[/caption]
Until fairly recently, the search for life elsewhere in the solar system has focused primarily on Mars, as it is the most Earth-like of all the other planets in the solar system. The possibility of finding any kind of life farther out in the outer solar system was considered very unlikely at best; too cold, too little sunlight, no solid surfaces on the gas giants and no atmospheres to speak of on any of the moons apart from Titan.
But now, some of the places that were previously considered the least likely to hold life have turned out to be perhaps some of the most likely to provide habitable environments. Moons that were thought be cold and frozen for eons are now known to be geologically active, in surprising ways. One of them is the most volcanically active place known in the solar system. At least two others appear to have oceans of liquid water beneath their surfaces. That’s right, oceans. And geysers. On the surface, they are ice worlds, but below, they are water worlds. Then there’s the one with rain, rivers, lakes and seas, but made of liquid methane instead of water. Billions of kilometres farther out from the Sun than the Earth. Who would have thought? Let’s look at those last three in a bit more detail…
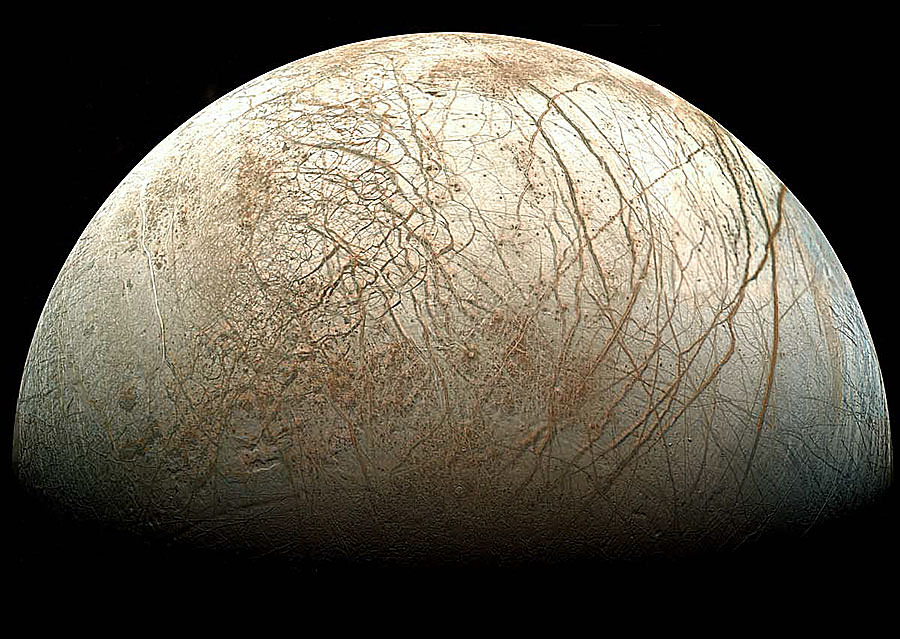
Ever since the film 2001: A Space Odyssey first came out, Europa has been the subject of fascination. A small, icy moon orbiting Jupiter, its depiction in that movie, as an inhabited world beneath its ice crust was like a sort of foreshadowing, before the Voyager and Galileo spacecraft gave us our first real close-up looks of this intriguing place. Its surface shell of ice is covered with long cracks and fissures, giving it an appearance much like ice floes at the poles on Earth. More surprising though, was the discovery that, also like on Earth, this ice cover most likely is floating on top of a deep layer of liquid water below. In Europa’s case though, the water layer appears to cover the entire moon, a global subsurface ocean. How is this possible? If there is liquid water, there must be heat (or high concentrations of salts or ammonia), and if you have water and heat, could there be something living in those waters? Gravitational tugging from Jupiter indeed appears to provide enough heat to keep the water liquid instead of frozen. The environment is now thought to be similar to ocean bottoms on Earth. No sunlight, but if there are volcanic vents generating heat and minerals, as on Earth, such a spot could be ideal for at least simple forms of life. On Earth, places like these deep in the oceans are brimming with organisms which don’t require sunlight to survive.

Then there’s Enceladus. Another very small icy moon, orbiting Saturn. Geological activity was considered very unlikely on such a tiny world, only a few hundred kilometres in diameter. But then Cassini saw the geysers, plumes of material erupting from the south polar region through large, warmer cracks nicknamed “tiger stripes.” Cassini has now flown directly through the geysers, analyzing their composition, which is mostly water vapour, ice particles, salts and organics. The latest analysis based on the Cassini data indicates that they almost certainly originate from a sea or ocean of liquid water below the surface. Warm, salty water loaded with organics; could Enceladus be another possible niche for extraterrestrial life? As with Europa, only further missions will be able to answer these questions, but the possibilities are exciting.
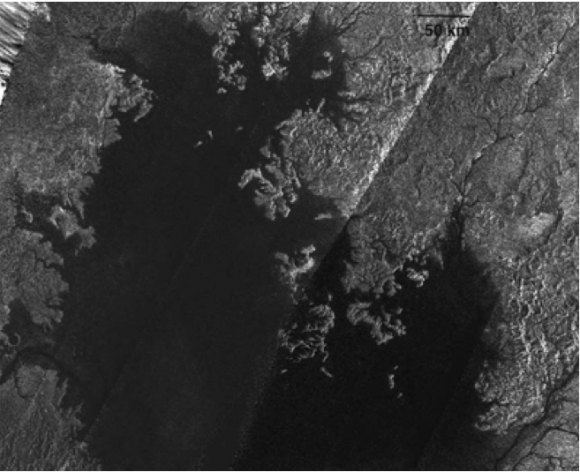

Titan is even more fascinating in some ways, the largest moon of Saturn. It is perpetually shrouded in a thick smoggy atmosphere of nitrogen and methane, so the surface has never been visible until now, when Cassini, and its small lander probe Huygens, first looked below the smog and clouds. Titan is like an eerily alien version of Earth, with rain, rivers, lakes and seas, but being far too cold for liquid water (not much heat here), its “water cycle” is composed of liquid methane/ethane. Appearance-wise, the surface and geology look amazingly Earth-like, but the conditions are uniquely Titan. For that reason, it has long been considered that the chances of any kind of life existing here are remote at best. In the last few years however, some scientists are starting to consider the possibility of life forming in just such environments, using liquids other than water, even in such cold conditions. Could life occur in a liquid methane lake or sea? How would it differ from water-based life? Last year, a discovery was made which might be interpreted as evidence of methane-based life on Titan – a seeming disappearance of hydrogen from the atmosphere near the surface and a lack of acetylene on the surface. Previous theoretical studies had suggested that those two things, if ever found, could be evidence for methane-based lifeforms consuming the hydrogen and acetylene. All of this is still highly speculative, and while a chemical explanation is probably more likely according to the scientists involved, a biological one cannot be ruled out yet. Future proposed missions for Titan include a floating probe to land in one of the lakes and a balloon to soar over the landscape, pursuing such mysteries as never before. How cool is that?
Oh, and the moon that is the most volcanically active place in the solar system? Io, although with the only known forms of liquid there being extremely hot lavas on that sulfuric hothouse, the chances of life are still thought to be unbelievably slim. But that’s ok when you start to find out that worlds with oceans and lakes, etc. may be much more common than previously imagined…