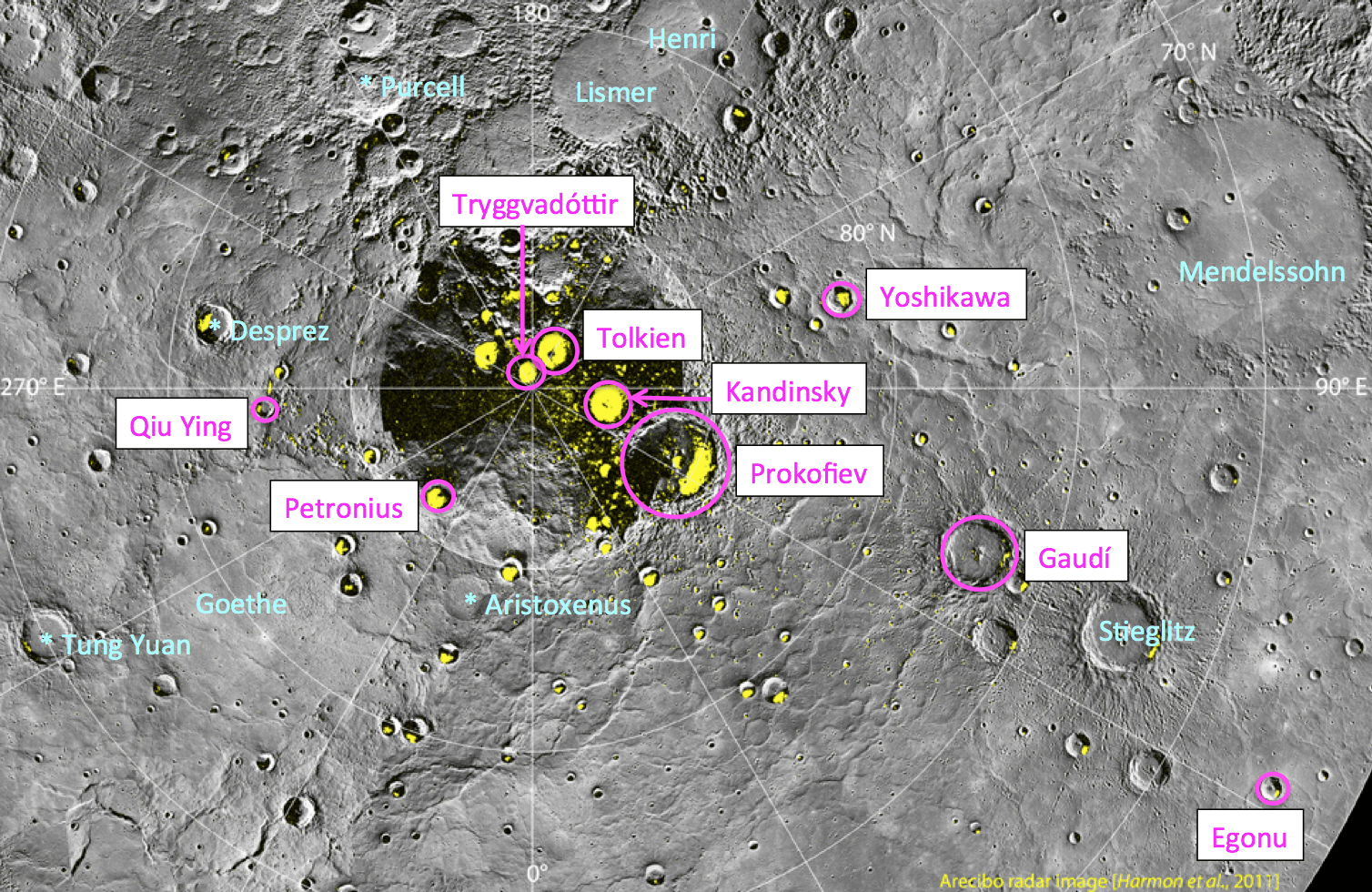
Here’s a little something to please fans of space, art and fantasy alike (and those who enjoy all three): on August 6 the International Astronomical Union approved names for 9 craters on Mercury, one of which is named for J.R.R. Tolkien, revered author of The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings (among other seminal fantasy works.)
The crater Tolkien is approximately 30 miles (48 km) in diameter. All 9 newly-named craters are located in Mercury’s north polar region and exhibit radar evidence of water ice hidden in their shadowy pocketses.
IAU procedure for craters on Mercury has them named after “deceased artists, musicians, painters, and authors who have made outstanding or fundamental contributions to their field and have been recognized as art historically significant figures for more than 50 years.” Find out who all 9 new craters are named for after the jump:
Egonu, for Uzo Egonu (1931-1996), a Nigerian-born painter who at 13 was sent to England to study art, first at a private school in Norfolk and later at the Camberwell School of Arts and Crafts. Exile, alienation, and the pain of displaced peoples were recurrent themes in his work.
Gaudí, after Antoni Gaudí (1852-1926), a Spanish architect whose work concentrated largely on the Catalan capital of Barcelona. He was very skilled with ceramics, stained glass, wrought-iron forging, and carpentry and integrated these crafts into his architecture.
Kandinsky, for Wassily Kandinsky (1866-1944), a Russian painter and art theorist credited with painting the first purely abstract works.
Petronius, for Titus Petronius (c. AD 27-66), a Roman courtier during the reign of Nero. He is generally believed to be the author of the Satyricon, a satirical novel believed to have been written during the Neronian era.
Prokofiev, for Sergei Prokofiev (1891-1953), a Russian composer, pianist, and conductor who is considered one of the major composers of the 20th century. His best-known works include the ballet Romeo and Juliet — from which “Dance of the Knights” is taken — and Peter and the Wolf.
Tolkien, for John Ronald Reuel (J. R. R.) Tolkien (1892-1973), an English writer, poet, philologist, and university professor, best known as the author of the classic fantasy novels The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings.
Tryggvadóttir, for Nina Tryggvadóttir (1913-1968), one of Iceland’s most important abstract expressionist artists and one of very few Icelandic female artists of her generation. She primarily worked in painting, but she also created collages, stained glass work, and mosaics.
Qiu Ying, for Shifu Qiu Ying (1494-1552), a Chinese painter who specialized in the gongbi brush technique, a careful realist method in Chinese painting. He is regarded as one of the Four Great Masters of the Ming Dynasty.
Yoshikawa, for Eiji Yoshikawa (1892-1962), a Japanese historical novelist best known for his revisions of older classics including The Tale of the Heike, Tale of Genji, Outlaws of the Marsh, and Romance of the Three Kingdoms.
“These designations expand the opportunities to recognize the contributions to the arts by the most creative individuals from many cultures and eras. The names of those individuals are now linked in perpetuity to the innermost planet.”
– Sean Solomon, MESSENGER Principal Investigator
The craters were imaged by NASA’s MESSENGER spacecraft, currently in extended mission around Mercury. Learn more about the preciousss MESSENGER mission here. (Gollum! Gollum!)
Image credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington







![PIA16011[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/PIA160111-580x74.jpg)



![673969main_PIA15993-43_full[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/08/673969main_PIA15993-43_full1-580x435.jpg)
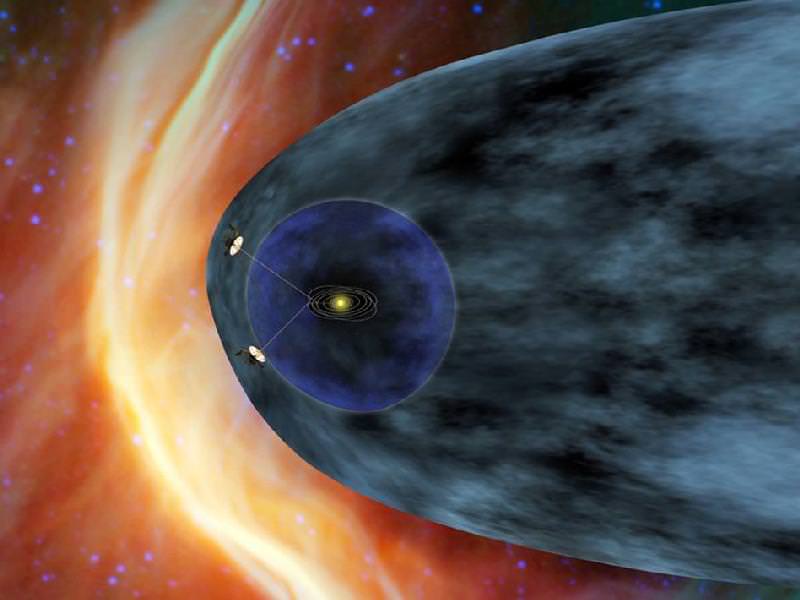

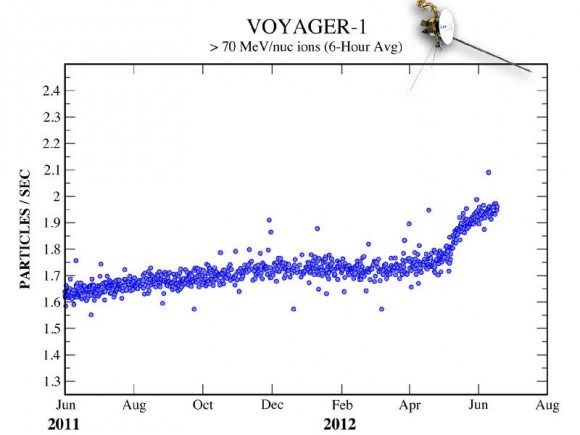
 Data sent from Voyager 1 — a trip that currently takes the information nearly 17 hours to make — have shown steadily increasing levels of cosmic radiation as the spacecraft moves farther from the Sun. But on July 28, the levels of high-energy cosmic particles detected by Voyager jumped by 5 percent, with levels of lower-energy radiation from the Sun dropping by nearly half later the same day. Within three days both levels had returned to their previous states.
Data sent from Voyager 1 — a trip that currently takes the information nearly 17 hours to make — have shown steadily increasing levels of cosmic radiation as the spacecraft moves farther from the Sun. But on July 28, the levels of high-energy cosmic particles detected by Voyager jumped by 5 percent, with levels of lower-energy radiation from the Sun dropping by nearly half later the same day. Within three days both levels had returned to their previous states.