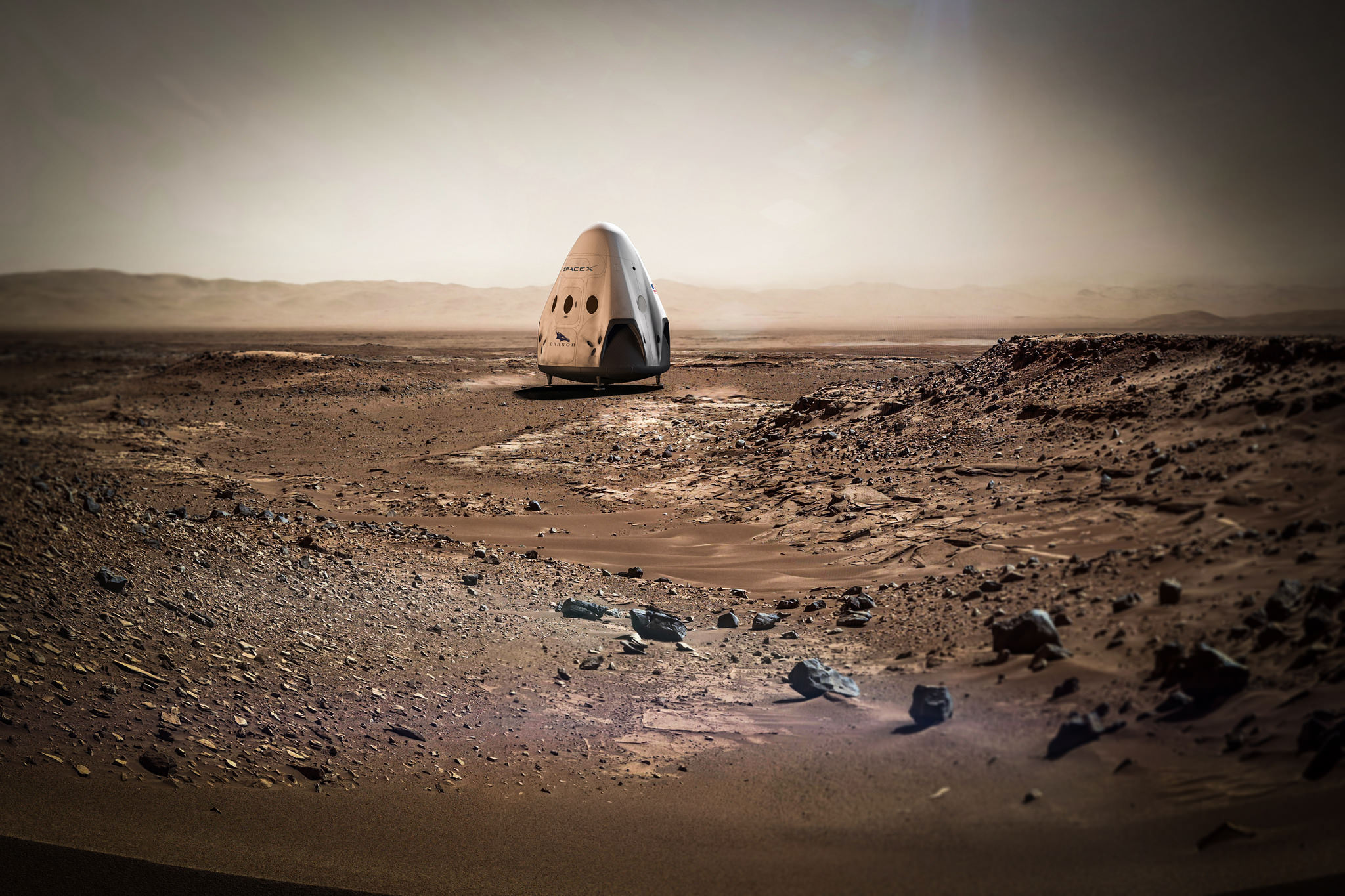
SpaceX announced plans today, April 27, for the first ever private mission to Mars which involves sending an uncrewed version of the firms Dragon spacecraft to accomplish a propulsive soft landing – and to launch it as soon as 2018 including certain technical assistance from NASA.
Under a newly signed space act agreement with NASA, the agency will provide technical support to SpaceX with respect to Mars landing technologies for the new spacecraft known as a ‘Red Dragon’ and possibly also for science activities.
“SpaceX is planning to send Dragons to Mars as early as 2018,” the company posted in a brief announcement today on Facebook and other social media about the history making endeavor.
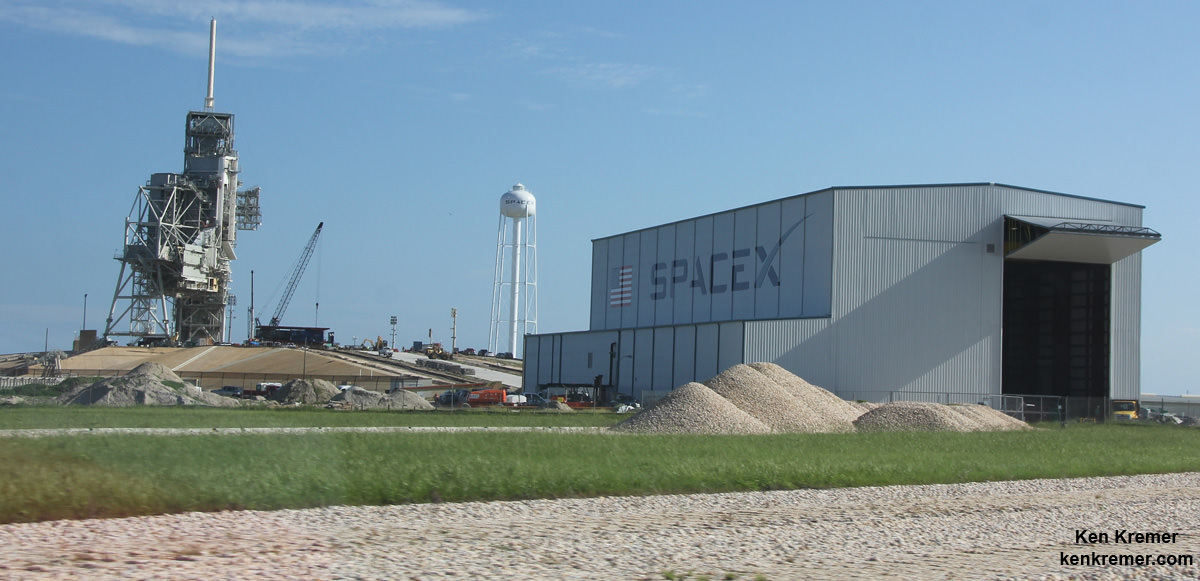
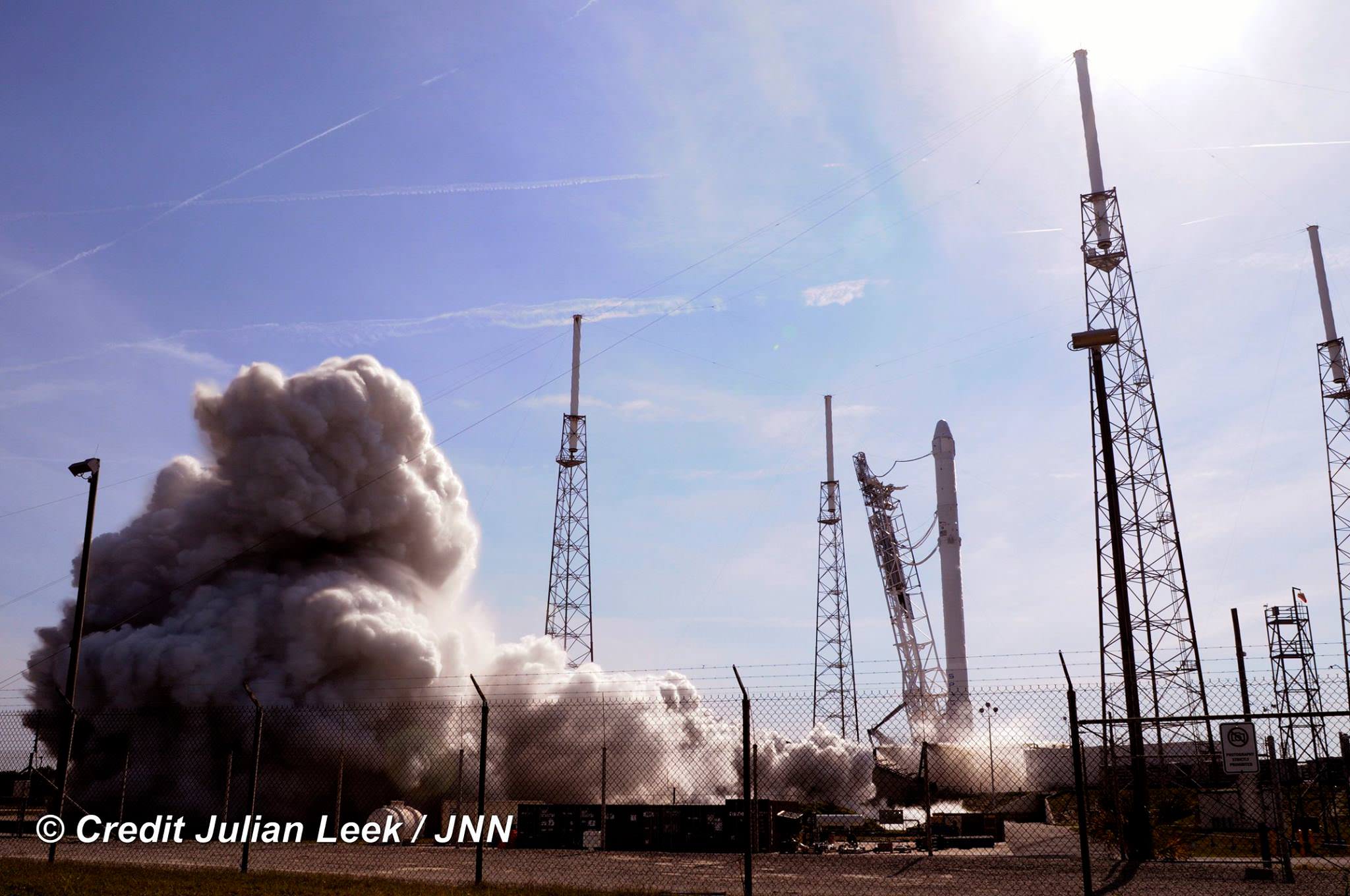
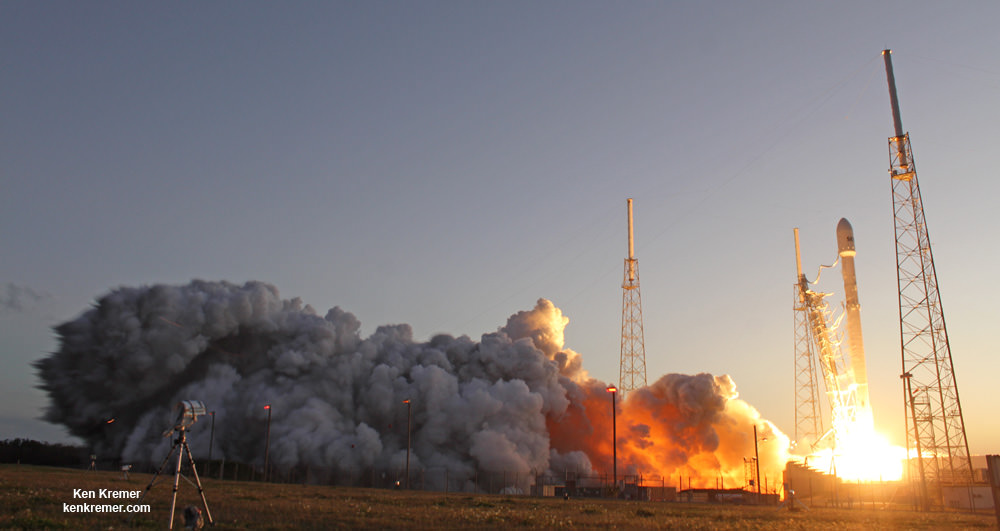
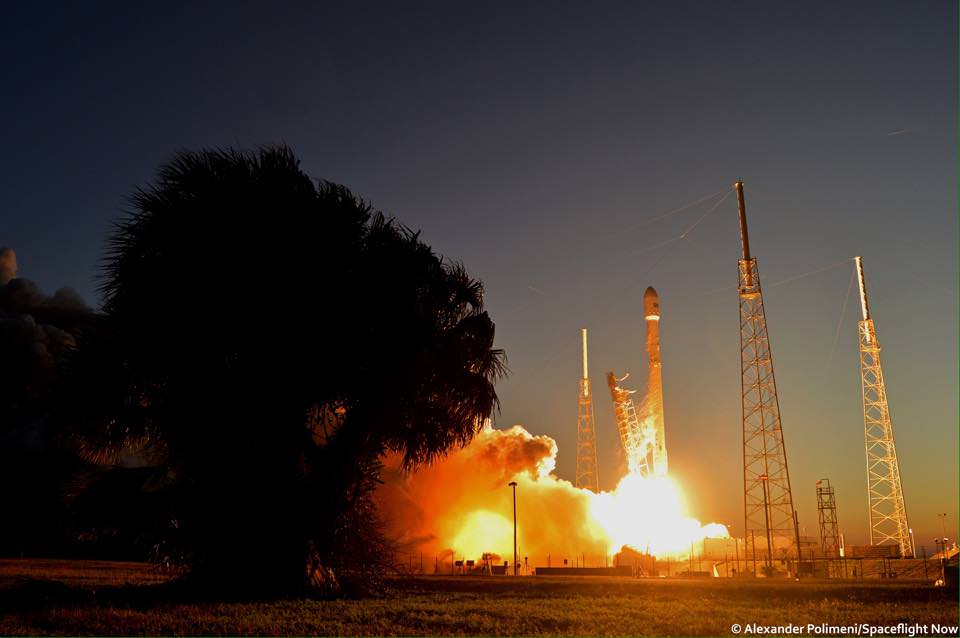
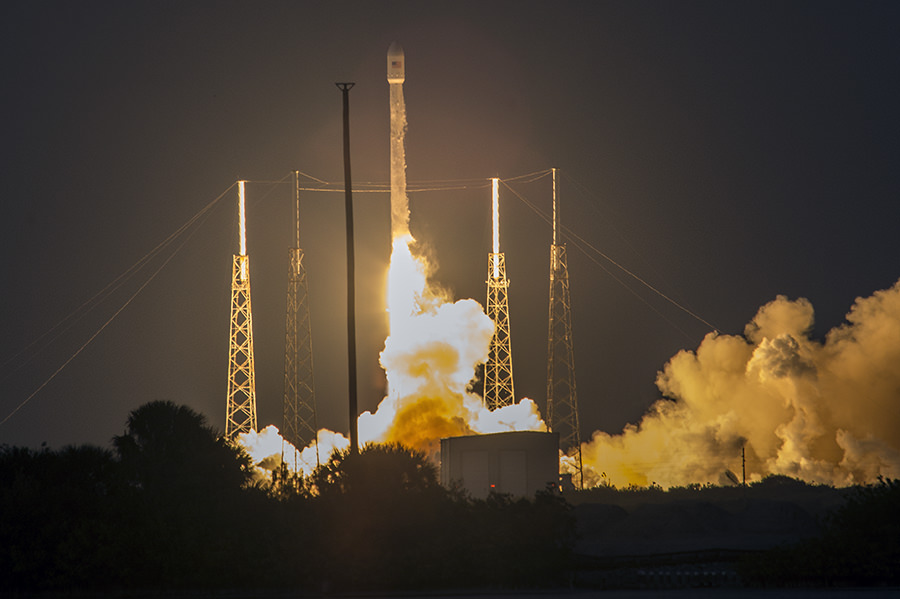
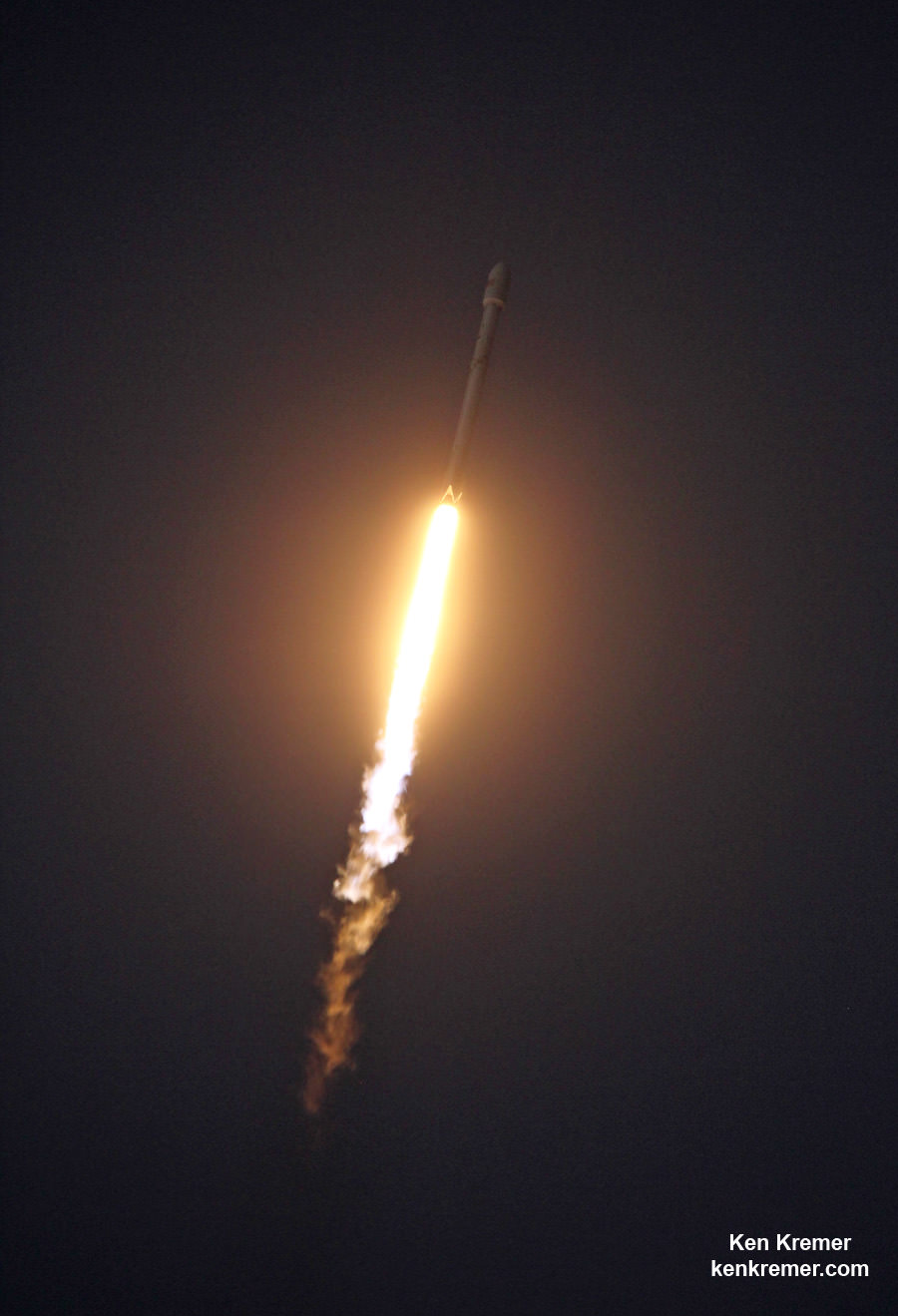
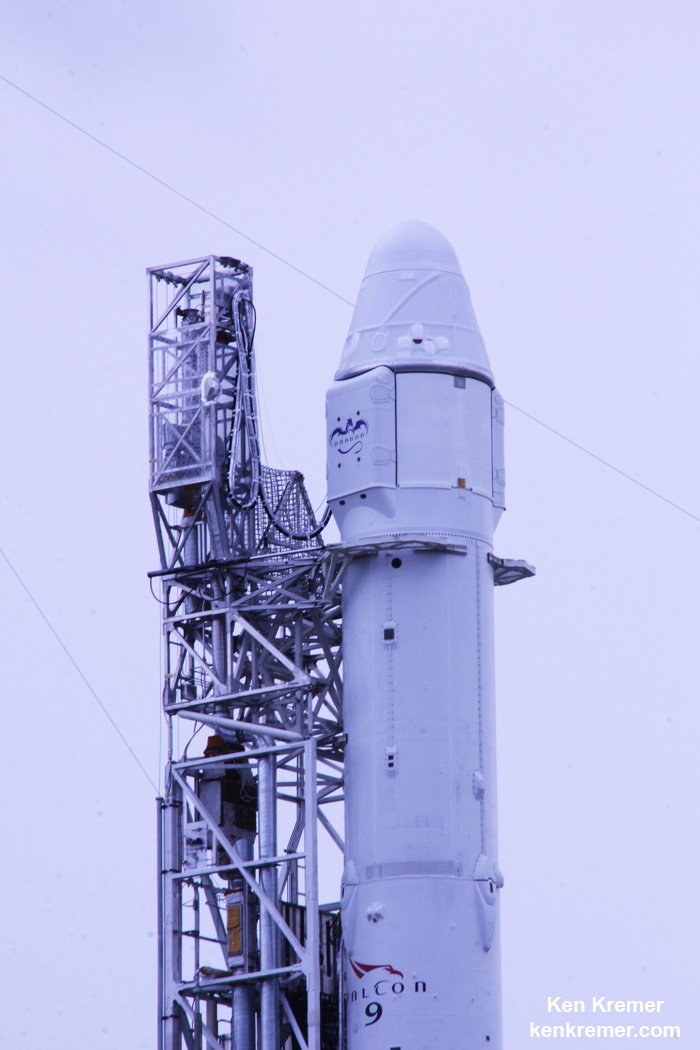
The 2018 commercial Mars mission involves launching the ‘Red Dragon’ – also known as Dragon 2 – on the SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket from Launch Pad 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It’s a prelude to eventual human missions.
The Red Dragon initiative is a commercial endeavor that’s privately funded by SpaceX and does not include any funding from NASA. The agreement with NASA specifically states there is “no-exchange-of-funds.”
As of today, the identity and scope of any potential science payload is undefined and yet to be determined.
Hopefully it will include a diverse suite of exciting research instruments from NASA, or other entities, such as high powered cameras and spectrometers characterizing the Martian surface, atmosphere and environment.
SpaceX CEO and billionaire founder Elon Musk has previously stated his space exploration goals involve helping to create a Mars colony which would ultimately lead to establishing a human ‘City on Mars.’
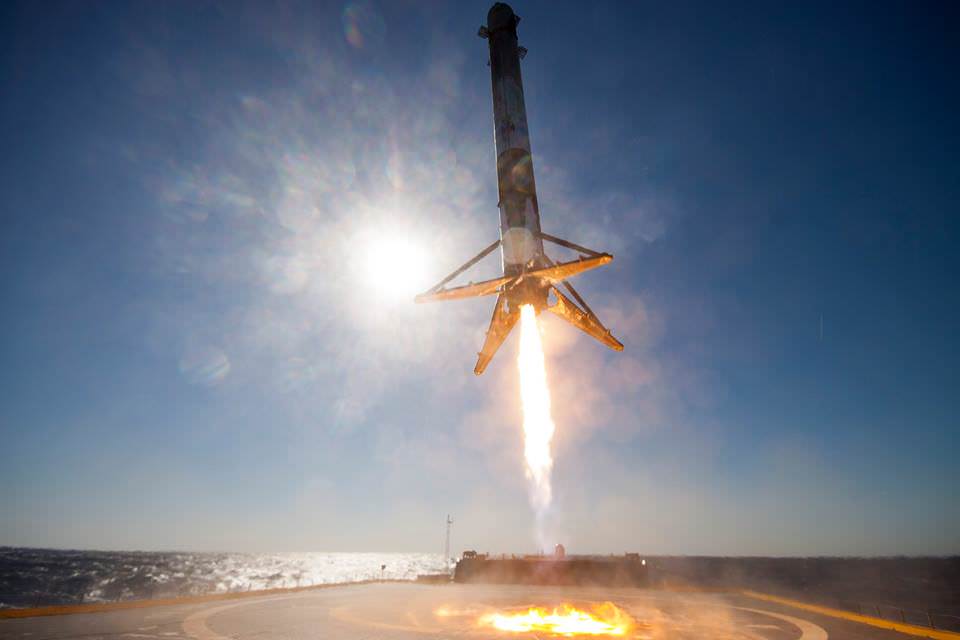
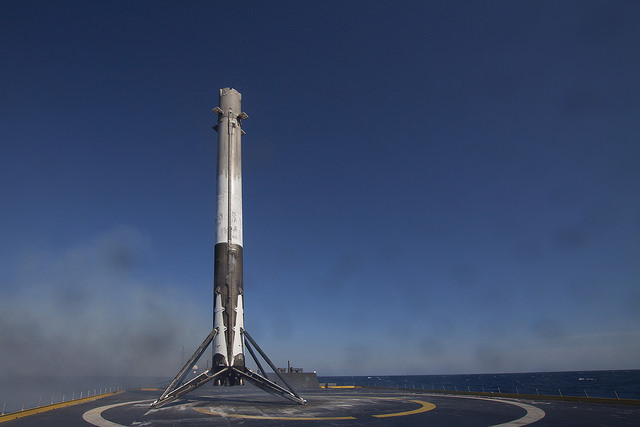
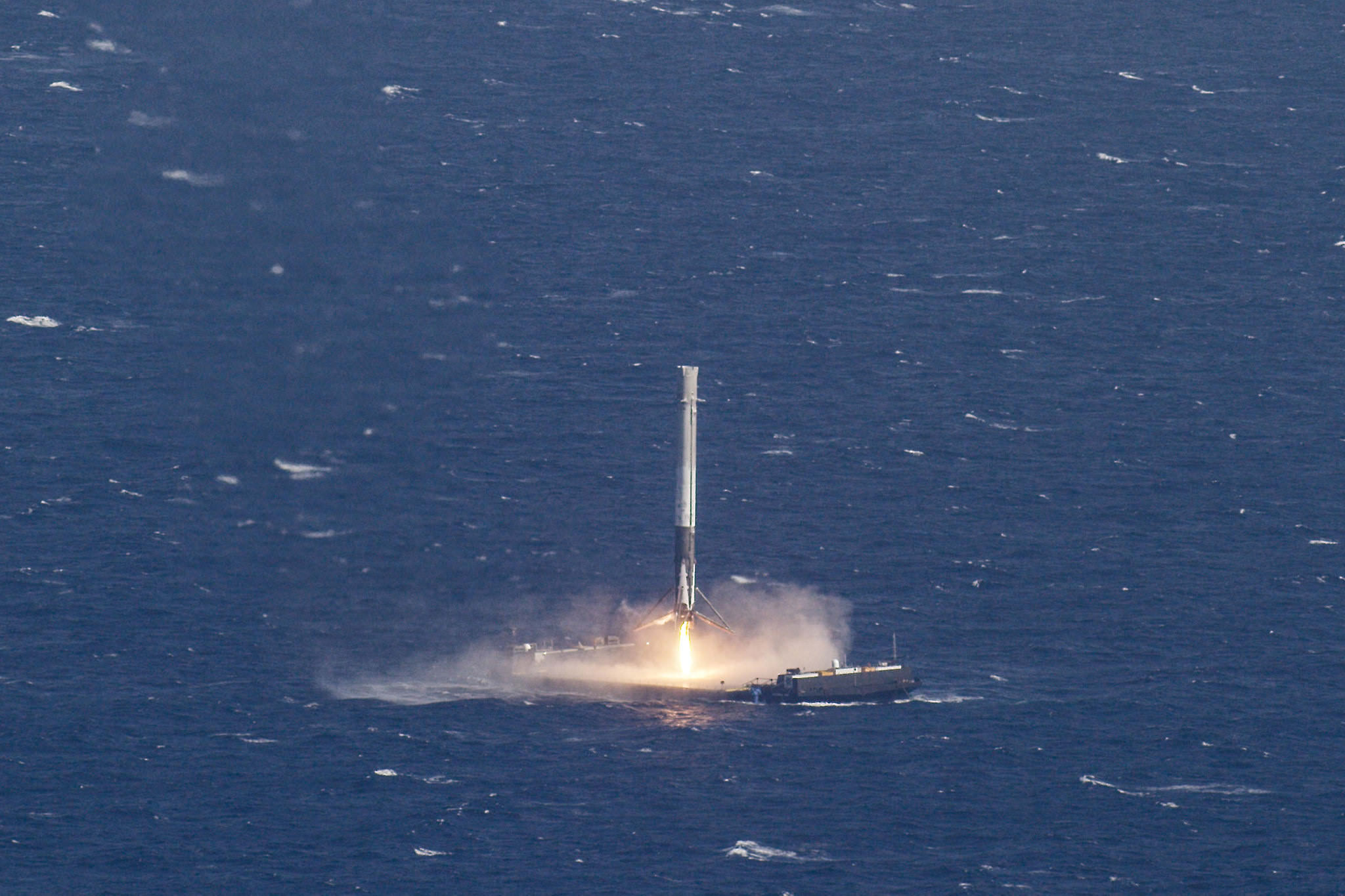
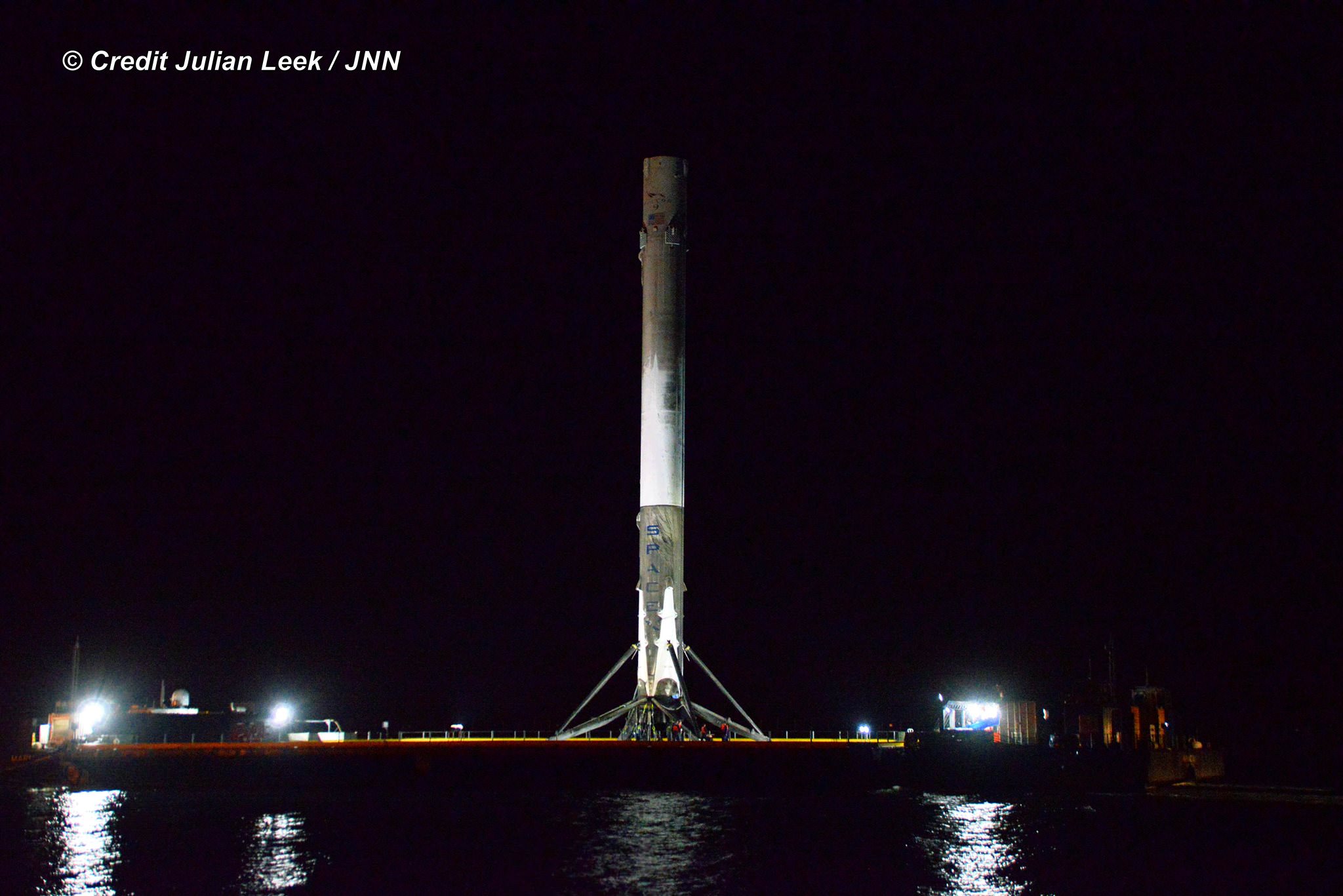
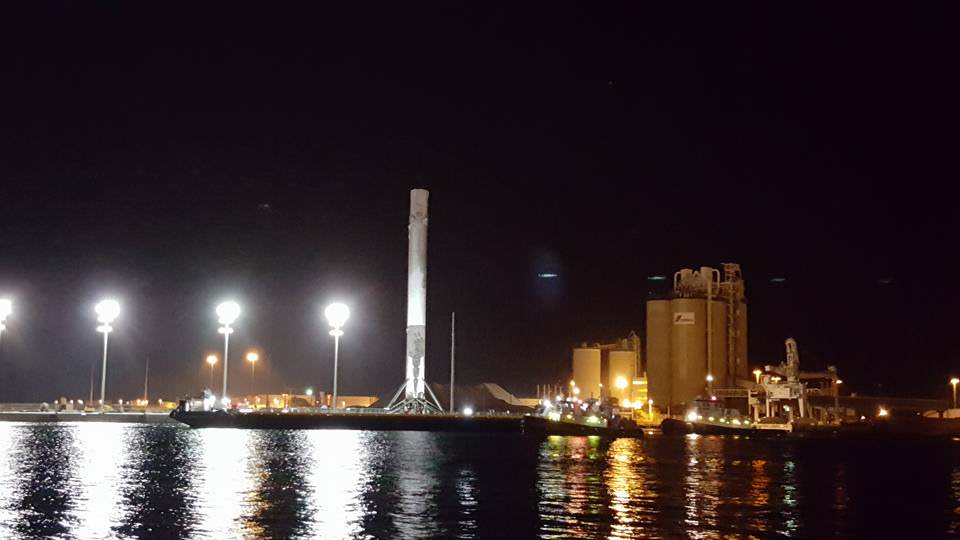
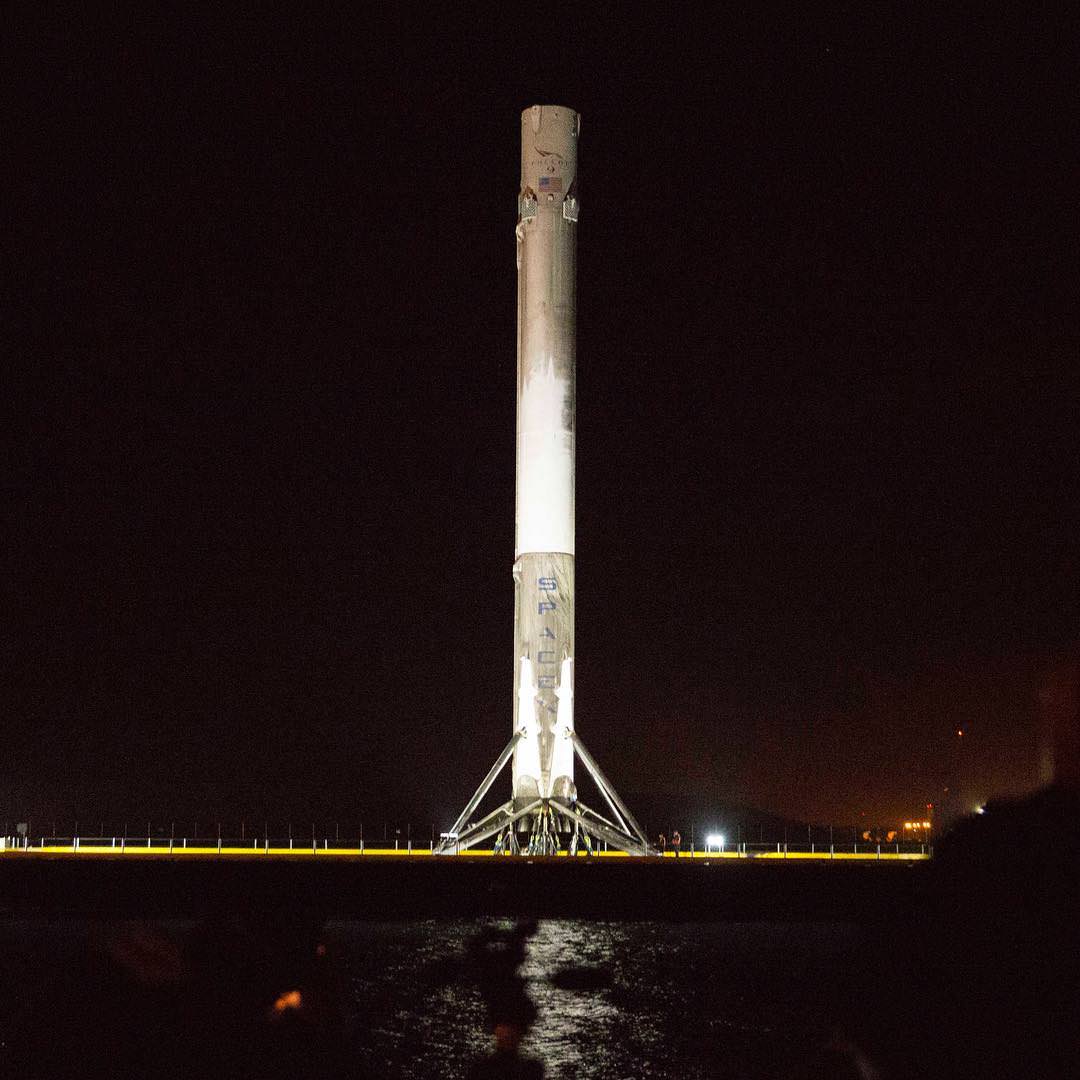
Musk is also moving full speed ahead with his goal of radically slashing the cost of access to space by recovering a pair of SpaceX Falcon 9 first stage boosters via successful upright propulsive landings on land and at sea – earlier this month and in Dec. 2015.

The 2018 liftoff campaign marks a significant step towards fulfilling Musk’s Red Planet vision. But we’ll have to wait another 5 months for concrete details.
“Red Dragon missions to Mars will also help inform the overall Mars colonization architecture that SpaceX will reveal later this year,” SpaceX noted.
Musk plans to reveal the details of the Mars colonization architecture later this year at the International Astronautical Congress (IAC) being held in Guadalajara, Mexico from September 26 to 30, 2016.
Landing on Mars is not easy. To date only NASA has successfully soft landed probes on Mars that returned significant volumes of useful science data.
In the meantime a few details about the SpaceX Red Dragon have emerged.
The main goal is to propulsively land something 5-10 times the size of anything previously landed before.
“These missions will help demonstrate the technologies needed to land large payloads propulsively on Mars,” SpaceX further posted.
NASA’s 1 ton Curiosity rover is the heaviest spaceship to touchdown on the Red Planet to date.
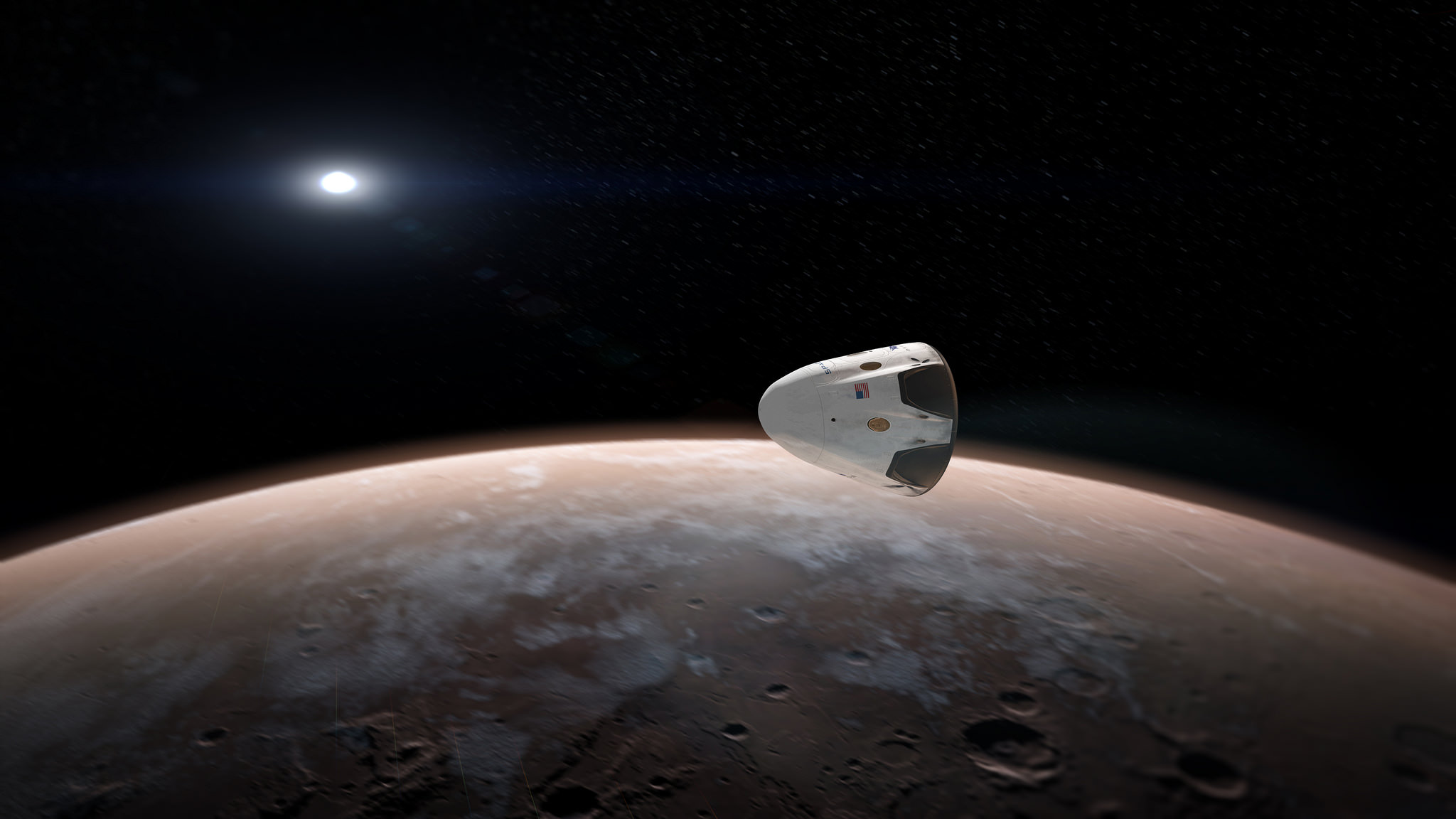

As part of NASA’s agency wide goal to send American astronauts on a human ‘Journey to Mars’ in the 2030s, NASA will work with SpaceX on some aspects of the Red Dragon initiative to further the agency’s efforts.
According to an amended space act agreement signed yesterday jointly by NASA and SpaceX officials – that originally dates back to November 2014 – this mainly involves technical support from NASA and exchanging entry, descent and landing (EDL) technology, deep space communications, telemetry and navigation support, hardware advice, and interplanetary mission and planetary protection advice and consultation.
“We’re particularly excited about an upcoming SpaceX project that would build upon a current “no-exchange-of-funds” agreement we have with the company,” NASA Deputy Administrator Dava Newman wrote in a NASA blog post today.
“In exchange for Martian entry, descent, and landing data from SpaceX, NASA will offer technical support for the firm’s plan to attempt to land an uncrewed Dragon 2 spacecraft on Mars.”
“This collaboration could provide valuable entry, descent and landing data to NASA for our journey to Mars, while providing support to American industry,” NASA noted in a statement.
The amended agreement with NASA also makes mention of sharing “Mars Science Data.”
As of today, the identity, scope and weight of any potential science payload is undefined and yet to be determined.
Perhaps it could involve a suite of science instruments from NASA, or other entities, such as cameras and spectrometers characterizing various aspects of the Martian environment.
In the case of NASA, the joint agreement states that data collected with NASA assets is to be released within a period not to exceed 6 months and published where practical in scientific journals.
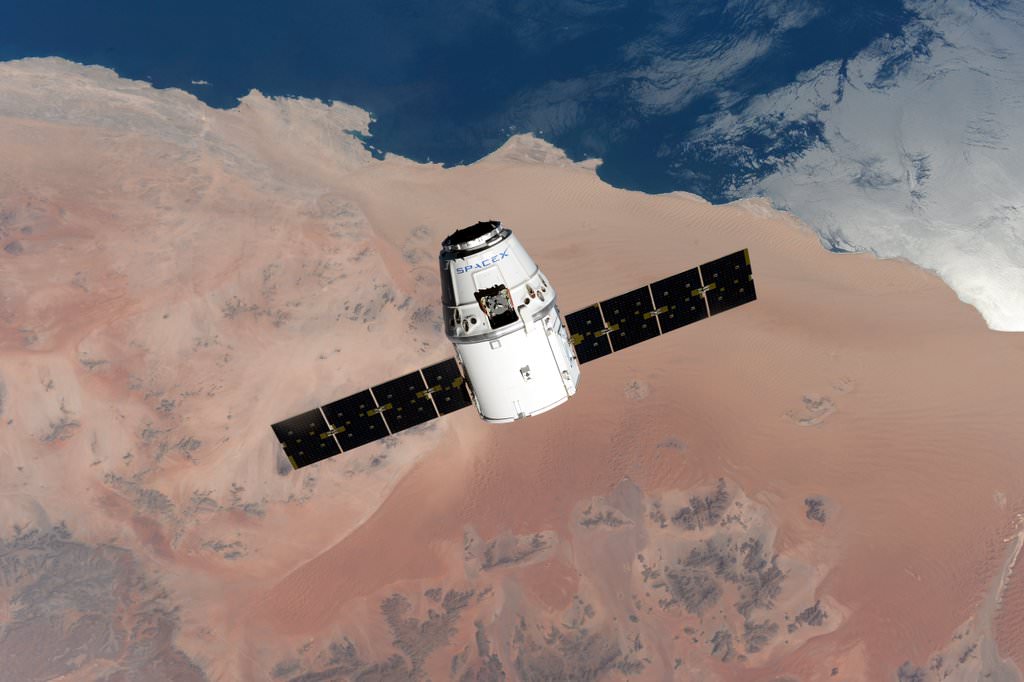
The Red Dragon envisioned for blastoff to the Red Planet as soon as 2018 would launch with no crew on board on a critical path finding test flight that would eventually pave the way for sending humans to Mars – and elsewhere in the solar system.
“Red Dragon Mars mission is the first test flight,” said Musk.
“Dragon 2 is designed to be able to land anywhere in the solar system.”
However, the Dragon 2 alone is far too small for a round trip mission to Mars – lasting some three years or more.
“But wouldn’t recommend transporting astronauts beyond Earth-moon region,” tweeted Musk.
“Wouldn’t be fun for longer journeys. Internal volume ~size of SUV.”
Furthermore, for crewed missions it would also have to be supplemented with additional modules for habitation, propulsion, cargo, science, communications and more. Think ‘The Martian’ movie to get a realistic idea of the complexity and time involved.
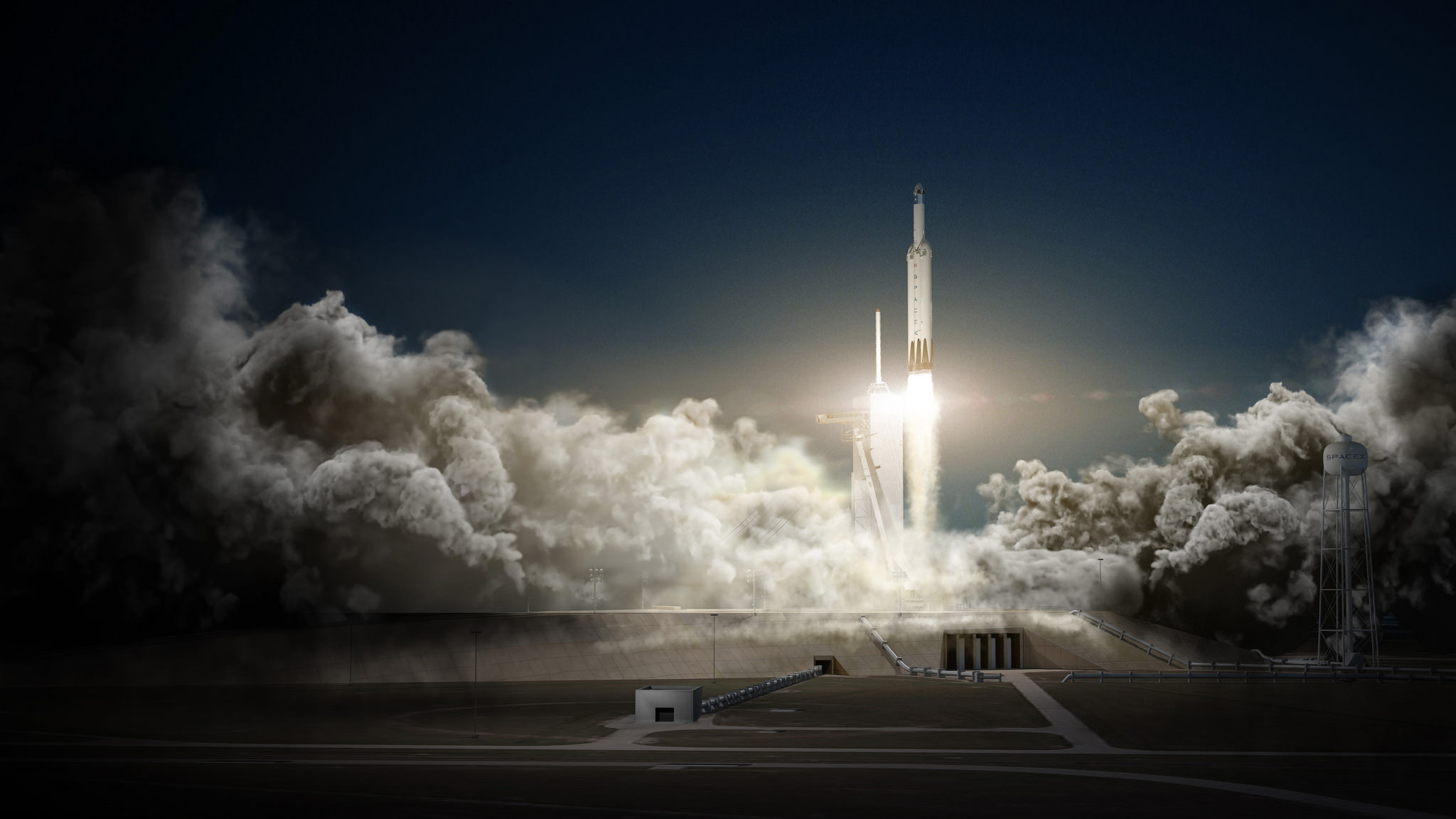
Red Dragon’s blastoff from KSC pad 39A is slated to take place during the Mars launch window opening during April and May 2018.
The inaugural liftoff of the Falcon Heavy is currently scheduled for late 2016 after several years postponement.
If all goes well, Red Dragon could travel to Mars at roughly the same time as NASA’s next Mission to Mars – namely the InSight science lander, which will study the planets deep interior with a package of seismometer and heat flow instruments.
InSight’s launch on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V is targeting a launch window that begins May 5, 2018, with a Mars landing scheduled for Nov. 26, 2018. Liftoff was delayed from this year due to a flaw in the French-built seismometer.

Whoever wants to land on Mars also has to factor in the relevant International treaties regarding ‘Planetary Protection’ requirements.
Wherever the possibility for life exists, the worlds space agency’s who are treaty signatories, including NASA, are bound to adhere to protocols limiting contamination by life forms from Earth.
SpaceX intends to take planetary protection seriously. Under the joint agreement, SpaceX is working with relevant NASA officials to ensure proper planetary protection procedures are followed. One of the areas of collaboration with NASA is for them to advise SpaceX in the development a Planetary Protection Plan (PPP) and assist with the implementation of a PPP including identifying existing software/tools.
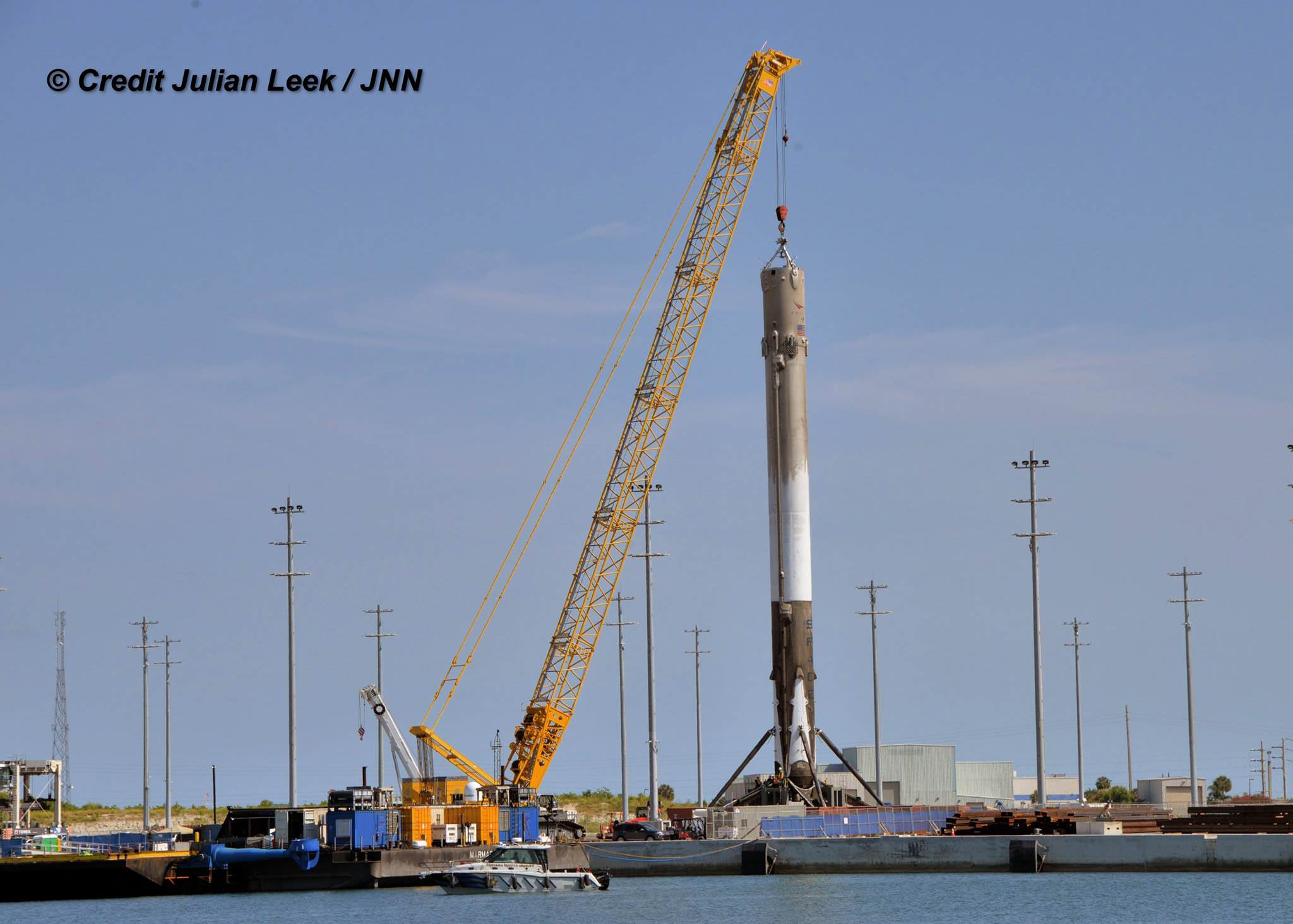
Red Dragon is derived from the SpaceX crew Dragon vehicle currently being developed under contract for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) to transport American astronauts back and forth to low Earth orbit and the International Space Station (ISS).
SpaceX and Boeing were awarded commercial crew contracts from NASA back in September 2014.
Both firms hope to launch unmanned and manned test flights of their SpaceX Crew Dragon and Boeing CST-100 Starliner spacecraft to the ISS starting sometime in 2017.
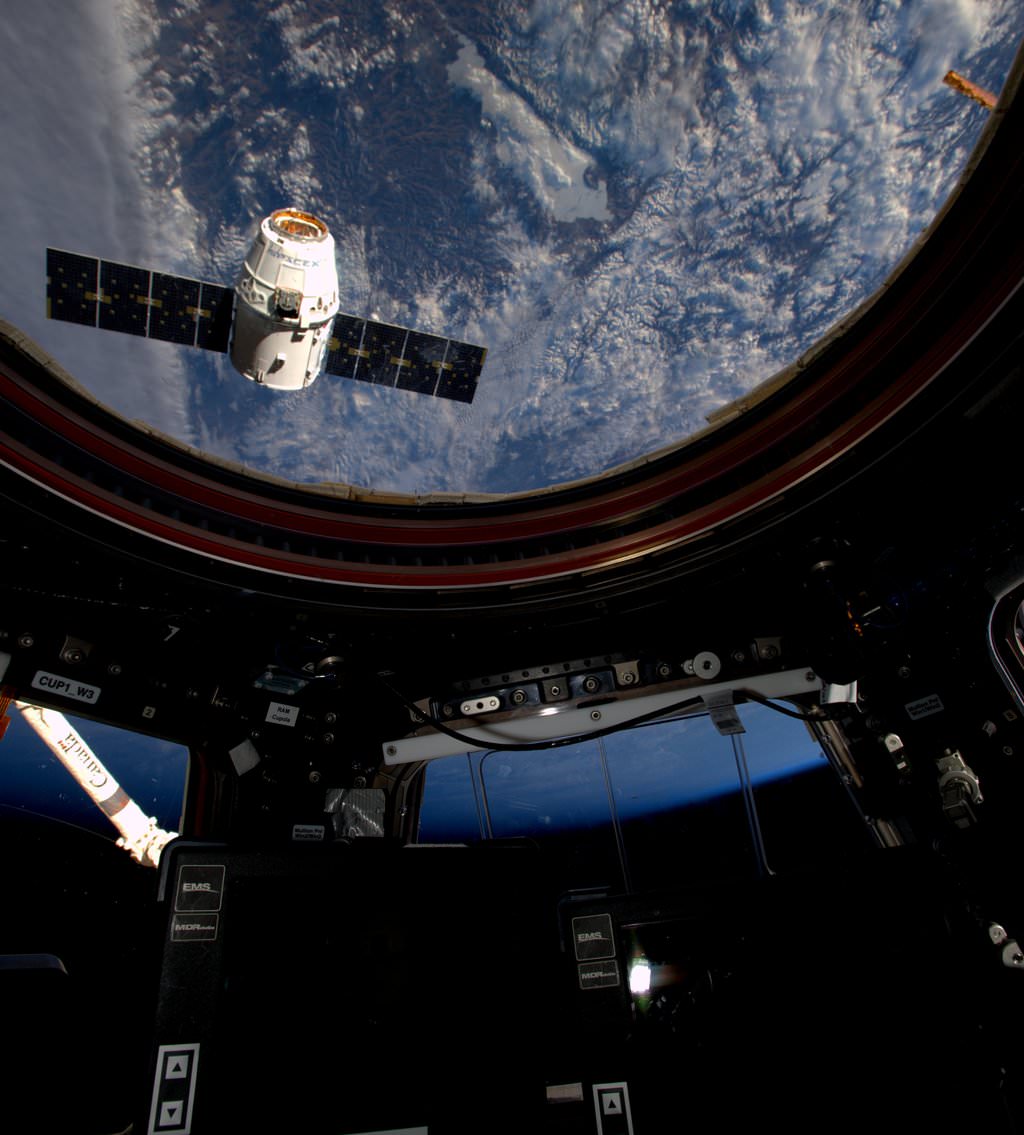
The crew Dragon is also an advanced descendent of the original unmanned cargo Dragon that has ferried tons of science experiments and essential supplies to the ISS since 2012.

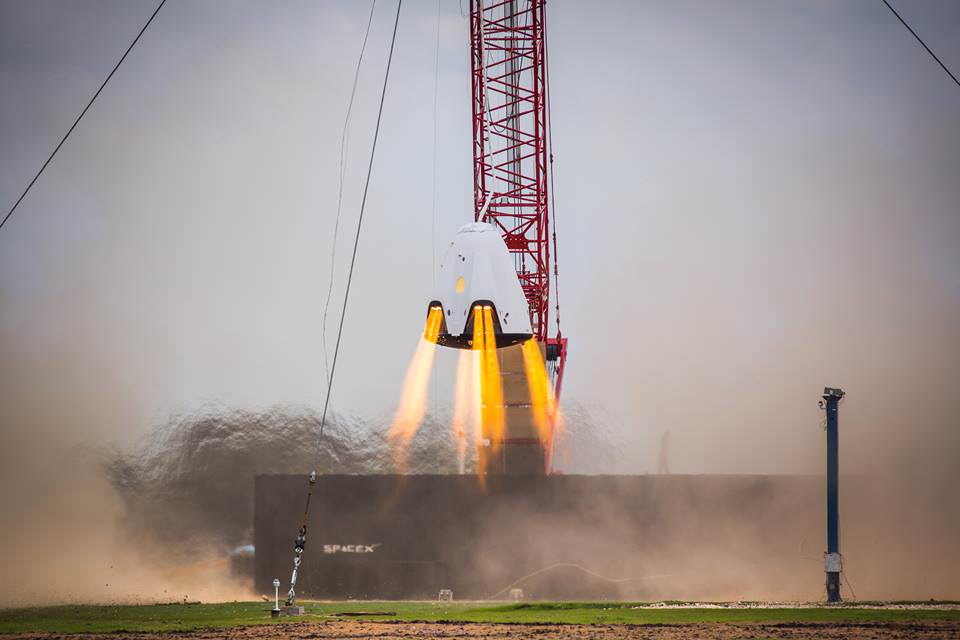
To enable propulsive landings, SpaceX recently conducted hover tests using a Dragon 2 equipped with eight side-mounted SuperDraco engines at their development testing facility in McGregor, TX.
These are “Key for Mars landing,” SpaceX wrote.
“We are closer than ever before to sending American astronauts to Mars than anyone, anywhere, at any time has ever been,” Newman states.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.