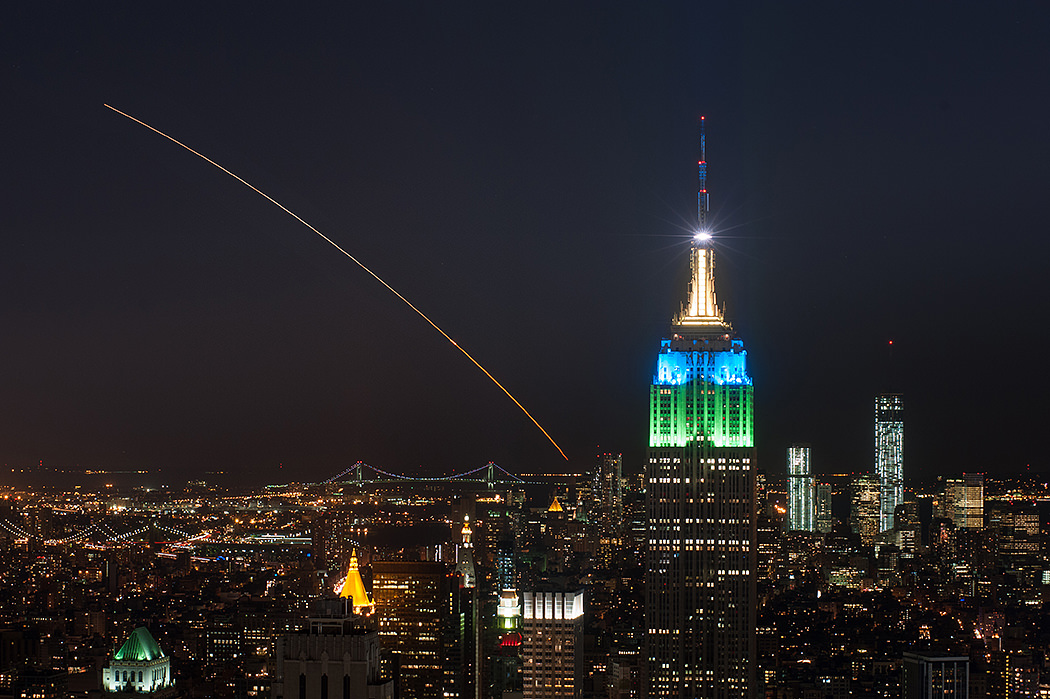
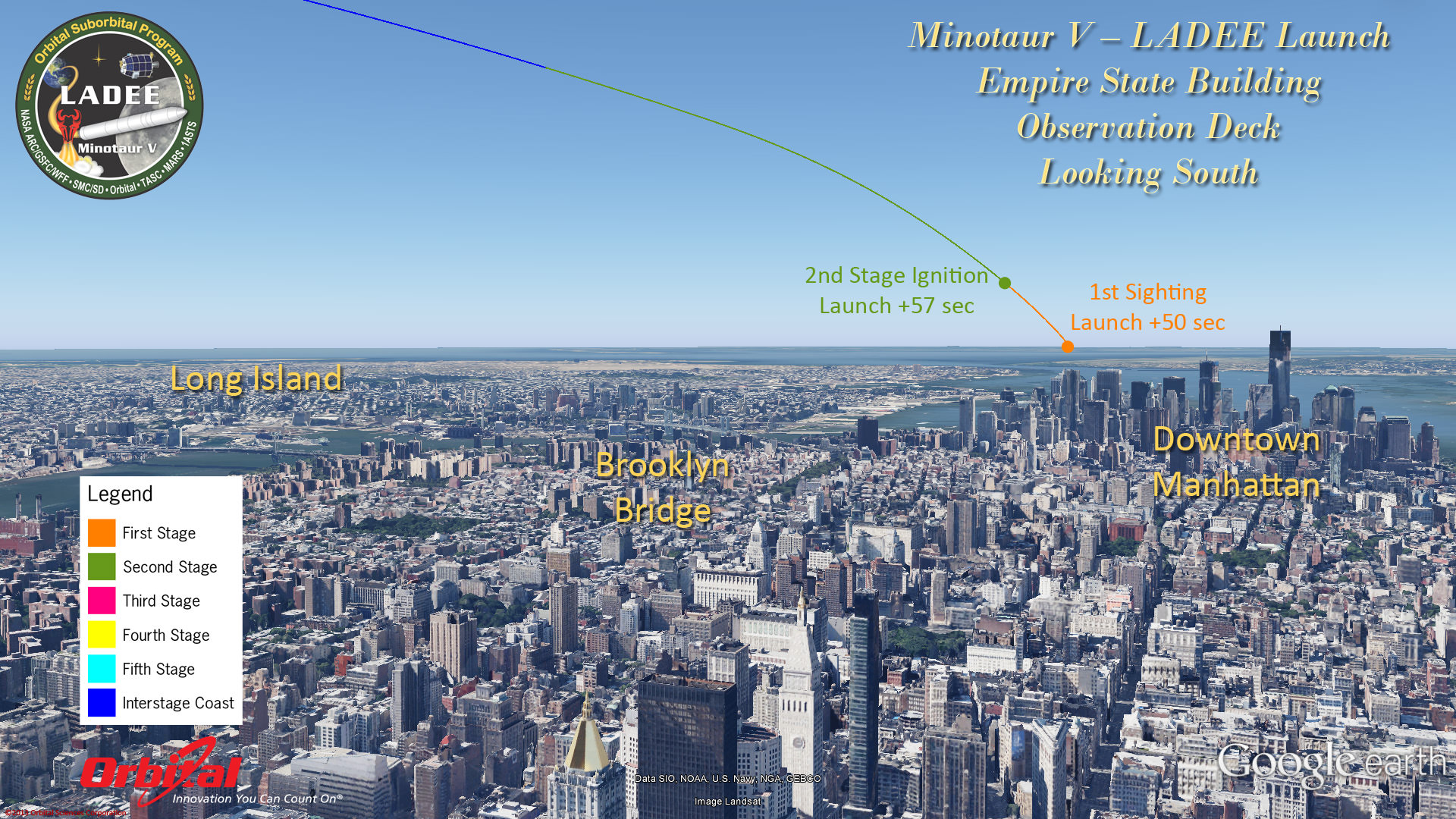
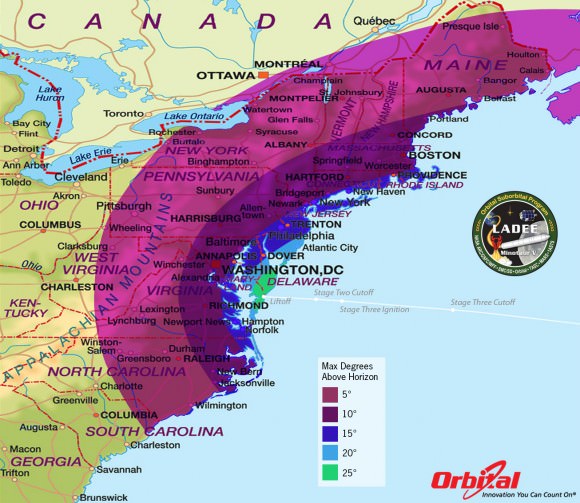
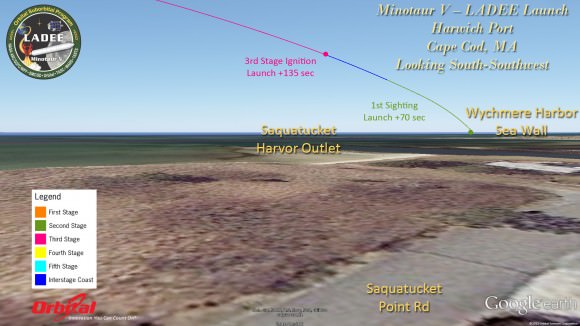
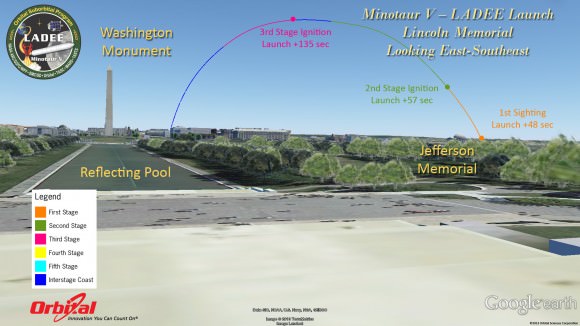
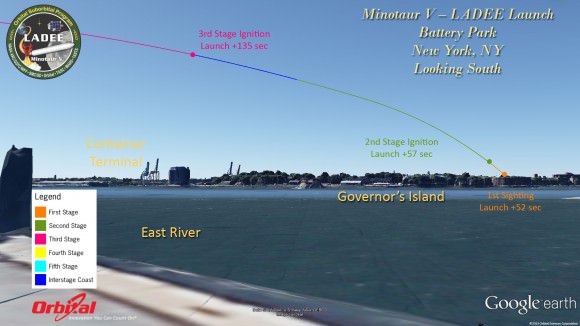
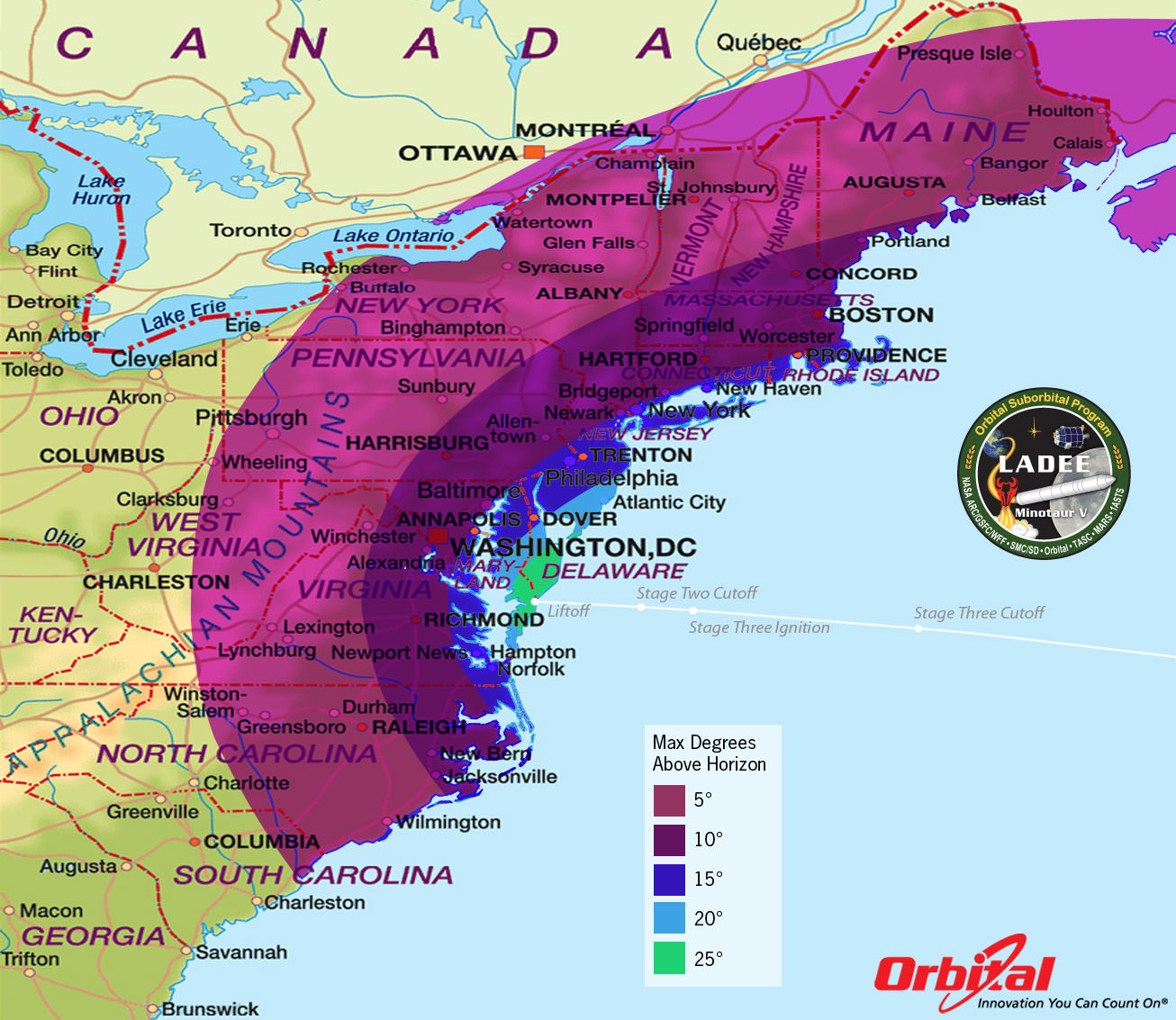
This magnificent view of NASA’s LADEE lunar orbiter launched on Friday night Sept 6, on the maiden flight of the Minotaur V rocket from Virginia was captured by space photographer Ben Cooper perched atop Rockefeller Center in New York City. Credit: Ben Cooper/Launchphotography.com
Story updated[/caption]
WALLOPS ISLAND, VA – A NASA moon probe named LADEE thundered to space tonight, Sept. 6, blazing a spectacular trail to orbit from a beachside launch pad in Virginia that was easily visible to tens of millions of spectators along the eastern seaboard as a result of crystal clear skies and the night time liftoff – see magnificent photo shot from NYC above by Ben Cooper/Launchphotography.com.
The drama at the LADEE launch site on the eastern shore of Virginia at NASA’s Wallops Island facility was palpable due to the historic and experimental nature of the mission.
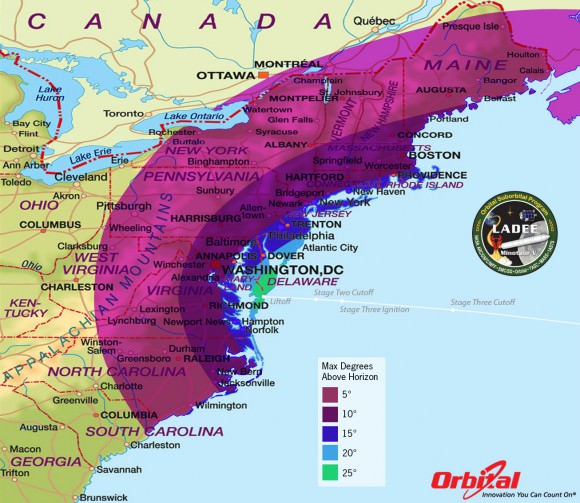
Hordes of tourists flooded into Virginia to be eyewitnesses to an unprecedented space spectacle that marked Americas ‘Return to the Moon’ and a chance to see the type of big and exciting rocket launches previously reserved for Florida and California.
Everyone I spoke too was absolutely overwhelmed with the amazing beauty of the Minotaur V blastoff carrying LADEE to orbit, whooping and hollering, far beyond our wildest expectations as the crackling fire pierced through the night and reverberated in our ears!
“It was a picture perfect launch,” said NASA Associate Administrator John Grunsfeld at a post launch media briefing at NASA Wallops.
“LADEE will help us unravel the mysteries of the lunar atmosphere.”
Blastoff of NASA’s dust exploring Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) Observatory marked the first space probe of any kind ever launched beyond Earth orbit from NASA Wallops, as well as being the first planetary science mission from Wallops.

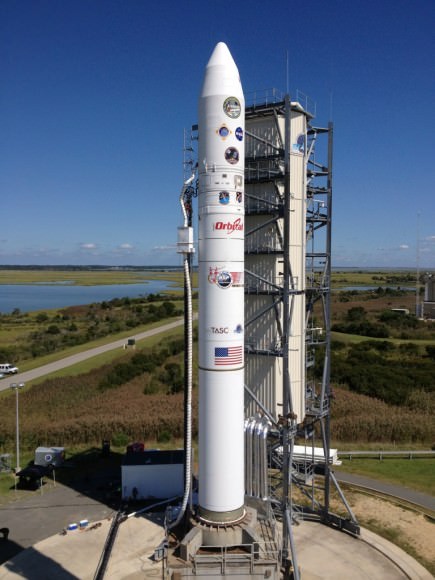
The Minotaur V rocket launched precisely on time at 11:27 p.m. EDT on the maiden flight of the powerful new Minotaur V rocket Launch Pad 0B on NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility.
“The spacecraft is healthy and power positive and separated from the fifth and last stage on time, approximately 23 minutes into the flight,” said Pete Worden to Universe Today after the liftoff. Worden is the Director of NASA’s Ames Research Center which designed and built LADEE using a revolutionary new design to reduce costs and increase science output.
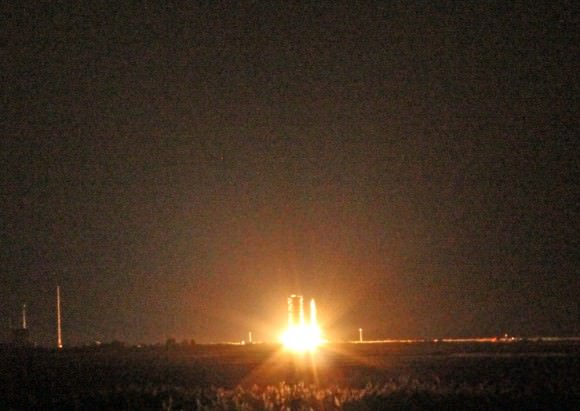



The liftoff of LADEE (pronounced ‘laddie’ not ‘lady’) also marks the first launch of a five stage rocket and the first launch of a decommissioned Peacekeeper missile from Wallops. The Peacekeeper was a nuclear armed intercontinental ballistic missile ICBM built during the Cold War – now retired and refurbished by Orbital for peaceful uses.
The Minotaur V fifth stage boosted LADEE into a highly elliptical orbit. Over about the next 23 days, as LADEE orbits Earth 3.5 times, the Moon’s gravitational field will increase the apogee of its orbit. The spacecraft will fire its on-board braking thrusters to achieve lunar orbit.

The mission will fly in a very low science orbit of about 50 kilometers altitude above the moon that will require considerable fuel to maintain. The science mission duration is approximately 100 days.
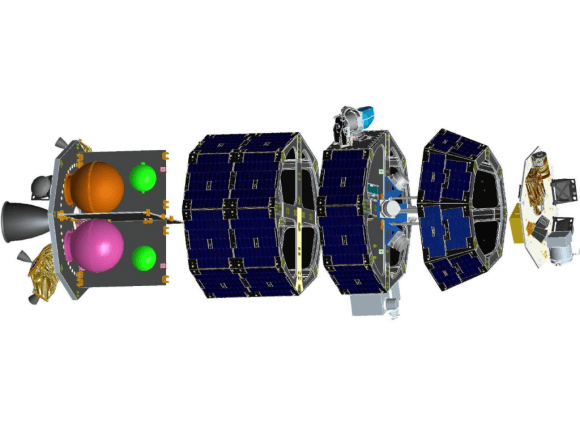
The 844 pound (383 kg) robot explorer is the size of a couch and was assembled at NASA’s Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif., and is a cooperative project with NASA Goddard Spaceflight Center in Maryland.
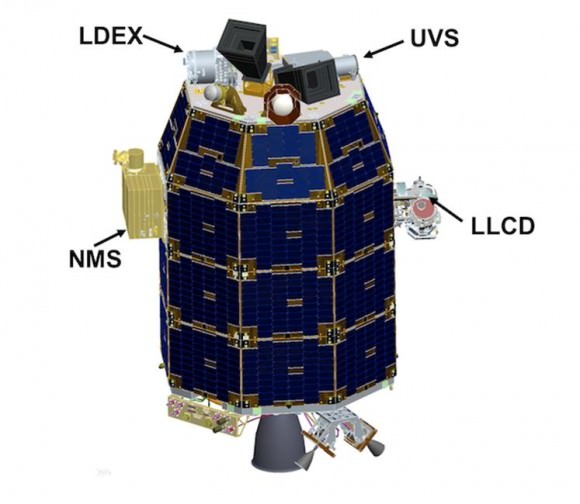
It is equipped with a trio of science instruments whose purpose is to collect data that will inform scientists in unprecedented detail about the ultra thin lunar atmosphere, environmental influences on lunar dust and conditions near the surface.
The goal of the $280 Million mission is to gain a thorough understanding of long-standing unknowns about the tenuous atmosphere, dust and surface interactions that will help scientists understand other planetary bodies as well.

The couch sized probe is built on a revolutionary ‘modular common spacecraft bus’, or body, that could dramatically cut the cost of exploring space and also be utilized on space probes to explore a wide variety of inviting targets in the solar system. The overall mission cost is approximately $280 million.
“LADEE is the first in a new class of interplanetary exploration missions,” NASA Ames Director Worden told Universe Today. “It will study the pristine moon to study significant questions.”
“This is probably our last best chance to study the pristine Moon before there is a lot of human activity there changing things.”
The five stage Minotaur V rocket stands 80.6 feet (24.6 meters) tall, is 7.6 feet (2.3 m) in diameter and weighs 197,034 pounds (89,373 kilograms).
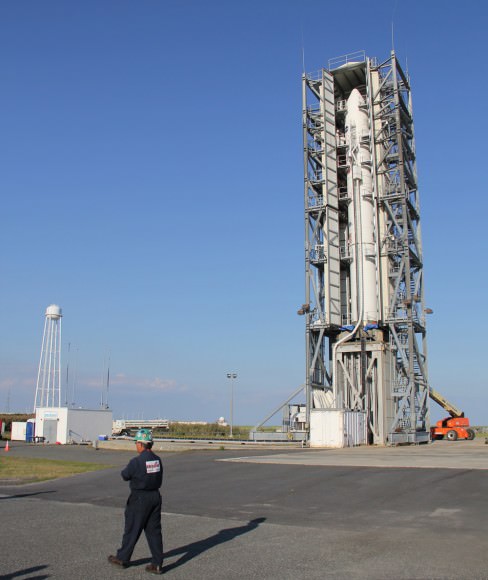

The first three stages of the Minotaur V are based on the nuclear armed Peacekeeper ICBM intercontinental ballistic missile built during the Cold War – now retired and refurbished by Orbital Sciences for peaceful uses.
The upper 5th stage is a new addition and what makes this Minotaur a new rocket class. The additional thrust is what converts the Minotaur V into an interplanetary booster that enables shooting for the Moon.
“I dreamed all my life about launching a rocket to the moon. And now we are doing it,” Lou Amorosi, told Universe Today at the Minotuar launch pad. Amorosi is the Senior Vice President of Orbital’s Small Space Launch Vehicle business.
“This mission further demonstrates the capabilities of our well-established Minotaur rocket family and our commitment to providing reliable access to space,” Amorosi noted in a post launch statement.
…………….
Learn more about LADEE, Cygnus, Antares, MAVEN, Orion, Mars rovers and more at Ken’s upcoming presentations:
Sep 16/17: “LADEE Lunar & Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, 8 PM
Oct 3: “Curiosity, MAVEN and the Search for Life on Mars – (3-D)”, STAR Astronomy Club, Brookdale Community College & Monmouth Museum, Lincroft, NJ, 8 PM
Oct 8: “LADEE Lunar & Antares/Cygnus ISS Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Princeton University, Amateur Astronomers Assoc of Princeton (AAAP), Princeton, NJ, 8 PM