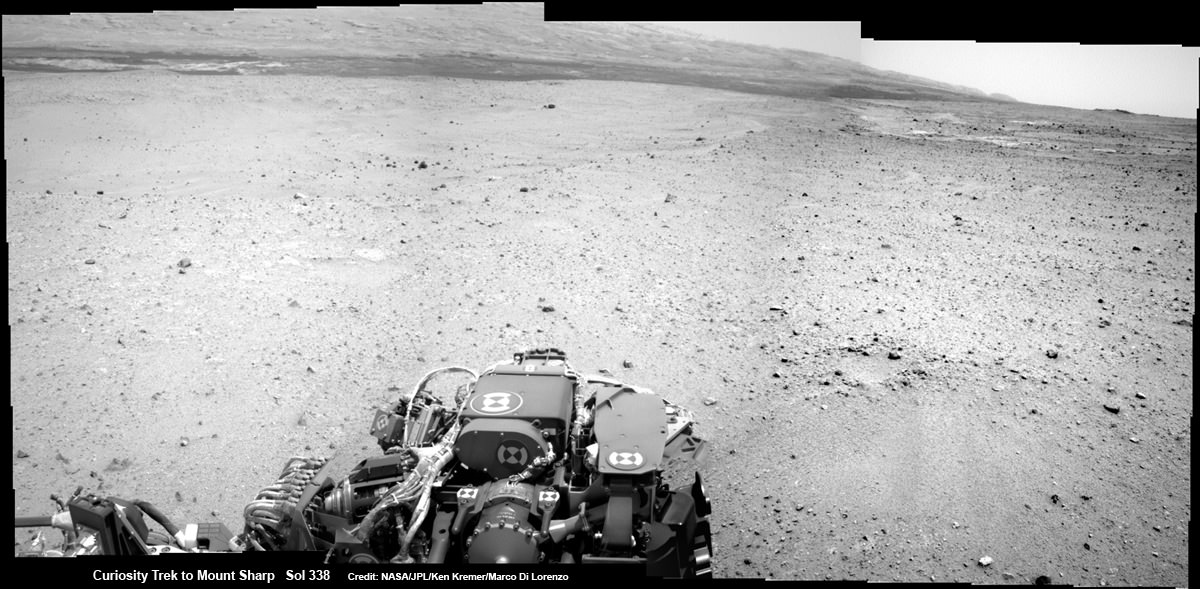
Curiosity On the Road to Mount Sharp and treacherous Sand Dunes – Sol 338 – July 19
Curiosity captured this panoramic view of the path ahead to the base of Mount Sharp and potentially dangerous sand dunes after her most recent drive on July 19, 2013. She must safely cross over the dark dune field to climb and reach the lower sedimentary layers of Mount Sharp. Stowed robotic arm on rover deck seen at center.
See JPL traverse map below pinpointing the view from this location
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer-(kenkremer.com)/Marco Di Lorenzo[/caption]
NASA’s state-of-the-art Curiosity Mars rover is stepping up the driving pace and rolling relentlessly across alien Martian terrain towards the towering mystery mountain known as Mount Sharp that’s holds the keys to the Red Planets past evolution and whether its an abode for Life.
To uncover the latest scoop on the robots otherworldly adventures, Universe Today conducted an exclusive interview with the Curiosity Project Manager Jim Erickson, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
In Part 2 of my conversation with Jim Erickson we’ll discuss more about the rover’s traverse across alien territory that’s simultaneously a science gold mine and a potential death trap, as well as Comet ISON and nighttime observations and science planning.
Read Part 1 – here.
“When Comet ISON is in the sky I’m sure we’ll do some observations of it depending on when its visible,” Erickson told me.
Today, July 20, is Sol 339 of the rovers mission to Mars. And also the 44th anniversary of the 1st human Moonwalks in 1969.
And Curiosity just drove another 34 meters yesterday, Sol 338 (July 19) – for a total distance exceeding 1.1 kilometers.
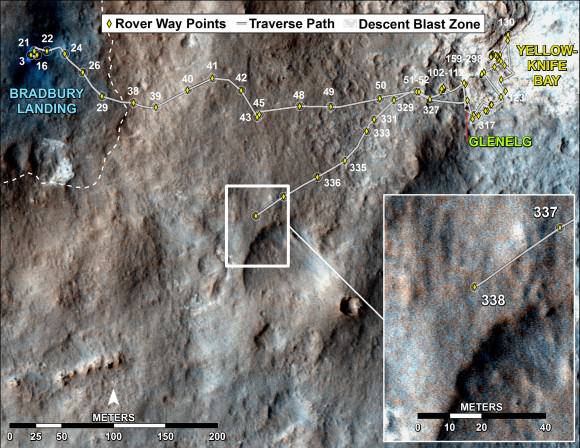
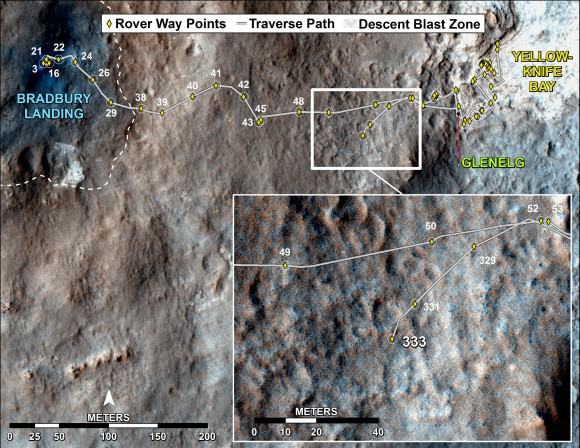
This map shows the route driven by NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity through Sol 338 of the rover’s mission on Mars (July 19, 2013). Numbering of the dots along the line indicate the sol number of each drive. North is up. The scale bar is 200 meters (656 feet). From Sol 337 to Sol 338, Curiosity had driven a straight line distance of about 122.90 feet (32.59 meters). The base image from the map is from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment Camera (HiRISE) in NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona
As for Martian sand dunes, they dunes offer both exciting opportunities and lurking dangers to the rovers well being.
Indeed fields of Martian sand dunes are potential death traps and the six wheeled rover has no choice but to traverse across an extensive dune field as she closes in on the base of Mount Sharp
Recall that NASA’s now long lived Opportunity rover nearly perished rather early in her mission at the ‘Purgatory’ dune field on Meridiani Planum.
Spirit died after more than six highly productive years on the Red Planet when she was unable to escape a hidden sand trap she had accidentally fallen wheels deep into as the vehicle was merrily roving beside an eroded volcano at Gusev Crater on the approach to the mysterious Von Braun mound.
So, dunes are serious business
Here is Part 2 of my interview with Jim Erickson.
Ken Kremer: Which direction is Curiosity headed? Will she be following the southwest route shown in the ellipse on the JPL map – see traverse map below – or reinvestigate any other spots nearer the landing site first?
Jim Erickson: We have a good general idea. We will be on a general heading of southwest, not west which would have taken us back near the landing site [at Bradbury Landing].
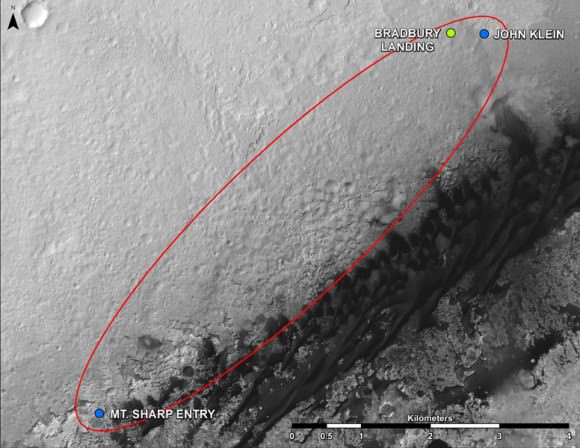

This map shows where NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity landed in August 2012 at “Bradbury Landing”; the area where the rover worked from November 2012 through May 2013 at and near the “John Klein” target rock in the “Glenelg” area; and the mission’s next major destination, the entry point to the base of Mount Sharp. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona
Ken: So the rover will not pass by the Hottah outcrop of concretions formed in water and investigated early in the mission?
Jim Erickson: No. The intent for the ellipse [shown on the map] is that we will be traveling in it to get to an area where the sand dunes look better for crossing [to the base of Mount Sharp]. When we get there we will know reality. And we will pick a safe spot to cross.
The dunes can be both an issue or in some cases easy sailing.
My experience on MER [Spirit & Opportunity] was that when you are going with the dunes, down a trough, they tend to be well packed and that was great driving.
But if you need to make a right turn, that can be a challenge for a couple of reasons. It is harder to see what is inside the next trough. And you have to drive to the top of the dune. So your driving is limited until you can see what’s inside the next dune.
Level ground is more straightforward. You know exactly what to look for if the terrain doesn’t change the next day. So you can do the same thing you did last night based on the new set of images.
If the terrain is changing then it gets more complicated.
Ken: Will you be straddling the dunes or driving alongside some safe distance away?
Jim Erickson: We have been going through various options of different planned routes. At some point we have to go with the dune directions.
So we’ll be traveling down some troughs later on. We will definitely have to pick our way through them.
Part of it is gaining experience in this new area of Mars with how the sand dunes and troughs themselves actually are.
So we’ll have to wait and see. We know we’ll have to deal with the dunes. Depending on how these dunes act we may have to do different things compared to MER.
Ken: What’s the health status of Curiosity?
Jim Erickson: We’re doing great. There are always active things we are looking at.
We had the anomaly before conjunction and have put in place a number of software mitigations and reconfigured the A side memory so that we can work around the hardware problem that happened. If we have another problem, both the A and B side memory can handle it gracefully, unlike the last time.
Ken: Describe the rover’s power situation? And the ability to do nighttime observations like the recent imagery of Phobos rising?
Read earlier Phobos story – here
Jim Erickson: Yes. We have plenty of power.
And certainly will be able to do nighttime observations.
Ken: What’s the plan for observations of Comet ISON?
Jim Erickson: When we get to the point when Comet ISON is in the sky I’m sure we’ll do some observations of it, depending on the time period when its visible.
Note: NASA’s Curiosity and Opportunity rovers will have a view of ISON in October with Oct. 1, 2013, being the comet’s closest approach to Mars.
NASA’s Directory of Planetary Science Jim Green told me previously that NASA is very interested in using its orbiting and surface assets at Mars to study Comet ISON. It’s a once in a lifetime opportunity.
Early October 2013 will be the prime viewing time for ISON from the vicinity of the Red Planet.
Let’s hope that NASA’s quartet of spacecraft and ESA’s lone orbiter capture some breathtaking imagery and science observations.
Ken: About the recent Phobos nighttime images, a Universe Today reader asked whether the other points of light beside Phobos were stars or hot pixels?
Jim Erickson: The specks are hot pixels [not stars], intensified by the long exposure times for the image.
Video Caption: ‘Phobos Rising’ – This movie clip shows Phobos, the larger of the two moons of Mars, passing overhead, as observed by Curiosity in a series of images centered straight overhead starting shortly after sunset on June 28, 2013. Phobos first appears near the lower center of the view and moves toward the top of the view. The apparent ring is an imaging artifact. The other bright spots are hot pixels – not stars. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Ken: How about the prospects for science along the way to the mountain?
Jim Erickson: We expect to do science along the way to Mount Sharp, for example in terms of atmospheric measurements.
We will stop at some preplanned sites. Exactly which ones is still being debated by the scientists.
And we’ll do the right thing – If we see something spectacular along the way. Just because we may not have identified it previously, that doesn’t mean we won’t stop and examine it.
Things are going very well, says Erickson.
Erickson has worked in key positions on many NASA planetary science missions dating back to Viking in the 1970’s. These include the Galileo mission to Jupiter, both MER rovers Spirit & Opportunity, as well as a stint with the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO).
I’ll have more upcoming from Jim about Curiosity’s Martian drilling activities.
As of today (July 20) Curiosity has driven nine times since leaving the Glenelg/Yellowknife Bay area on July 4 (Sol 324), totaling nearly 300 meters.
Stay tuned for more from Mars.