers at the foothills of the mountain in the middle of Gale Crater.
In addition to setting new driving records, the 1 ton rover is also driving more frequently and on repeated days too.
When everything synchs up, Curiosity can drive two or more days in row.
“We can drive two days in a row now if the timing is right. If we get the results of the day’s drive (n) in time before we have to plan the next day’s drive (n+1) – almost as if you’re on Mars time. Then that would work fine,” Erickson explained.
“Also, when we get the autonav capability we can plan two days in row. One day of directed driving and the second day can be ‘OK here’s your target from wherever you end up, try and go to this spot’.”
“This will increase the productivity!”
Erickson says the team is testing autonav now and should it be up and running within weeks, or sooner.
Read Part 1 & Part 2 of my interview with Jim Erickson for further details.

Meanwhile Curiosity’s older sister rover Opportunity is making fast tracks towards her own mountain goal and should arrive at the base of Solander Point rather soon in August.
Solander Point is a segment of the eroded rim of huge Endeavour crater and may also possess key ingredients essential to support an environment favorable for possible Martian microbes.
And it’s worth noting that older sis Opportunity stills holds the 1 day Martian distance driving world record of 219.89 meters – established more than 8 years ago on Sol 410 (March 20, 2005)!!
Stay tuned for more on NASA’s sojourning pair of Martian robots.