The most promising places to look for life in the Solar System are in the ocean moons Europa and Enceladus. But all that warm, salty, potentially life-supporting water is under thick sheets of ice: up to 30 km thick on Europa and up to 40 km thick for Enceladus.
The main obstacles to exploring all that water are the thick ice barriers. Assuming a spacecraft can be designed and built to melt its way through all that ice, what then?
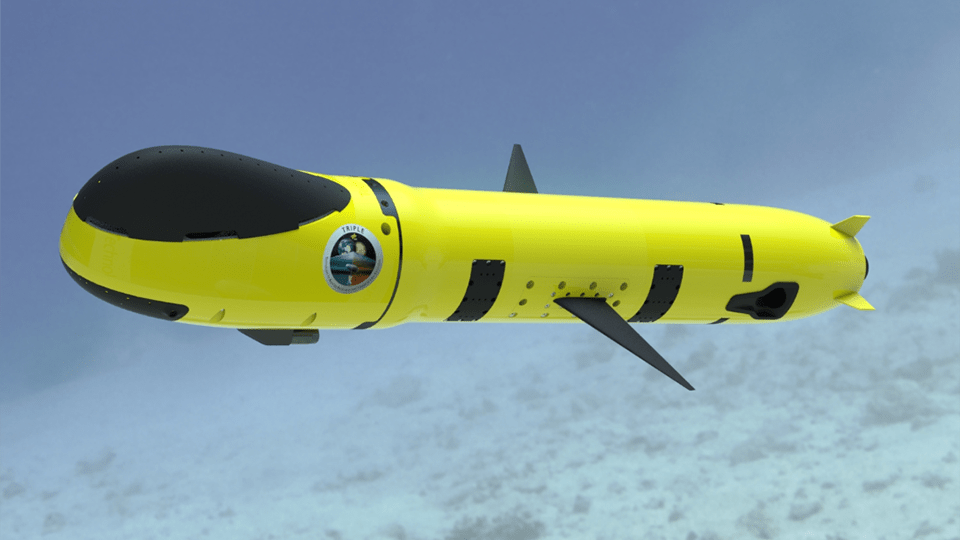
Submarines can do the actual exploring, and they needn’t be large.
Continue reading “Mini-Subs Could One Day Ply the Seas Under Europa’s Ice”