Routines. They tell you when to get up in the morning, what to do at your day job and how to handle myriad tasks ranging from house cleaning to using a computer. Memorizing these procedures makes it a lot easier to handle things that come up in life.
In space, establishing routines is even more important because they will help guide your thinking during an emergency. That’s why astronauts spend thousands of hours learning, simulating and memorizing before heading up to space.
European Space Agency astronaut Alexander Gerst, who will fly to the International Space Station in 2014 during Expedition 40/41, gave Universe Today some insight on how it’s done.
Why train so often? According to Gerst, practicing an emergency procedure on the ground makes it easier to think clearly during a situation up in space. An astronaut’s reaction to any problem on station — a fire, a depressurization, toxic air — is to begin with the procedures. “They sink in and become a memorized response or a natural reaction,” he said. In a fire situation, for example, “Immediately when you hear the sound of the alarm, I will grab the nearest gas mask and the nearest emergency book and head to our control post, which is part of the emergency response.” (Chris Cassidy, a former Navy SEAL on station right now, had more to say to Universe Today in March about “muscle memory” during emergencies.)

What’s the biggest challenge? The complexity of the station. The American and Russian sides have different procedures and different equipment. There are three types of gas masks on station, for example, and three kinds of fire extinguishing systems. (According to Gerst, all but the most stubborn fires on station are extinguished after cutting ventilation and electricity to the affected area.) To address the complexity, the astronauts spend hours in the classroom discussing what to look for in the fire sensors, pressure sensors, ammonia sensors and other parts of the vehicle. The signatures look different for depressurizations, fires and other conditions in space and it’s key to know what they mean at a glance.
What happens during a simulation? After discussing what actions to take, it’s time to play them out. “We don’t light our modules on fire, but the trainers are creative in creating that [emergency] condition,” Gerst said. Sometimes smoke machines will be used during a fire simulation, for example, or the astronauts will simply be informed by instructors that there is a fire in a section of the station. As the astronauts go through the procedures, trainers keep an eye on them and give feedback. In more complex situations, 10 to 20 flight controllers can join in to simulate communications with Mission Control in Houston or its equivalent in Russia.

What about dealing with emergencies in a smaller spacecraft? Astronauts can spend anywhere from hours to days on a Russian Soyuz getting to and from the station. If there’s a fire on board, the three people squashed inside the capsule wouldn’t have much room to deploy fire extinguishers. The response is essentially for astronauts to slam shut the visors on their spacesuits and vent the spacecraft. During a depressurization, the procedure is also to close the visor. “You don’t even have to get out of your seat to deal with the emergency, which makes it quite different,” Gerst said.
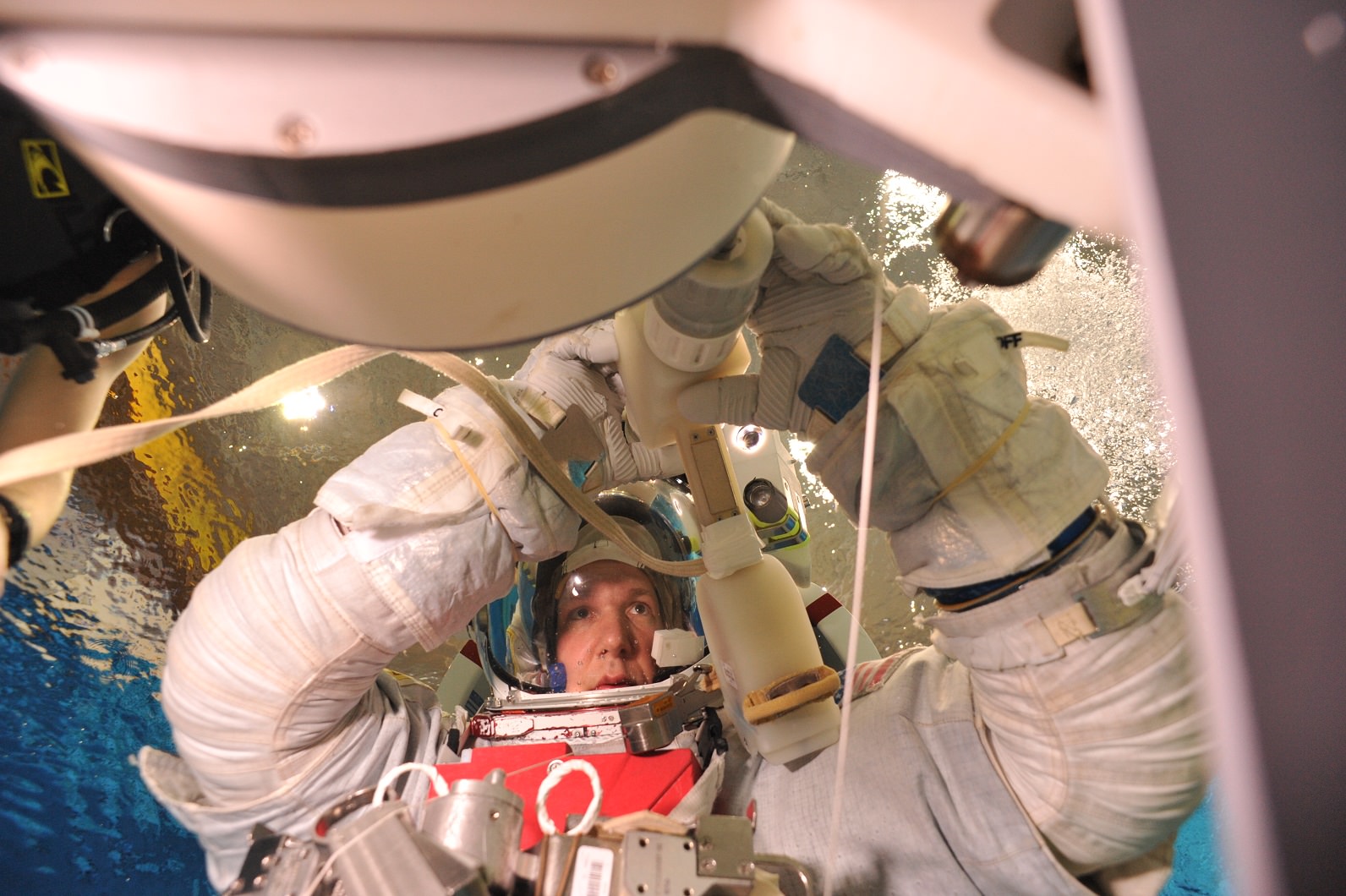
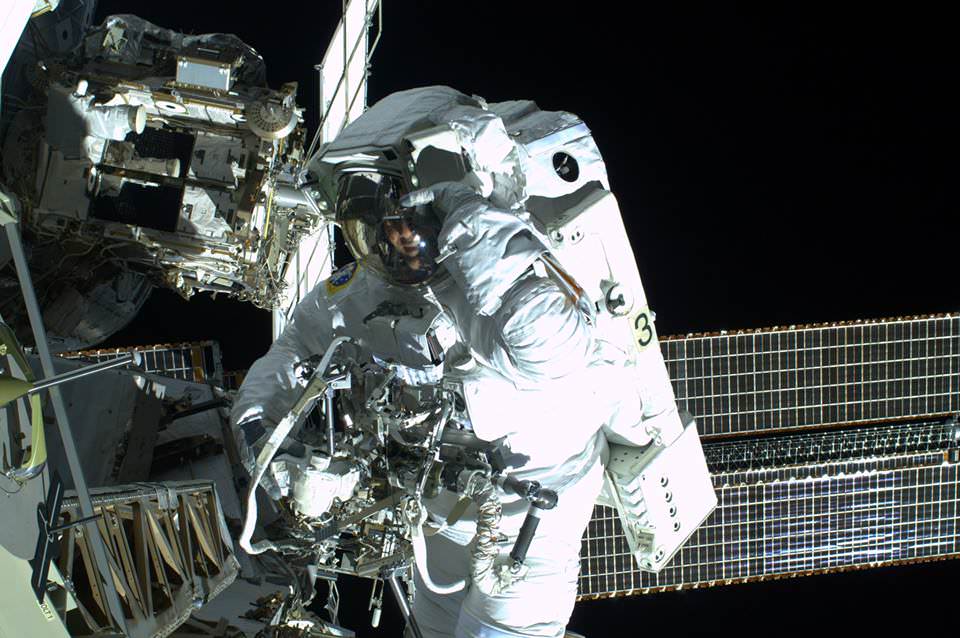
What about emergencies during a spacewalk? Astronauts spend hundreds of hours inside the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory in Houston, a huge pool with a mockup of most of the International Space Station inside. They practice spacewalk procedures such as how to bring an unconscious crew member back to the airlock, or what to do if air leaks out of a spacesuit. Gerst credits this sort of training for helping out during a recent incident involving fellow ESA astronaut Luca Parmitano. In July, emergency procedures kicked in for real when Parmitano’s spacesuit sprung a water leak during a spacewalk. In a nutshell, the crew worked to bring Parmitano back inside as quickly as possible, which led to a safe (but early) end to the work. (Read Parmitano’s nail-biting first-hand account of the incident here.)
What’s the big takeaway? Gerst emphasizes that emergency training is a “huge topic”. He and Reid Wiseman recently got checked out for emergency procedures on the United States side of the station, only to fly to Moscow and then have to do the same thing for the Russian side in mid-August. And there’s other training to do as well — another huge topic is medical emergencies , which Gerst practiced in a German hospital in July.