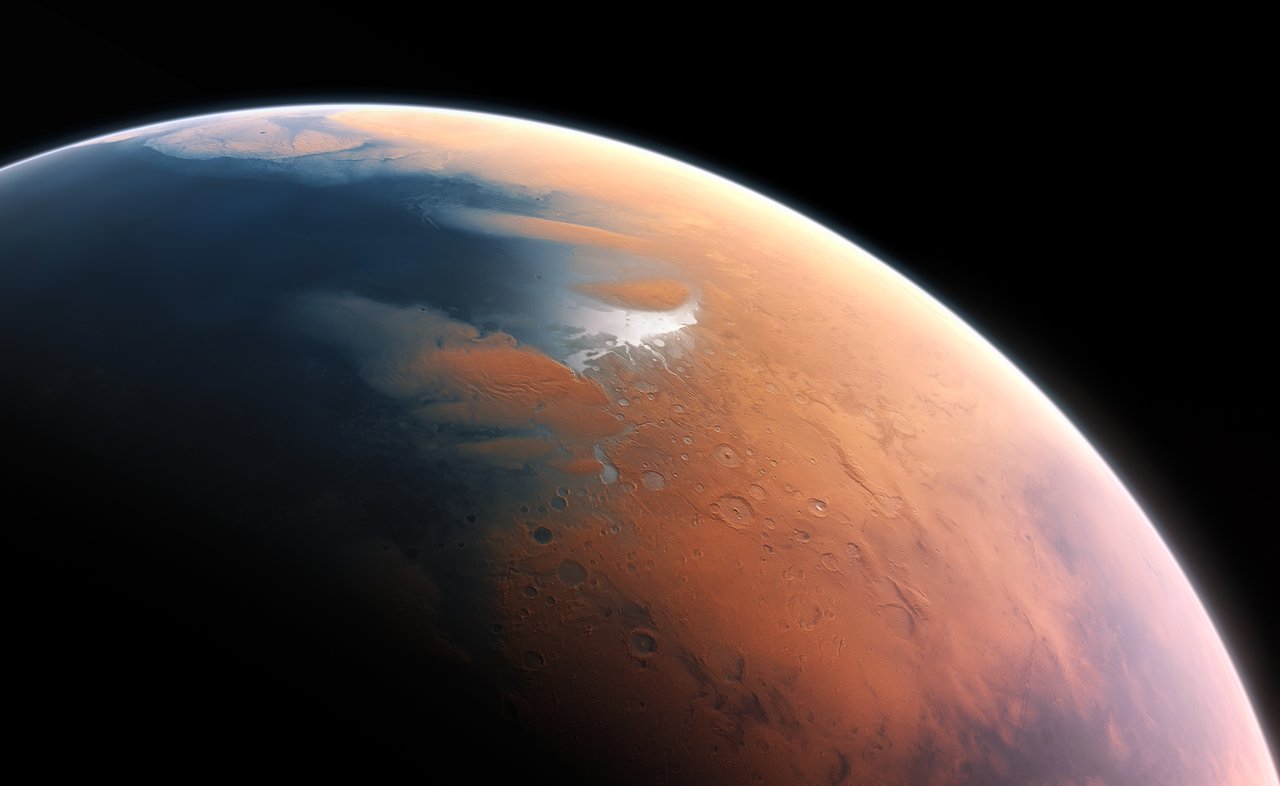
Today, Mars is colloquially known as the “Red Planet” on a count of how its dry, dusty landscape is rich in iron oxide (aka. “rust”). In addition, the atmosphere is extremely thin and cold, and no water can exist on the surface in any form other than ice. But as the Martian landscape and other lines of evidence attest, Mars was once a very different place, with a warmer, denser atmosphere and flowing water on its surface. For years, scientists have attempted to determine how long natural bodies existed on Mars and whether or not they were intermittent or persistent.
Another important question is how much water Mars once had and whether or not this was enough to support life. According to a new study by an international team of planetary scientists, Mars may have had enough water 4.5 billion years ago to cover it in a global ocean up to 300 meters (almost 1,000 feet) deep. Along with organic molecules and other elements distributed throughout the Solar System by asteroids and comets at this time, they argue, these conditions indicate that Mars may have been the first planet in the Solar System to support life.
Continue reading “Mars Once had Enough Water for a Planet-Wide Ocean 300 Meters Deep”