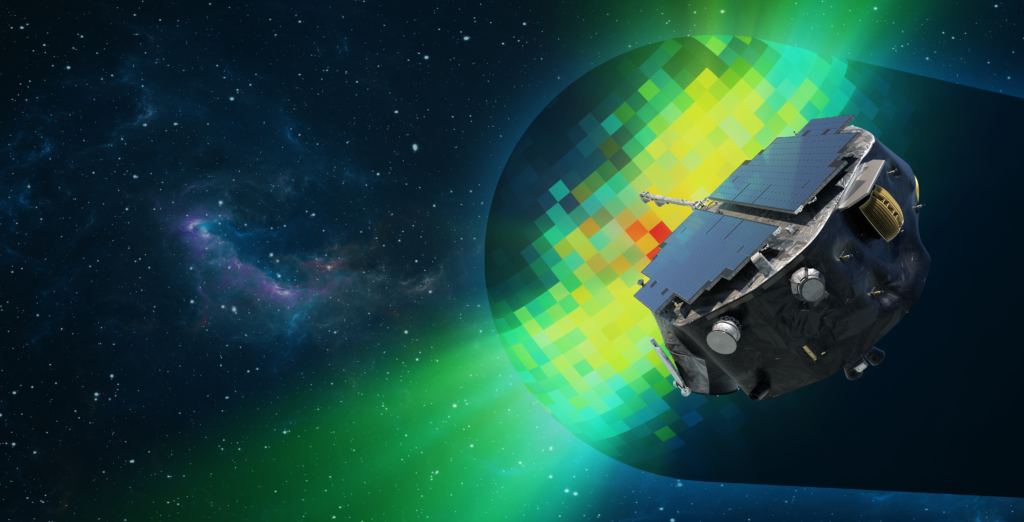
Engineers at NASA have completed an important milestone in developing the Interstellar Mapping and Acceleration Probe (IMAP) spacecraft. It’s now moving from development and design to the assembly, testing, and integration phase, targeting a launch in late Spring 2025. After launch, the spacecraft will fly to the Earth-Sun L1 Lagrange Point and analyze how the Sun’s solar wind interacts with charged particles originating from outside the Solar System.
IMAP will follow up on discoveries and insights from the two Voyager spacecraft and the Interstellar Boundary Explorer (IBEX) and will help investigate two of the most important overarching issues in heliophysics: the energization of charged particles from the Sun and the interaction of the solar wind at its boundary with interstellar space.
Continue reading “NASA's Interstellar Mapping Probe Prepares for a 2025 Launch”