[/caption]
“We are ready and so is Curiosity !”
-
- Says Rob Manning, Curiosity Chief Engineer at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif – in an exclusive interview with Universe Today for all fans of Curiosity and the unprecedented voyage of Science and Discovery about to take flight to Mars on November 26. Manning was also the Chief Engineer for the Entry, Descent and Landing (EDL) of NASA’s phenomenally successful Spirit, Opportunity and Phoenix Mars robotic explorers.
Read Rob Manning’s special greeting about Curiosity to readers of Universe Today below.
Meet Rob and other JPL Mars engineers in the cool Video describing the ‘Challanges of Getting to Mars’ – below

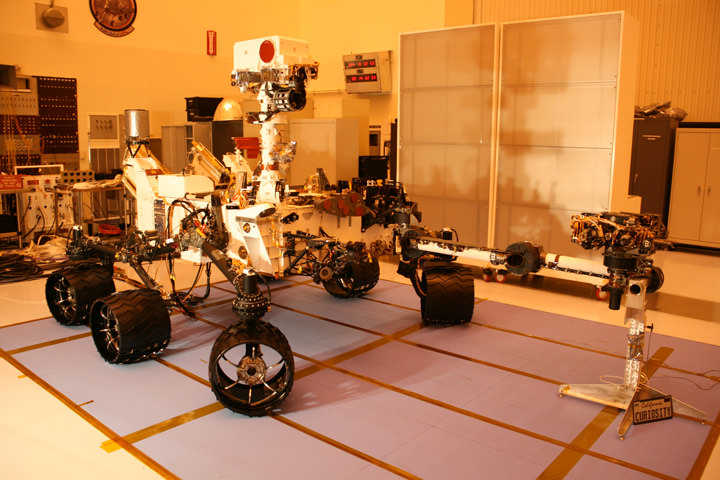
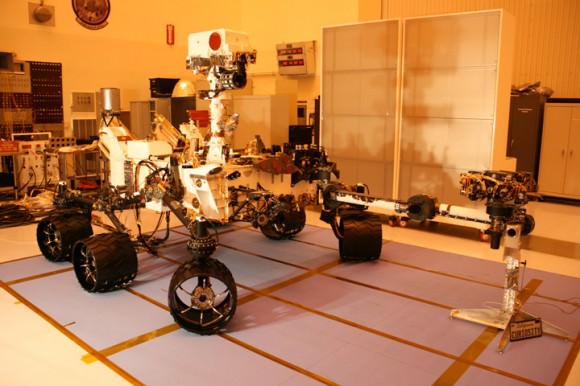
Curiosity is NASA’s next Mars rover and her MMRTG nuclear power source has been installed at the launch pad through special access panels in the Atlas booster payload fairing and protective aeroshell on Nov. 17.
The huge 1-ton robot is now due to blastoff for the Red Planet on Saturday, November 26 at 10: 02 a.m. EST from Space Launch Complex-41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. The launch window is open for one hour and 43 minutes.
Liftoff was postponed by one day to replace a battery in the on board flight termination system required in case the rocket were to veer off course.
Here is the very latest Curiosty update status from JPL’s Rob Manning as of Sunday evening – Nov. 20
“All seems well here at JPL in Pasadena,” Manning told me.
“We are having our last rehearsal at 1:30 a.m. on Monday, Nov 21.
“Weird ! As of a few hours ago the last human hands (in gloves) closed out the hatch door on the entry aeroshell and the two large doors in the rocket fairing have been closed. What is weird about it is that finally finally she is powered up and alone.”
“She has never been this alone before. Ironically all eyes are still upon her. Our team is monitoring her vitals 24-7,” Manning explained.
“The Challenges of Getting to Mars’ – Video caption: Meet Curiosity Chief Engineer Rob Manning and more members of the Curiosity Mars Rover Engineering Team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory explain the final assembly of Curiosity at the Kennedy Space Center and how Curiosity will land use the rocket assisted Sky Crane.
“By this time next week, Curiosity will be heading for the home she was meant for.”
“Soon she will feel the cold walls of deep space on her radiators. The x-band transmitter and receiver will have an broken view of the sky (with Earth but a shiny blue dot off to her left). The penetrating rays of the sun will push electrons out of the solar panels and keep her battery charged. (And perhaps a few solar flares will pass by, just to keep things interesting.)”
“Earth can be a rough place for a rover not designed for our planet. Worse are those of us who have poked and prodded, tested beyond spec and pushed in ways that can only be done on Earth.”
“Sometimes we over-do it and push near the breaking point. We are not perfect after all but we need to know that she will do what needs to be done for her very own survival. Well she seems to have survived us.”
“Of course Curiosity will never really be alone. We are right there with her every step of the way. She is us.”

Launch of MSL aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket is scheduled for Nov. 26 from Space Launch Complex 41 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Credit: NASA/Glenn Benson

“I will be at JPL during launch,” said Manning.
The JPL team is also working day and night to insure that the do or die Mars Insertion burn fires as planned.
“Once the Deep Space Network acquires the signal, I want to be there to make sure that we did not fail her and that the transition from being the Atlas’s payload to interplanetary cruise is as painless as possible.”
“It will be a bit of a surprise if we did not have a bit of a surprise – but we are ready and so is Curiosity”
Curiosity and the Atlas V booster that will propel her to Mars will roll out to Launch Pad 41 at the Florida Space Coast on Friday morning, Nov. 24, the day after the Thanksgiving holiday.
NASA TV will carry the MSL launch live
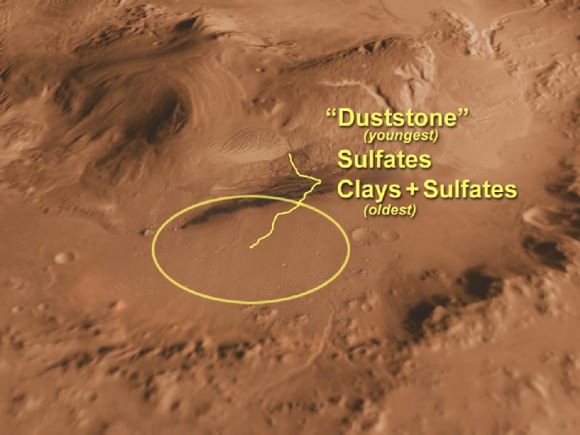
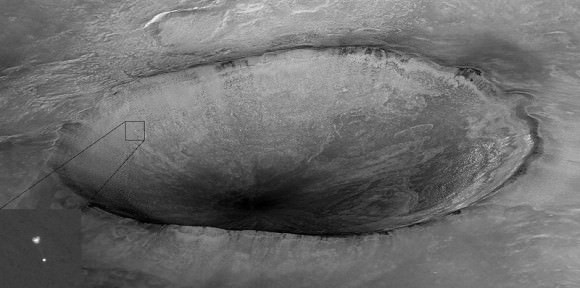
After a 10 month interplanetary journey to Mars, Curiosity will plummet through the atmosphere and fire up the rocket powered descent stage and ‘Sky Crane’ to safely touchdown astride a layered mountain at the Gale Crater landing site in August 2012.
Curiosity has 10 science instruments to search for evidence about whether Mars has had environments favorable for microbial life, including the chemical ingredients for life. The unique rover will use a laser to look inside rocks and release the gasses so that its spectrometer can analyze and send the data back to Earth.
Complete Coverage of Curiosity – NASA’s Next Mars Rover launching 26 Nov. 2011
Read continuing features about Curiosity by Ken Kremer starting here:
NASA’s Curiosity Set to Search for Signs of Martian Life
Curiosity Rover Bolted to Atlas Rocket – In Search of Martian Microbial Habitats
Closing the Clamshell on a Martian Curiosity
Curiosity Buttoned Up for Martian Voyage in Search of Life’s Ingredients
Assembling Curiosity’s Rocket to Mars
Encapsulating Curiosity for Martian Flight Test
Dramatic New NASA Animation Depicts Next Mars Rover in Action
Packing a Mars Rover for the Trip to Florida; Time Lapse Video
Test Roving NASA’s Curiosity on Earth