Drown yourself in stunning images from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center set to awesome music from indie band One Ring Zero. Don’t hold back, just dive right in. You’ll love it, we promise.
Via Geeked on Goddard.
Drown yourself in stunning images from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center set to awesome music from indie band One Ring Zero. Don’t hold back, just dive right in. You’ll love it, we promise.
Via Geeked on Goddard.

[/caption]
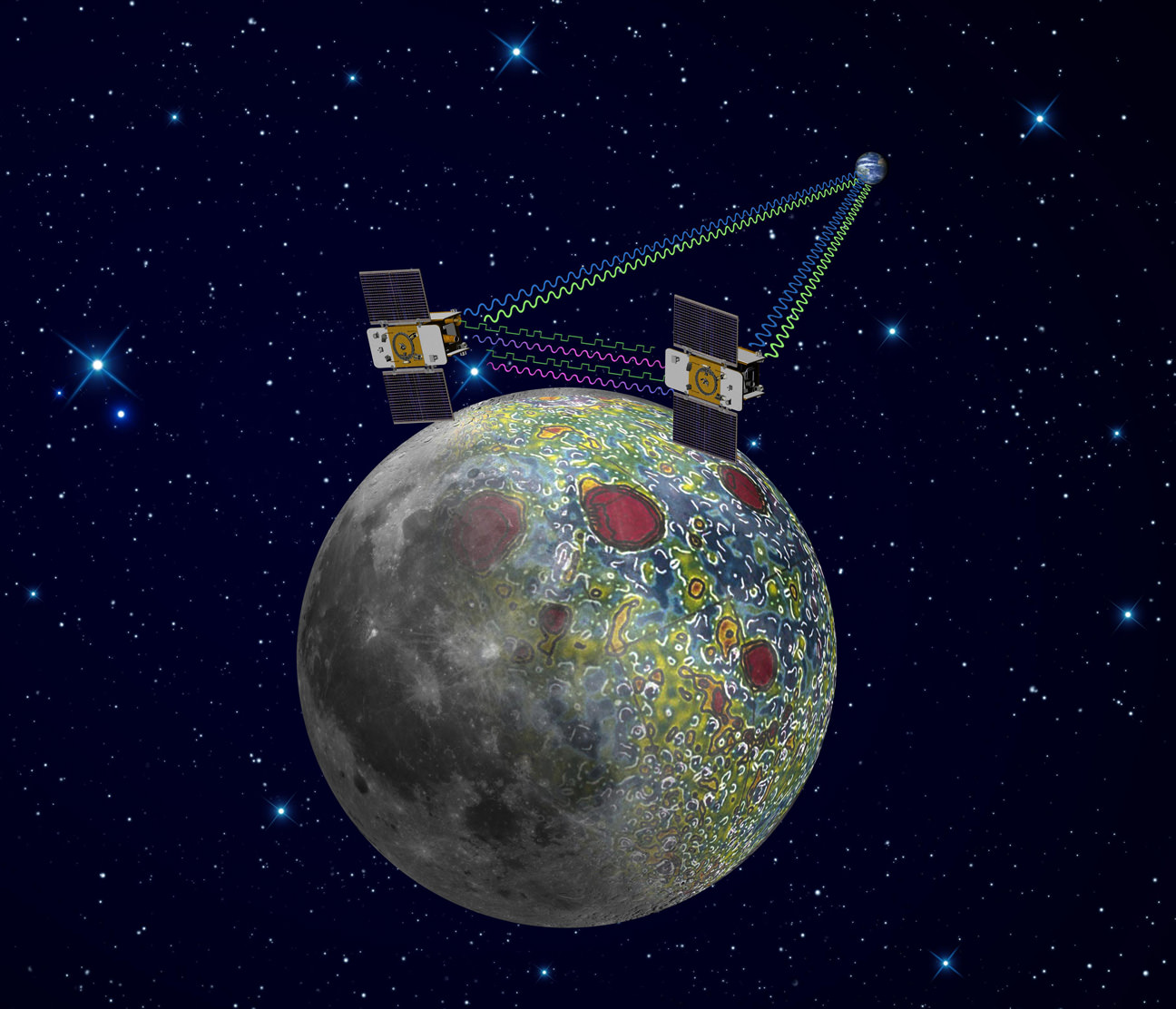
NASA’s twin lunar orbiting GRAIL (Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory) spacecraft christened Ebb and Flow have kicked off their science collection phase aimed at precisely mapping our Moon’s gravity field, interior composition and evolution, the science team informed Universe Today.
“GRAIL’s science mapping phase officially began Tuesday (March 6) and we are collecting science data,” said Maria Zuber, GRAIL principal investigator of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, to Universe Today.
“It is impossible to overstate how thrilled and excited we are !”
“The data appear to be of excellent quality,” Zuber told me.
GRAIL’s goal is to provide researchers with a better understanding of how the Moon, Earth and other rocky planets in the solar system formed and evolved over its 4.5 billion years of history.
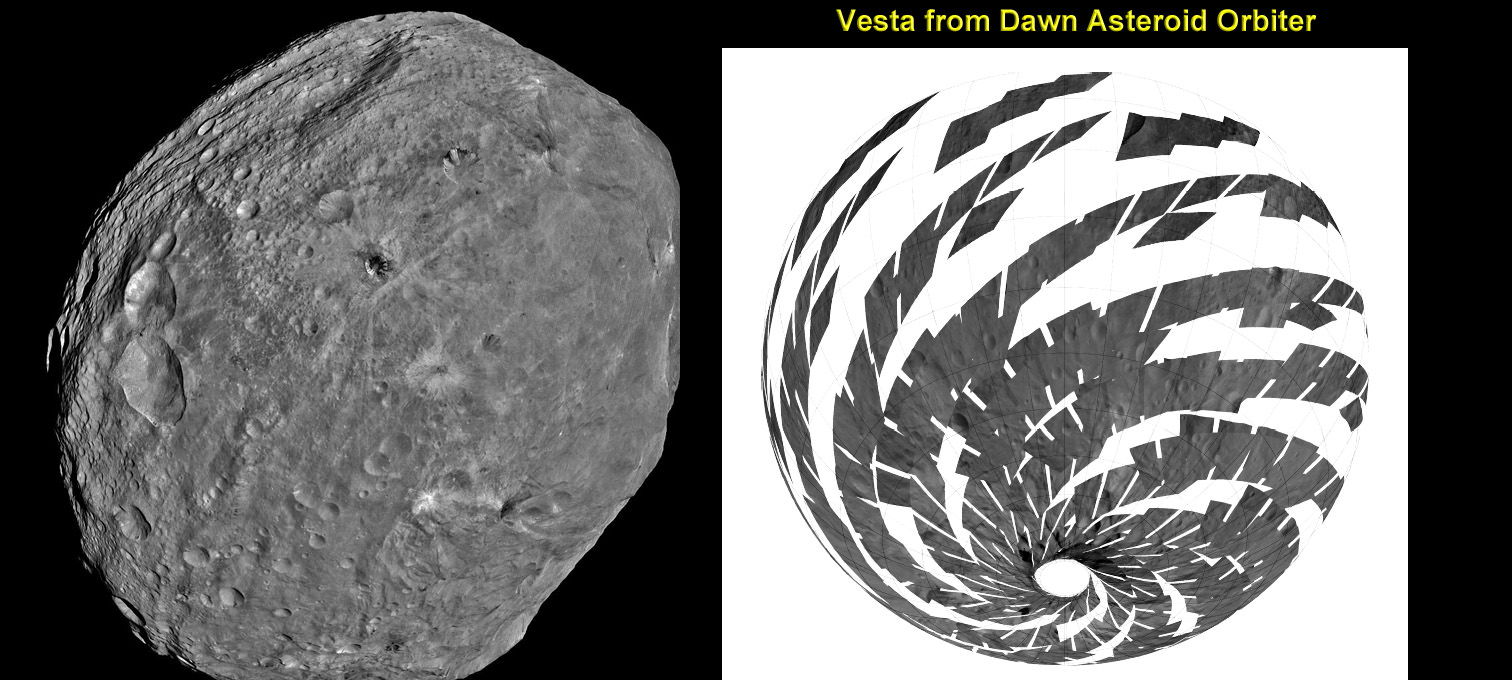
NASA’s Dawn spacecraft is currently mapping the gravity field of Asteroid Vesta in high resolution from low orbit.
Despite more than 100 missions to the Moon there is still a lot we don’t know about the Moon says Zuber, like why the near side is flooded with magma and smooth and the back side is rough, not smooth and completely different.

The formation-flying spacecraft will make detailed science measurements from lunar orbit with unparalleled precision to within 1 micron – the width of a human red blood cell – by transmitting Ka-band radio signals between each other and Earth to help unlock the mysteries of the Moon’s deep interior.
“We’ve worked on calibrating the alignment of the Ka-band antennae to establish the optimal alignment. We’ve verified the data pipeline and are spending a lot of time working with the raw data to make sure that we understand its intricacies,” Zuber explained.
The washing-machine sized probes have been flying in tandem around the Moon since entering lunar orbit in back to back maneuvers over the New Year’s weekend. Engineers have spent the past two months navigating the spaceship duo into lower, near-polar and near-circular orbits with an average altitude of 34 miles (55 kilometers), that are optimized for science data collection, and simultaneously checking out the spacecraft systems.

Ebb and Flow were launched to the Moon on September 10, 2011 aboard a Delta II rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida and took a circuitous 3.5 month low energy path to the moon to minimize the overall costs. The Apollo astronauts reached the Moon in just 3 days.
I asked Zuber to describe the team’s activities putting the mirror image probes to work peering to the central core of our nearest neighbor in unprecedented detail.
“Last Wednesday (Feb. 29) we achieved the science orbit and on Thursday (March 1) we turned the spacecraft to ‘orbiter point’ configuration to test the instrument and to monitor temperatures and power.”
“When we turned on the instrument we established the satellite-to-satellite radio link immediately. All vital signs were nominal so we left the spacecraft in orbiter point configuration and have been collecting science data since then. At the same time, we’ve continued performing calibrations and monitoring spacecraft and instrument performance, such as temperatures, power, currents, voltages, etc., and all is well,” said Zuber.
Measurements gathered over the next 84 days will be used to create high-resolution maps of the Moon’s near side and far side gravitational fields that are 100 to 1000 times more precise than ever before and that will enable researchers to deduce the internal structure and composition of our nearest neighbor from the outer surface crust down to the deep hidden core.
As one satellite follows the other, in the same orbit, they will perform high precision range-rate measurements to precisely measure the changing distance between each other. As they fly over areas of greater and lesser gravity caused by visible features such as mountains, craters and masses hidden beneath the lunar surface, the distance between the two spacecraft will change slightly.
“GRAIL is great. Everything is in place to get science data now,” said Sami Asmar, a GRAIL co-investigator from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Lab in Pasadena, Calif. “Soon we’ll get a very high resolution and global gravity map of the Moon.”
The data collected will be translated into gravitational field maps of the Moon that will help unravel information about the makeup of the Moon’s core and interior composition.
GRAIL will gather three complete gravity maps over the three month mission which is expected to conclude around May 29. If the probes survive a solar eclipse in June and if NASA funding is available, then they may get a bonus 3 month extended mission.
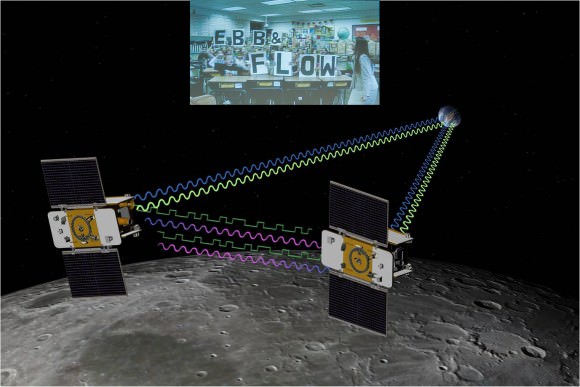
NASA sponsored a nation-wide student contest for America’s Youth to choose new names for the twin probes originally known as GRAIL A and GRAIL B. 4th graders from the Emily Dickinson Elementary School in Bozeman, Montana submitted the winning entries -Ebb and Flow. The new names won because they astutely describe the probes movements in orbit to collect the science data.
The GRAIL twins are also equipped with a very special camera dubbed MoonKAM (Moon Knowledge Acquired by Middle school students) whose purpose is to inspire kids to study science.
By having their names selected, the 4th graders from Emily Dickinson Elementary have also won the prize to choose the first target on the Moon to photograph with the MoonKAM cameras, which are managed by Dr Sally Ride, America’s first female astronaut.
“MoonKAMs on both Ebb and Flow were turned on Monday, March 5, and all appears well, Zuber said. “The Bozeman 4th graders will have the opportunity to target the first images a week after our science operations begin.”
[/caption]
NASA’s Dawn mission is getting a whopping boost in science observing time at the closest orbit around Asteroid Vesta as the probe passes the midway point of its 1 year long survey of the colossal space rock. And the team informs Universe Today that the data so far have surpassed all expectations and they are very excited !
Dawn’s bonus study time amounts to an additional 40 days circling Vesta at the highest resolution altitude for scientific measurements. That translates to a more than 50 percent increase beyond the originally planned length of 70 days at what is dubbed the Low Altitude Mapping Orbit, or LAMO.
“We are truly thrilled to be able to spend more time observing Vesta from low altitude,” Dr. Marc Rayman told Universe Today in an exclusive interview. Rayman is Dawn’s Engineer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, Calif.
“It is very exciting indeed to obtain such a close-up look at a world that even a year ago was still just a fuzzy blob.”
The big extension for a once-in-a-lifetime shot at up close science was all enabled owing to the hard work of the international science team in diligently handling any anomalies along the pathway through interplanetary space and since Dawn achieved orbit in July 2011, as well as to the innovative engineering of the spacecraft’s design and its revolutionary ion propulsion system.
“This is a reflection of how well all of our work at Vesta has gone from the beginning of the approach phase in May 2011,” Rayman told me.

Dawn’s initially projected 10 week long science campaign at LAMO began on Dec. 12, 2011 at an average distance of 210 kilometers (130 miles) from the protoplanet and was expected to conclude on Feb. 20, 2012 under the original timeline. Thereafter it would start spiraling back out to the High Altitude Mapping Orbit, known as HAMO, approximately 680 kilometers above the surface.
“With the additional 40 days it means we are now scheduled to leave LAMO on April 4. That’s when we begin ion thrusting for the transfer to HAMO2,” Rayman stated.
And the observations to date at LAMO have already vastly surpassed all hopes – using all three of the onboard science instruments provided by the US, Germany and Italy.
“Dawn’s productivity certainly is exceeding what we had expected,” exclaimed Rayman.
“We have acquired more than 7500 LAMO pictures from the Framing Camera and more than 1 million LAMO VIR (Visible and Infrared) spectra which afford scientists a much more detailed view of Vesta than had been planned with the survey orbit and the high altitude mapping orbit (HAMO). It would have been really neat just to have acquired even only a few of these close-up observations, but we have a great bounty!”
“Roughly around half of Vesta’s surface has been imaged at LAMO.”
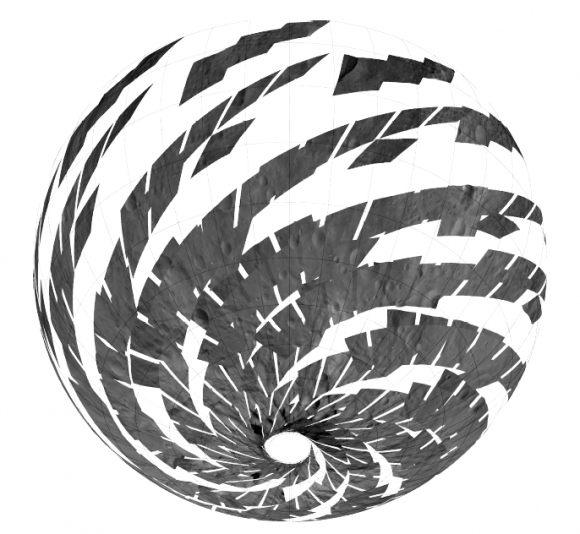

The bonus time at LAMO will now be effectively used to help fill in the gaps in surface coverage utilizing all 3 science instruments. Therefore perhaps an additional 20% to 25% extra territory will be imaged at the highest possible resolution. Some of this will surely amount to enlarged new coverage and some will be overlapping with prior terrain, which also has enormous research benefits.
“There is real value even in seeing the same part of the surface multiple times, because the illumination may be different. In addition, it helps for building up stereo,” said Rayman.
Researchers will deduce further critical facts about Vesta’s topography, composition, interior, gravity and geologic features with the supplemental measurements.
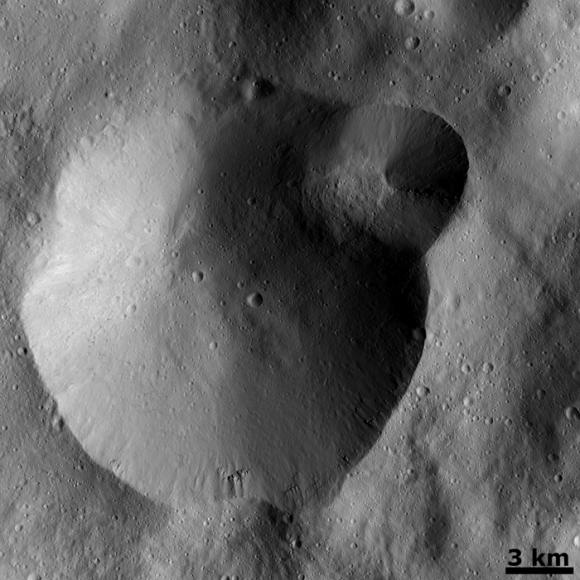

The foremost science goals at LAMO are collection of gamma ray and neutron measurements with the GRaND instrument – which focuses on determining the elemental abundances of Vesta – and collection of information about the structure of the gravitational field. Since GRaND can only operate effectively at low orbit, the extended duration at LAMO takes on further significance.
“Our focus is on acquiring the highest priority science. The pointing of the spacecraft is determined by our primary scientific objectives of collecting GRaND and gravity measurements.”
As Dawn continues orbiting every 4.3 hours around Vesta during LAMO, GRaND is recording measurements of the subatomic particles that emanate from the surface as a result of the continuous bombardment of cosmic rays and reveals the signatures of the elements down to a depth of about 1 meter.
“You can think of GRaND as taking a picture of Vesta but in extremely faint light. That is, the nuclear emissions it detects are extremely weak. So our long time in LAMO is devoted to making a very, very long exposure, albeit in gamma rays and neutrons and not in visible light,” explained Rayman.
Now with the prolonged mission at LAMO the team can gather even more data, amounting to thousands and thousands more pictures, hundreds of thousands of more VIR spectra and ultra long exposures by GRaND.
“HAMO investigations have already produced global coverage of Vesta’s gravity field,” said Sami Asmar, a Dawn co-investigator from JPL. Extended investigations at LAMO will likewise vastly improve the results from the gravity experiment.
“We always carried 40 days of “margin,” said Rayman, “but no one who was knowledgeable about the myriad challenges of exploring this uncharted world expected we would be able to accomplish all the complicated activities before LAMO without needing to consume some of that margin. So although we recognized that we might get to spend some additional time in LAMO, we certainly did not anticipate it would be so much.”
“As it turned out, although we did have surprises the operations team managed to recover from all of them without using any of those 40 days.”
“This is a wonderful bonus for science,” Rayman concluded.
“We remain on schedule to depart Vesta in July 2012, as planned for the past several years.”
Dawn’s next target is Ceres, the largest asteroid in the main Asteroid Belt between Mars and Jupiter

[/caption]
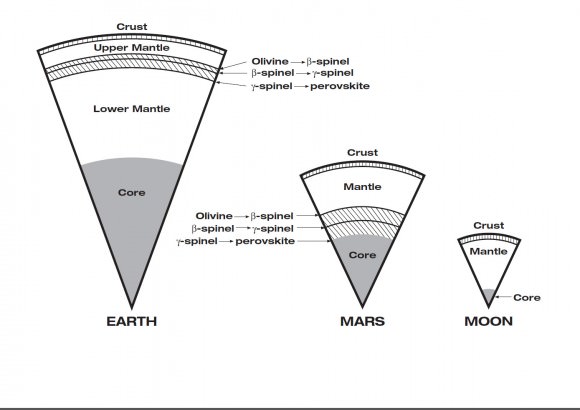
A Phoenix-like lander that would mine the deepest hole yet into Mars– to a depth of 5 meters – and unveil the nature of the mysterious deep interior and central core of the Red Planet is under consideration by NASA for a 2016 launch and sports a nifty new name – InSight.
The stationary “InSight” lander would be an international science mission and a near duplicate of NASA’s proven Phoenix spacecraft, Bruce Banerdt told Universe Today. Banerdt is the Principal Investigator of the proposed InSight mission.
“InSight is essentially built from scratch, but nearly build-to-print from the Phoenix design,” Banerdt, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena , Calif, told me. The team can keep costs down by re-using the blueprints pioneered by Phoenix instead of creating an entirely new spacecraft.
“The robotic arm is similar (but not identical) to the Phoenix arm.”
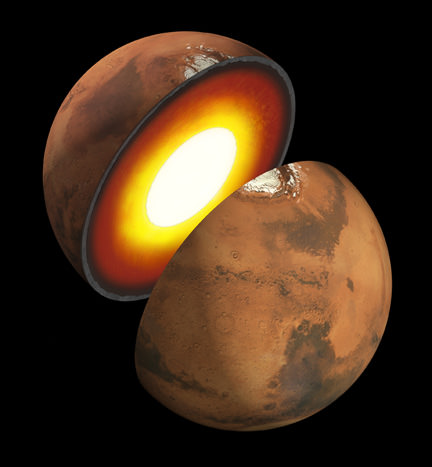

Insight’s goal is to investigate and deduce the nature of the interior of the Red Planet. Credit: JPL/NASA
However, the landing site and science goals for InSight are quite different from Phoenix.
InSight will have an entirely new suite of three science instruments, including two from Europe, designed to peer to the center of Mars and detect the fingerprints of the processes by which the terrestrial planets formed. It will determine if there is any seismic activity, the amount of heat flow from the interior, the size of Mars core and whether the core is liquid or solid.
NASA’s twin GRAIL lunar gravity probes are set to begin their own investigation into the interior and core of Earth’s Moon in early March 2012, and several science team members are common to GRAIL and InSight.
“The seismometer (SEIS, stands for Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure) is from France (built by CNES and IPGP) and the heat flow probe (HP3, stands for Heat flow and Physical Properties Probe) is from Germany (built by DLR),” Banerdt explained.
Phoenix successfully landed in the frigid northern polar regions of Mars in 2008 in search of potential habitats for life and quickly discovered water ice and salty soils that could be favorable for the genesis and support of extraterrestrial life.

InSight will intentionally land in a far warmer and sunnier location nearer the moderate climate of the equator to enable a projected lifetime of 2 years (or 1 Mars year) vs. the 5 months survival of Phoenix extremely harsh arctic touchdown zone.
“Our planned landing site is in Elysium Planitia,” Banerdt told me. “It was chosen for optimizing engineering safety margins for landing and power.”
The more equatorial landing site affords far more sun for the life giving solar arrays to power the instruments and electronics.
“We have global objectives and can do our science anywhere on the planet.”
Elysium Planitia is not too far from the landing sites of the Spirit and Curiosity rovers. The Elysium Mons volcano is also in the general area, but it’s a long way from precise site selection.
InSight is a geophysical lander targeted to delve deep beneath the surface into the Martian interior, check its “vital signs”; like “pulse” though seismology, “temperature”, though a heat flow probe, and “reflexes”, through precision tracking.
The purpose is to answer one of science’s most fundamental questions: How were the planets created?
InSight will accomplish much of its science investigations through experiments sitting directly in contact with the Martian surface. The robotic arm will pluck two of the instruments from the lander deck and place them onto Mars.
“The arm will pick the SEIS seismometer and HP3 heat flow probe off the deck and place each on the ground next to the lander. The arm doesn’t have a drill, but the heat flow probe itself will burrow down as deep as 5 meters,” Banerdt elaborated.
The third experiment named RISE (Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment) is to be provided by JPL and will use the spacecraft communication system to provide precise measurements of Mars planetary rotation and elucidate clues to its interior structure and composition.
Right now on Mars, NASA’s Opportunity rover is conducting a Doppler radio tracking experiment similar to what is planned for RISE, but InSight will have a big advantage according to Banerdt.
“The RISE experiment will be very similar to what we are doing right now on Opportunity, but will be able to do much better, said Banerdt. “The differences are that we will get more tracking every week (Opportunity is power-limited during the winter months; that’s why she is currently stationary!) and will make measurements for an entire Mars year – we will likely only get a handful of months from Opportunity.”
Insight will also be equipped with 2 cameras and make some weather measurements.
“We have a camera on the arm and one fixed to the deck, both primarily to support placing the instruments on the surface, although they will be able to scan the landscape around the spacecraft. Both are Black & White,” Banerdt told me.
“We will measure pressure, temperature and wind, mostly to support noise analysis on the seismic data, but will also supply information on the weather.”
InSight is one of three missions vying to be selected for flight in NASA’s Discovery Program, a series of low cost NASA missions to understand the solar system by exploring planets, moons, and small bodies such as comets and asteroids. All three mission teams are required to submit concept study reports to NASA on March 19.
Banerdt’s team is working hard to finalize the concept study report.
“It describes the mission design as we have refined it over the past 9 months since the NASA Step-1 selection.”
So there is no guarantee that InSight will fly. Because of severe budget cuts to NASA’s Planetary Science Division, NASA had to cancel its scheduled participation in two other Mars missions dubbed ExoMars and jointed planned with ESA, the European Space Agency, for launch in 2016 and 2018.
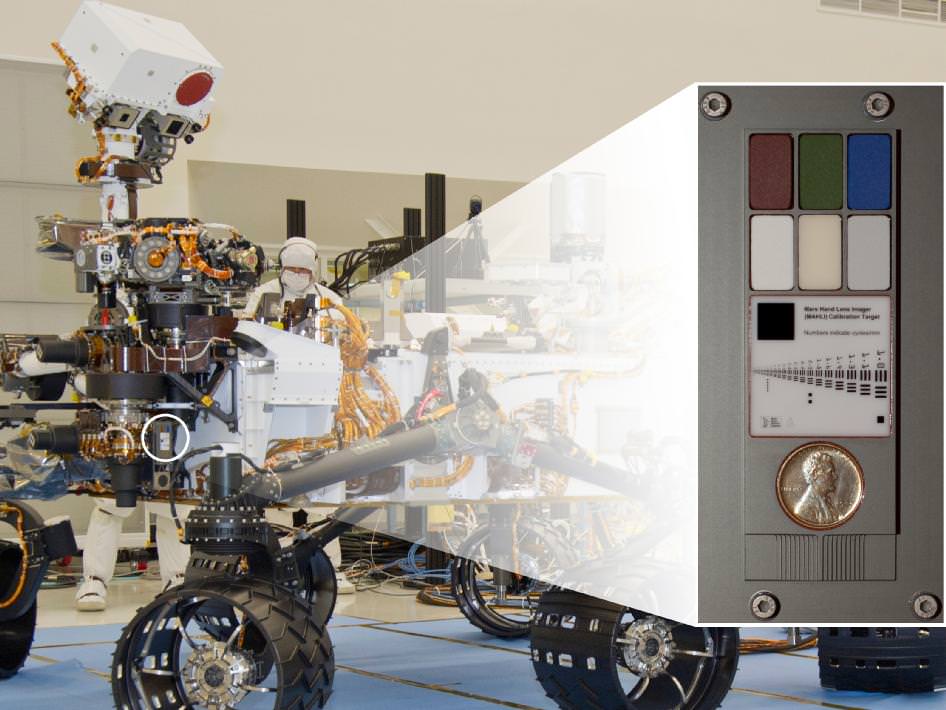

[/caption]
NASA’s huge Curiosity Mars Science Lab (MSL) rover is carrying a vintage Lincoln penny along for the long interplanetary journey to Mars – and it’s not to open the first Martian savings account.
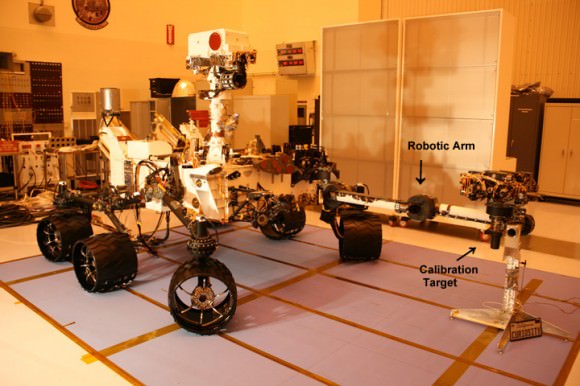
Scientists will use the century old Lincoln penny – minted back in 1909 – as a modern age calibration target for one of Curiosity’s five powerful science cameras attached to the end of the hefty, 7 foot (2.1 meter) long robotic arm.
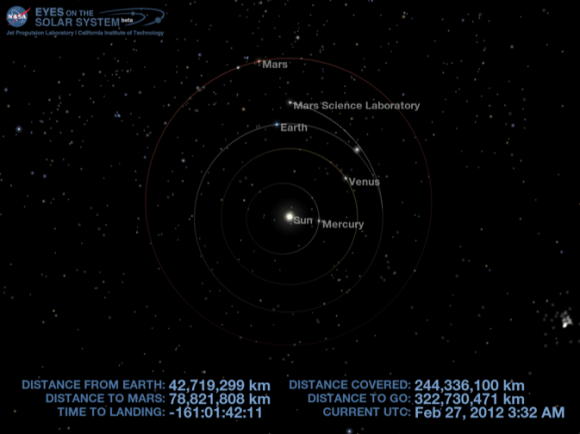
The car sized rover is on course to touchdown at the foothills of a towering and layered mountain inside Gale Crater in just 161 days on Aug. 6, 2012.
So far Curiosity has traveled 244 million kilometers since blasting off on Nov. 26, 2011 from Florida and has another 322 million kilometers to go to the Red Planet.
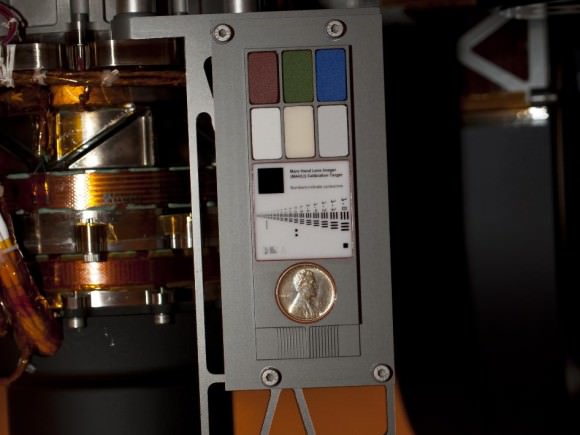
The copper penny is bundled to a shoulder joint on the rovers arm along with the other elements of the calibration target, including color chips, a metric standardized bar graphic, and a stair-step pattern for depth calibration.
The whole target is about the size of a smart phone and looks a lot like an eye vision chart in an ophthalmologist’s office. And it serves a similar purpose, which will be to check the performance of Curiosity eyes – specifically the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera located at the terminus of the robotic arm.
MAHLI will conduct close-up inspections of Martian rocks and soil. It can show tiny details, finer than a human hair.
The term “hand lens” in MAHLI’s name refers to the standard practice by field geologists’ of carrying a hand lens during expeditions for close up, magnified inspection of rocks they find along the way. So it’s also critical to pack various means of calibration so that researchers can interpret their results and put them into proper perspective.
MAHLI can also focus on targets over a wide range of distances near and far, from about a finger’s-width away out to the Red Planets horizon, which in this case means the mountains and rim of the breathtaking Gale Crater landing site.
“When a geologist takes pictures of rock outcrops she is studying, she wants an object of known scale in the photographs,” said MAHLI Principal Investigator Ken Edgett, of Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego, which supplied the camera to NASA.
The target features a collection of marked black bars in a wide range of labeled sizes to correlate calibration images to each image taken by Curiosity.
“If it is a whole cliff face, she’ll ask a person to stand in the shot. If it is a view from a meter or so away, she might use a rock hammer. If it is a close-up, as the MAHLI can take, she might pull something small out of her pocket. Like a penny.”
Edgett donated the special Lincoln penny with funds from his own pocket. The 1909 “VDB” cent stems from the very first year that Lincoln pennies were minted and also marks the centennial of President Abraham Lincoln’s birth. The VDB initials of the coin’s designer – Victor David Brenner — are on the reverse side. In mint condition the 1909 Lincoln VDB copper penny has a value of about $20.
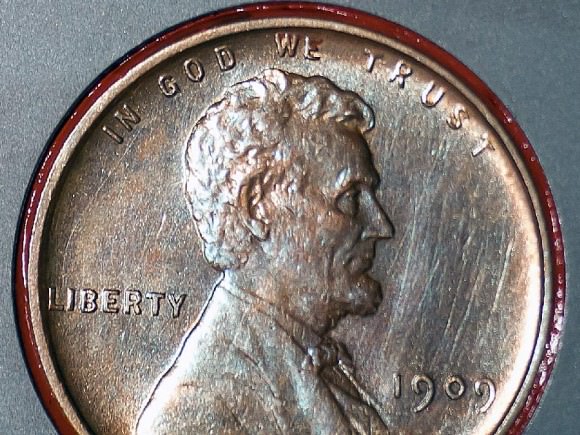
“The penny is on the MAHLI calibration target as a tip of the hat to geologists’ informal practice of placing a coin or other object of known scale in their photographs. A more formal practice is to use an object with scale marked in millimeters, centimeters or meters,” Edgett said. “Of course, this penny can’t be moved around and placed in MAHLI images; it stays affixed to the rover.”
“Everyone in the United States can recognize the penny and immediately know how big it is, and can compare that with the rover hardware and Mars materials in the same image,” Edgett said.
“The public can watch for changes in the penny over the long term on Mars. Will it change color? Will it corrode? Will it get pitted by windblown sand?”
MAHLI’s calibration target also features a display of six patches of pigmented silicone to assist in interpreting color and brightness in the images. Five of them are leftovers from Spirit and Opportunity. The sixth has a fluorescent pigment that glows red when exposed to ultraviolet light, allows checking of an ultraviolet light source on MAHLI. The fluorescent material was donated to the MAHLI team by Spectra Systems, Inc., Providence, R.I.
Three-dimensional calibration of the MSL images will be done using the penny and a stair-stepped area at the bottom of the target.
“The importance of calibration is to allow data acquired on Mars to be compared reliably to data acquired on Earth,” said Mars Science Laboratory Project Scientist John Grotzinger, of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena.
Curiosity is a 1 ton (900 kg) behemoth. She measures 3 meters (10 ft) in length and is nearly twice the size and five times as heavy as Spirit and Opportunity, NASA’s prior set of twin Martian robots. The science payload is 15 times heavier than the twin robots.
Curiosity is packed to the gills with 10 state of the art science instruments that are seeking the signs of life in the form of organic molecules – the carbon based building blocks of life as we know it.
NASA could only afford to build one rover this time.
Curiosity will be NASA’s last Mars rover since the 4th generation ExoMars rover due to liftoff in 2018 was just cancelled by the Obama Administration as part of a deep slash to NASA’s Planetary Science budget.
[/caption]
Opportunity, the Princess of Martian Robots, phoned home dusty new self portraits – above and below – of her beautiful bod basking in the utterly frigid sunshine during her 5th winter on the Red Planet whilst overlooking a humongous crater offering bountiful science.
NASA’s endearing robot is simultaneously carrying out an ambitious array of ground breaking science experiments this winter – providing insight into the mysterious nature of the Martian core – while sitting stationary until the energy augmenting rays of the springtime Sun shower down on Mars from the heavens above.
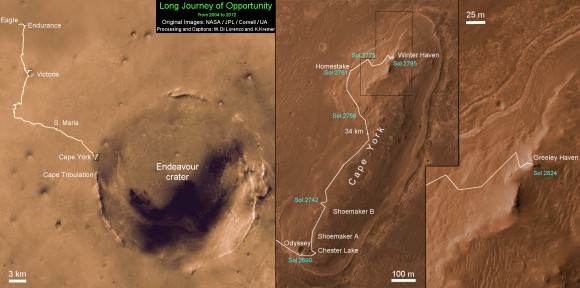
Opportunity’s current winter worksite is located at the rim of the vast crater named Endeavour, some 14 miles (22 kilometers) in diameter. The robot will remain parked for the winter on a slope at the north end of the crater rim segment called Cape York with an approximate 15-degree northerly tilt towards the life-giving sun to maximize solar energy production. The park-site is at an outcrop dubbed “Greeley Haven”, named in honor of Ronald Greeley, a beloved and recently deceased science team member.
The power killing dust buildup is readily apparent on the solar arrays and High Gain Antenna pictured in the new panoramic self-portraits of Opportunity’s wing-like deck. The red Martian dust also functions as a rather effective camouflage agent, sometimes blending the rover to near invisibility with the surface.
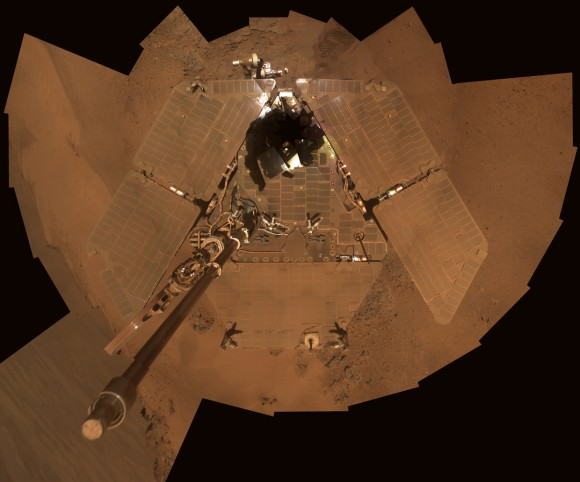

Indeed because Opportunity is covered with a thicker film of dust compared to her prior four Martian winters, the rover team was forced to employ the same “tilting” strategy they successfully used to keep her twin sister Spirit alive during her trio of Antarctic-like winters. This is the first winter that Opportunity did not have sufficient power to continue roving across the surface.
Since Opportunity is located just south of the Martian equator, the daylight hours for solar power generation are growing shorter until the southern Mars winter solstice occurs on March 30, 2012. As of mid- February 2012, the latest measure of solar array energy production was 274 watt-hours, compared to about 900 watt-hours at the start of the mission. See Solar Power energy graph below.
Power generation from the solar arrays has fluctuated up and down throughout Opportunity’s lifetime depending on when the completely unpredictable and fortuitous Martian wind storms chance by and miraculously clean the arrays of the rusty red dust.
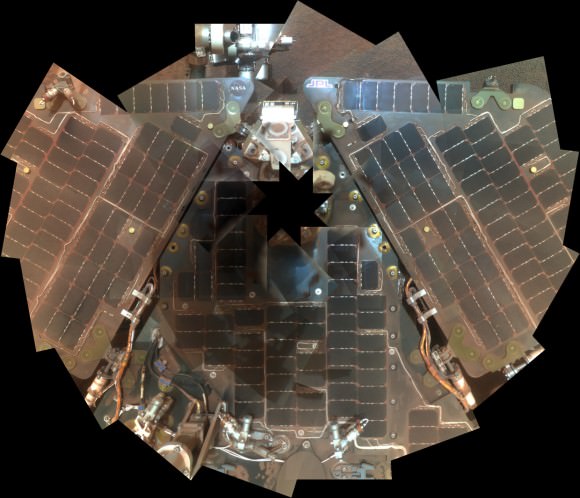

The rover science team is ingeniously using the lack of movement to their advantage and Opportunity is still vigorously hard at work doing breakthrough research each and every day.
From her stationary position, Opportunity is conducting her first ever radio science Doppler tracking measurements to support geo-dynamic investigations and to elucidate the unknown structure of the Martian interior and core. The team was eager for the long awaited chance to carry out the radio tracking experiment with the High Gain Antenna (HGA) and determine if Mars core is liquid or solid. Months of data collection are required while the rover stays stationary.
“This winter science campaign will feature two way radio tracking with Earth to determine the Martian spin axis dynamics – thus the interior structure, a long-neglected aspect of Mars,” Ray Arvidson told Universe Today. Arvidson, of Washington University in St. Louis, is the deputy rover Principal Investigator.
Opportunity has nearly finished snapping the 13 filter, 360 degree stereo Greeley” panorama. The rover deployed the robotic arm onto the surface of the “Amboy” outcrop to collect multi-sol integrations with the Mössbauer Spectrometer and the largest ever mosaic campaign using the Microscopic Imager.
“We’ll do good science while we’re at Greeley Haven. But as soon as we catch a wind gust or the seasons change, we’ll be on our way again,” Steve Squyres told Universe Today. Squyres, of Cornell University is the rover Science Principal Investigator
“The Martian southern winter solstice occurs at the end of March. A few months after that date we will drive her off the outcrop and further explore Cape York,” Arvidson told me
The team will drive Opportunity in search of further evidence of the gypsum mineral veins like “Homestake” – indicative of ancient water flow – previously discovered at Cape York. Thereafter they’ll rove further south to investigate deposits of phyllosilicates, the clay minerals which stem from an earlier epoch when liquid water flowed on Mars eons ago and perhaps may have been more favorable to sustaining life.
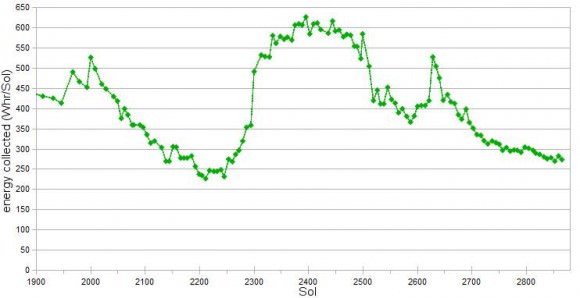

Opportunity is now well into her 9th year exploring hitherto unknown terrain on Mars, far exceeding anyone’s expectation. She landed inside a tiny crater on Jan. 24. 2004 for what was expected to be a mission of merely 90 Martian days, or Sols.
Today is Martian Sol 2873, that’s 32 times beyond the rover designers “warranty” for NASA’s Opportunity rover.
Altogether, Opportunity has journeyed more than 21 miles (34 kilometers) across the Red Planet’s surface, marking the first overland expedition on another Planet. See our route map below.
Meanwhile, NASA’s Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory rover is rocketing through space and on course for a pinpoint touchdown inside the layered terrain of Gale Crater on August 6, 2012. Curiosity is now America’s last planned Mars rover following the cancellation of the joint NASA/ESA ExoMars rover mission in the Obama Administrations newly announced Fiscal 2013 NASA budget.
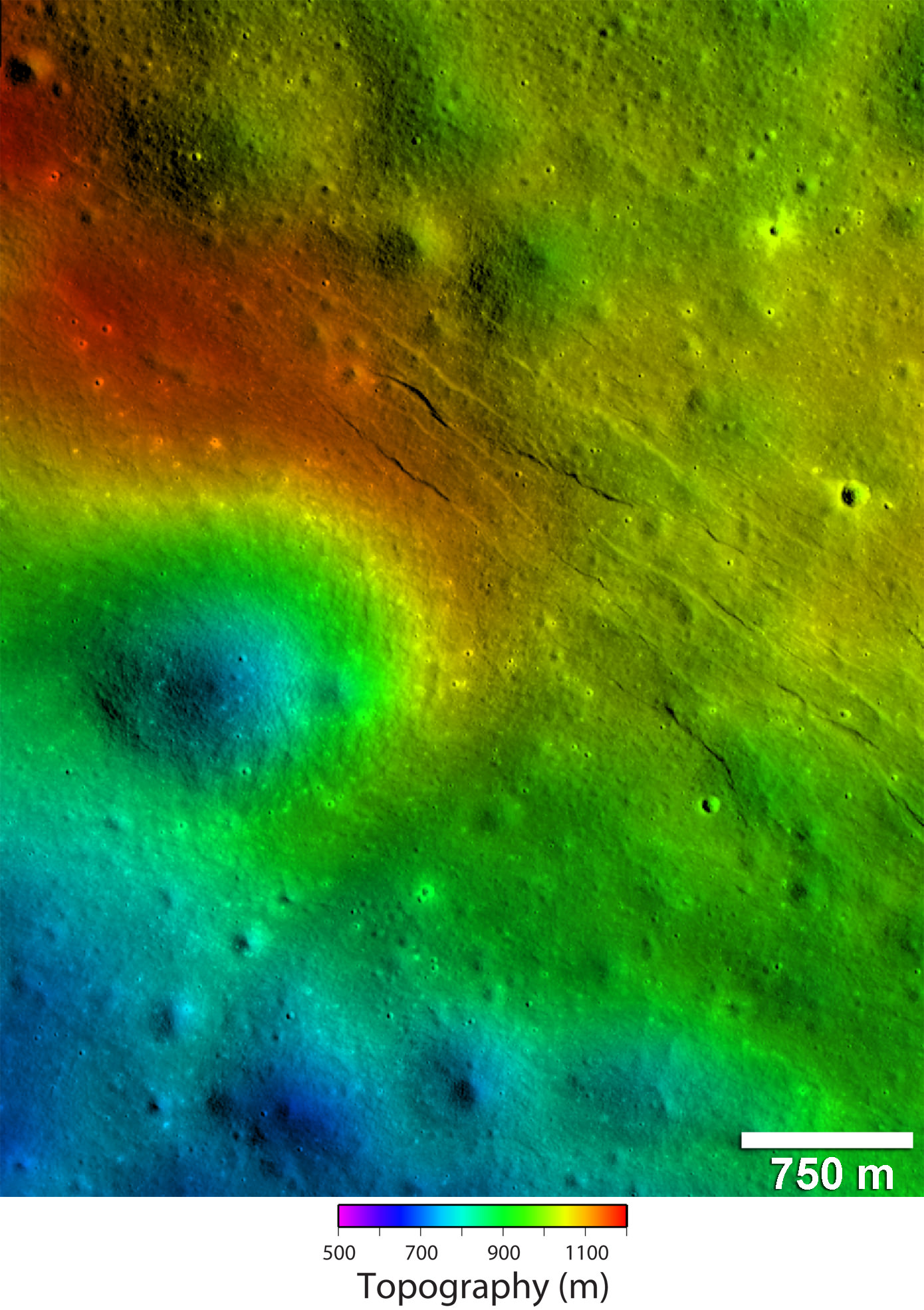

[/caption]
Recent images from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera provide evidence that the lunar crust may be pulling apart in certain areas. The images reveal small trenches less than a kilometer in length, and less than a few hundred meters wide. Only a small number of these features, known as graben, have been discovered on the lunar surface.
There are several clues in the high-resolution images that provide evidence for recent geologic activity on the Moon.
The LROC team detected signs of contraction on the lunar surface as early as August of 2010. The contractions were in the form of lobe-shaped ridges known as lobate scarps. Based on the data, the team suggests the widely-distributed scarps indicate the Moon shrank in diameter, and may be continuing to shrink. Interestingly enough, the new image data featuring graben presents a contradiction, as they indicate lunar crust being pulled apart and theorize that the process that created the graben may have occurred within the past 50 million years.
“We think the Moon is in a general state of global contraction due to cooling of a still hot interior, said thomas Watters from the Center for Earth and Planetary Studies. “The graben tell us that forces acting to shrink the Moon were overcome in places by forces acting to pull it apart. This means the contractional forces shrinking the Moon cannot be large, or the small graben might never form.”
Based on the size of the graben, the forces responsible for contraction of the lunar surface are assumed to be fairly weak. It is further theorized that, unlike the early terrestrial planets, the Moon was not completely molten during its early history.
“It was a big surprise when I spotted graben in the farside highlands,” said Mark Robinson, LROC Principal Investigator at Arizona State University. “I immediately targeted the area for high resolution stereo images so we could create a 3-dimensional view of the graben. It’s exciting when you discover something totally unexpected. Only about half the lunar surface has been imaged in high resolution. There is much more of the Moon to be explored.”
If you’d like to learn more about the recently discovered graben on the moon, you can watch a short video by Thomas Watters below:
To learn more about the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera, visit: http://www.lroc.asu.edu/
Source: Arizona State University News
[/caption]
The 68-mile (109-km) -wide Amaral crater on Mercury reveals its brightly-tipped central peaks in this image, acquired by NASA’s MESSENGER spacecraft on Feb. 4, 2012. Long shadows are cast by the crater’s peaks and rugged rim (north is to the left.)
The image was acquired as a high-resolution targeted observation with MESSENGER’s Narrow-Angle Camera (NAC) on its Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS).
Amaral’s bright peaks were first spotted during MESSENGER’s first flyby of Mercury in Jan. 2008. With a smooth floor, visible ejecta and small secondary craters, Amaral appeared noticeably younger than the heavily cratered surface around it.

Its central peaks also attracted astronomers’ interest, as they were seen to possess a striking blue hue in color-enhanced images that likely indicates rocks with different composition from the surrounding surface.
Amaral’s peaks resemble those of the slightly larger crater Eminescu, which is now known to contain recently-discovered features called hollows. It’s not yet known if Amaral also contains hollows, but it’s suspected that they may be present on the tips of the peaks.
The crater is named after Brazilian artist Tarsila do Amaral. She lived from 1886 to 1973 and is considered to be one of the leading Latin American modernist painters.
Image credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington.

[/caption]
Earth’s next Mars Rover – NOT Made in USA
Just days after President Obama met with brilliant High School students at the 2012 White House Science Fair to celebrate their winning achievements and encourage America’s Youth to study science and take up careers in the Science, Technology, Engineering and Math (STEM) technical fields, the Obama Administration has decided on deep budgets cuts slashing away the very NASA science programs that would inspire those same students to shoot for the Stars and Beyond and answer the question – Are We Alone ?
Last year, the Obama Administration killed Project Constellation, NASA’s Human Spaceflight program to return American astronauts to the Moon. This year, the President has killed NASA’s ExoMars Robotic Spaceflight program aimed at dispatching two ambitious missions to Mars in 2016 and 2018 to search for signs of life.
Both ExoMars probes involved a joint new collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) carefully crafted to share costs in hard times and get the most bang for the buck – outlined in my earlier Universe Today story, here.
Expert Scientists and Policy makers have been voicing their opinions.

All of NASA’s “Flagship” Planetary Science missions have now been cancelled in the 2013 Fiscal Year Budget proposed on Feb. 13, and others missions have also been curtailed due to the severe economy.
“There is no room in the current budget proposal from the President for new Flagship missions anywhere,” said John Grunsfeld, NASA’s Associate Administrator for Science at a NASA budget briefing for the media on Feb. 13.
ESA is now looking to partner with Russia as all American participation in ExoMars is erased due to NASA’ s forced pull out.
On Feb. 13, NASA’s Fiscal 2013 Budget was announced and the Obama Administration carved away nearly half the Mars mission budget. Altogether, funding for NASA’s Mars and Planetary missions in the Fiscal 2013 budget would be sliced by $300 million – from $1.5 Billion this year to $1.2 Billion in 2013. NASA was forced to gut the Mars program to pay for the cost overruns of the James Webb Space Telescope.
Mars rover scientist Prof. Jim Bell of Arizona State University and President of The Planetary Society (TPS) told Universe Today that “no one expects increases”, but cuts of this magnitude are “cause for concern”.
NASA’s robotic missions to Mars and other solar system bodies have been highly successful, resulted in fundamental scientific breakthroughs and are wildly popular with students and the general public.
“With these large proposed cuts to the NASA Mars exploration program, there will be a lot of cause for concern,” said Bell.
“The Mars program has been one of NASA’s crown jewels over the past 15 years, both in terms of science return on investment, and in terms of public excitement and engagement in NASA’s mission. It would also represent an unfortunate retreat from the kind of international collaboration in space exploration that organizations like The Planetary Society so strongly support.”

Bell and other scientists feel that any cuts should be balanced among NASA programs, not aimed only at one specific area.
“Certainly no one expects increasing budgets in these austere times, and it is not useful or appropriate to get into a battle of “my science is better than your science” among the different NASA Divisions and Programs.” Bell told me.
“However, it would be unfortunate if the burden of funding cuts were to befall one of NASA’s most successful and popular programs in a disproportionate way compared to other programs. As Ben Franklin said, “We should all hang together, or surely we will all hang separately.”
Bell added that science minded organizations should work with Congress to influence the debate over the coming months.
“Of course, this would only be an initial proposal for the FY13 and beyond budget. Over the winter, spring, and summer many professional and public organizations, like TPS, will be working with Congress to advocate a balanced program of solar system exploration that focuses on the most important science goals as identified in the recent NRC Planetary Decadal Survey, as well as the most exciting and publicly compelling missions that are supported by the public–who ultimately are the ones paying for these missions.”
“Let’s hope that we can all find a productive and pragmatic way to continue to explore Mars, the outer solar system, and our Universe beyond,” Bell concluded.
“The impact of the cuts … will be to immediately terminate the Mars deal with the Europeans,” said Scott Hubbard, of Stanford University and a former NASA planetary scientist who revived the agency’s Mars exploration program after failures in 1999, to the Washington Post. “It’s a scientific tragedy and a national embarrassment.”
“I encourage whoever made this decision to ask around; everyone on Earth wants to know if there is life on other worlds,” Bill Nye, CEO of The Planetary Society, said in a statement. “When you cut NASA’s budget in this way, you’re losing sight of why we explore space in the first place.”
“There is no other country or agency that can do what NASA does—fly extraordinary flagship missions in deep space and land spacecraft on Mars.” Bill Nye said. “If this budget is allowed to stand, the United States will walk away from decades of greatness in space science and exploration. But it will lose more than that. The U.S. will lose expertise, capability, and talent. The nation will lose the ability to compete in one of the few areas in which it is still the undisputed number one.”
Ed Weiler is NASA’s recently retired science mission chief (now replaced by Grunsfeld) and negotiated the ExoMars program with ESA. Weiler actually quit NASA specifically in opposition to the Mars Program cuts ordered by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and had these comments for CBS News;
“To me, it’s bizarro world,” Weiler said an interview with CBS News. “Why would you do this? The President of the United States, President Obama, declared Mars to be the ultimate destination for human exploration. Obviously, before you send humans to the vicinity of Mars or even to land on Mars, you want to know as much about the planet as you possibly can. … You need a sample return mission. The president also established a space policy a few years ago which had the concept of encouraging all agencies to have more and more foreign collaboration, to share the costs and get more for the same bucks.”
“Two years ago, because of budget cuts in the Mars program, I had to appeal to Europe to merge our programs. … That process took two long years of very delicate negotiations. We thought we were following the president’s space policy exactly. Congressional reaction was very positive about our activities. You put those factors in place and you have to ask, why single out Mars? I don’t have an answer.”
Space Analysts and Political leaders also weighed in:
“The president’s budget is just a proposal,” said Howard McCurdy, a space-policy specialist at American University in Washington to the Christian Science Monitor.
The cuts “reflect the new reality” in which the economy, budget deficits, and the federal debt have elbowed their way to the top of Washington’s agenda, McCurdy adds.
“You don’t cut spending for critical scientific research endeavors that have immeasurable benefit to the nation and inspire the human spirit of exploration we all have,” said Rep. John Culberson (R-Tex.). Texas is home to NASA’s Johnson Space Center.
Rep. Adam Schiff (D-CA), who represents the district that’s home to the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), released this statement following his meeting with NASA Administrator Charles Bolden to discuss the agency’s 2013 budget proposal:
“Today I met with NASA Administrator Charles Bolden to express my dismay over widespread reports that NASA’s latest budget proposes to dramatically reduce the planetary science program, and with it, ground breaking missions to Mars and outer planetary bodies like Jupiter’s icy moon Europa, and to inform him of my vehement opposition to such a move.”
“America’s unique expertise in designing and flying deep-space missions is a priceless national asset and the Mars program, one of our nation’s scientific crown jewels, has been a spectacular success that has pushed the boundaries of human understanding and technological innovation, while also boosting American prestige worldwide and driving our children to pursue science and engineering degrees in college.
“As I told the Administrator during our meeting, I oppose these ill-considered cuts and I will do everything in my power to restore the Mars budget and to ensure American leadership in space exploration.”
In an interview with the San Gabriel Valley Tribune, Schiff said, “What they’re proposing will be absolutely devastating to planetary science and the Mars program. I’m going to be fighting them tooth and nail. Unfortunately if this is the direction the administration is heading, it will definitely hurt JPL – that’s why I’m so committed to reversing this.”
NASA still hopes for some type of scaled back Mars missions in the 2016 to 2020 timeframe which will be outlined in an upcoming article.
In the meantime, the entire future of America’s Search for Life on the Red Planet now hinges on NASA’s Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory rover speeding thru interplanetary space and a pinpoint touchdown inside the layered terrain of Gale Crater on August 6, 2012.
Curiosity will be NASA’s third and last generation of US Mars rovers – 4th Generation Axed !
NASA’s Opportunity Rover is now Earth’s only surviving robot on Mars
[/caption]
The pale-orange coloration around the 39-mile (62-km) -wide Kuiper crater on Mercury is evident in this image, a color composition made from targeted images acquired by NASA’s MESSENGER spacecraft on September 2, 2011.
The color may be due to compositional differences in the material that was ejected during the impact that formed the crater.
Kuiper crater is named after Gerard Kuiper, a Dutch-American astronomer who was a member of the Mariner 10 team. He is regarded by many as the father of modern planetary science.
“Kuiper studied the planets… at a time when they were scarcely of interest to other astronomers. But with new telescopes and instrumentation, he showed that there were great things to discover, which is as true today as it was then.”
– Dr. Bill McKinnon, Professor of Planetary Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis
Airless worlds like Mercury are constantly bombarded with micrometeoroids and charged solar particles in an effect known as “space weathering”. Craters with bright rays — like Kuiper — are thought to be relatively young because they have had less exposure to space weathering than craters without such rays.
See the original image release on the MESSENGER site here.
Image credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington