[/caption]
The epic multi-year trek of NASA’s Opportunity Mars rover to the gigantic Endeavour crater is nearly complete as the plucky rover blazes to within a football fields distance and first landfall at a spot dubbed “Spirit Point” – named in honor of her long lived twin sister “Spirit”. Endeavour beckons because it may hold clues to a time billions and billions of years ago when Mars was warmer and wetter and harbored an environment that was far more conducive to the formation of life beyond Earth.
Opportunity is racing towards the western foothills of Endeavour’s rim and is at long last transmitting stunningly clear images of portions of the crater ridges, revealing gorgeous vistas and intriguing details up the sloped walls. See our new photo mosaics above and below.
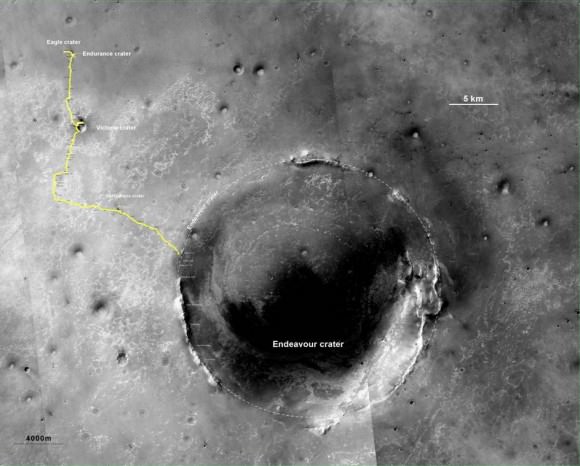
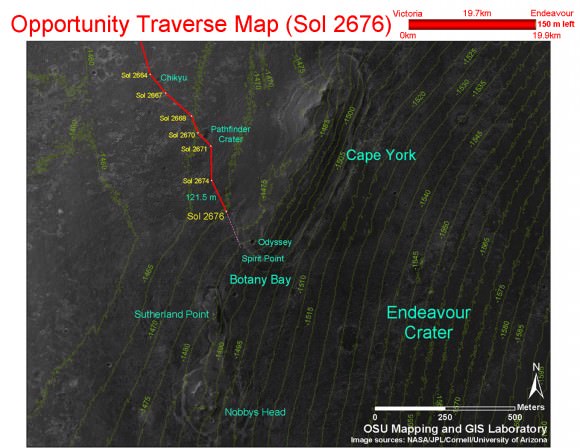
As of today, Aug. 8 on Sol 2680 of the mission, the Martian robot is less than 400 feet (150 m) away from Endeavour’s rim at Spirit Point – which lies at the southern tip of one of the ridges known as “Cape York,” on the western side of Endeavour (see map and photo below). The humongous crater is 14 miles (22 km) in diameter.
“Our primary goal is to get onto the older material at Cape York with the phyllosilicate signatures in CRISM,” said Dr. Matt Golembek in an interview with Universe Today. Golembek is a Senior Research Scientist with the Mars Exploration Program at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, Calif.
The phyllosilicate signatures are based on observations by the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM) aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). Phyllosilicates are clay minerals that form in the presence of neutral water and that are more far more hospitable to the possible genesis of life compared to the rocks studied from the more highly acidic aqueous environments examined by the rover thus far.

Opportunity was less than 0.3 miles (500 m) from the foothills of Endeavour Crater on Sol 2668 and will soon make first landfall at Spirit Point - off to the left. Endeavour holds minerals deposits from billions of years ago when Mars was far warmer and wetter and potentially more hospitable to the formation of ancient microbial life. This photo mosaic was stitched together to show portions of the discontinuous crater rim with segmented ridges from left to right. Distant Iazu crater is faintly visible at top left. Opportunity is now transmitting highly detailed and clear images of Endeavour’s rim.
Mosaic Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Kenneth Kremer
In mid- 2008, Endeavour crater was chosen as the long term destination for Opportunity by the rover science team because it offers access to older geological deposits than any Opportunity has visited and investigated before. These mineral deposits include phyllosilicates.
Opportunity has been sprinting across the plains of Meridiani since departing her last major science stop at Santa Maria crater in March 2011. See our APOD here.
Opportunity is now heading to a spot called “Odyssey crater” on the way to Spirit Point. See JPL route map below.
“In the end of drive Navcams [navigation camera] from Sols 2678-9, large ejecta blocks on the rim of Odyssey crater are clearly visible and that is our next target to see what those blocks are made of,” Golembek told me.
“After that we will travel north into Cape York to better understand the older rocks in Cape York.”
The rover team is being very careful to not over plan the science activities to far in advance and are keeping their options open.
Eventually, Opportunity will scale the ridge and become the 2nd Martian mountain climber. Spirit was the first Earthly emissary to climb to the summit of a mountain on Mars.
“As we explore we will make more specific plans depending on what we see,” Golembek added.
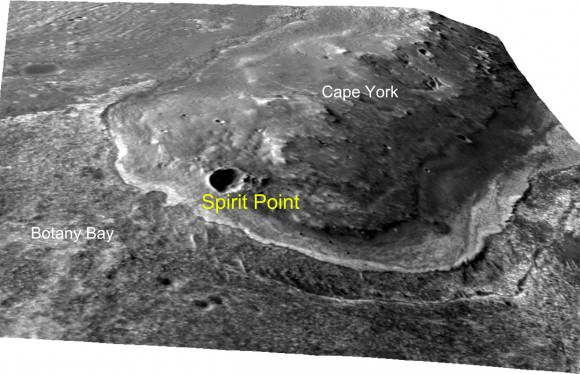
This oblique view with moderate vertical exaggeration shows the portion of the rim of Endeavour crater known as Spirit Point. The science and engineering team has driven Opportunity to a spot less than 400 feet from Spirit Point as of early August 2011. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona
Measurements from orbiting spacecraft like MRO allowed the science team to target Opportunity more precisely toward those ridges of older exposures of rock outcrops and phyllosilicates observed along Endeavour’s western rim.
Given Opportunity’s rapid progress, it’s now almost certain that she will reach the phyllosiliocates before the Curiosity rover is even launched in Nov. 2011.
Endeavour’s crater rim is discontinuous and divided into a series of segmented mountainous ridges – making it all the more beautiful and a bonanza for science. See the new photo mosaics above and below stitched together by Marco Di Lorenzo and Ken Kremer, illustrating Opportunity’s current vistas.
The Spirit rover succumbed to the bitter Martian arctic-like cold weather during her 4th winter on Mars after roving nearly seven years across Gusev crater. In May 2011, NASA declared Spirit’s mission had concluded after no further communications were received.
Opportunity remains healthy, generates sufficient solar power and has traversed an unbelievable 20.6 miles or 33.2 km since landing on Jan. 24, 2004.

Read my continuing features about Mars starting here
Dramatic New NASA Animation Depicts Next Mars Rover in Action
Opportunity Rover Heads for Spirit Point to Honor Dead Martian Sister; Science Team Tributes
Opportunity Rover Completes Exploration of fascinating Santa Maria Crater
Opportunity Surpasses 30 KM Driving and Snaps Skylab Crater in 3 D