[/caption]
Only time now stands in the way of Curiosity’s long awaited date with the Red Planet. NASA’s next, and perhaps last Mars rover was transported to the launch pad at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and then hoisted on top of the mighty Atlas V rocket that will propel her on a 10 month interplanetary journey to Mars to seek out the potential habitats of Extraterrestrial life.
In less than three weeks on November 25 – the day after Thanksgiving – the Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover will soar to space aboard the Atlas V booster. Touchdown astride a layered mountain at the Gale Crater landing site is set for August 2012.

The $2.5 Billion rover must liftoff by Dec. 18 at the latest, when the launch window to Mars closes for another 26 months. Any delay would cost hundreds of millions of dollars.
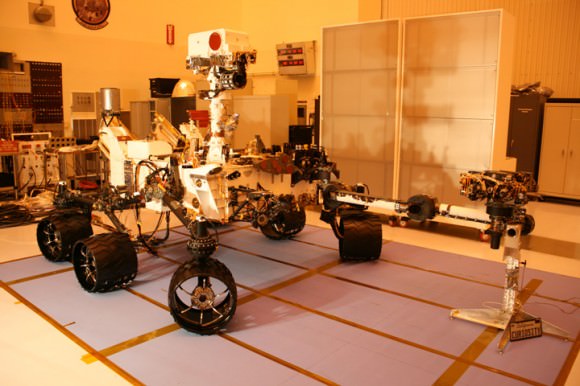
Curiosity represents a quantum leap in science capabilities and is by far the most advanced robotic emissary sent to the surface of another celestial body. MSL will operate for a minimum of one Martian year, equivalent to 687 days on earth.
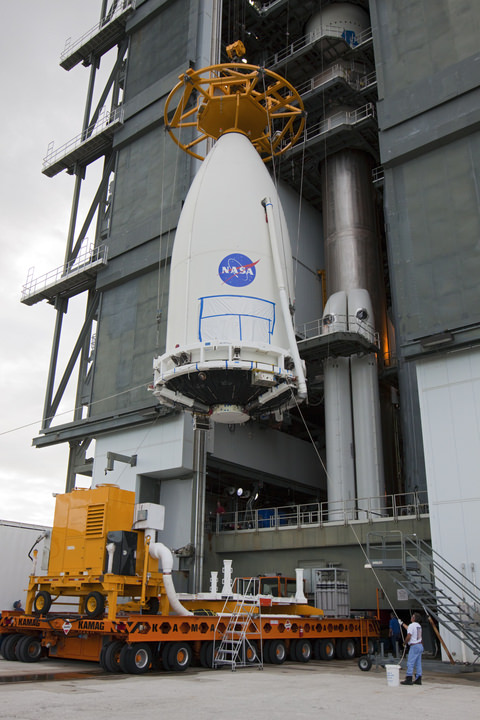
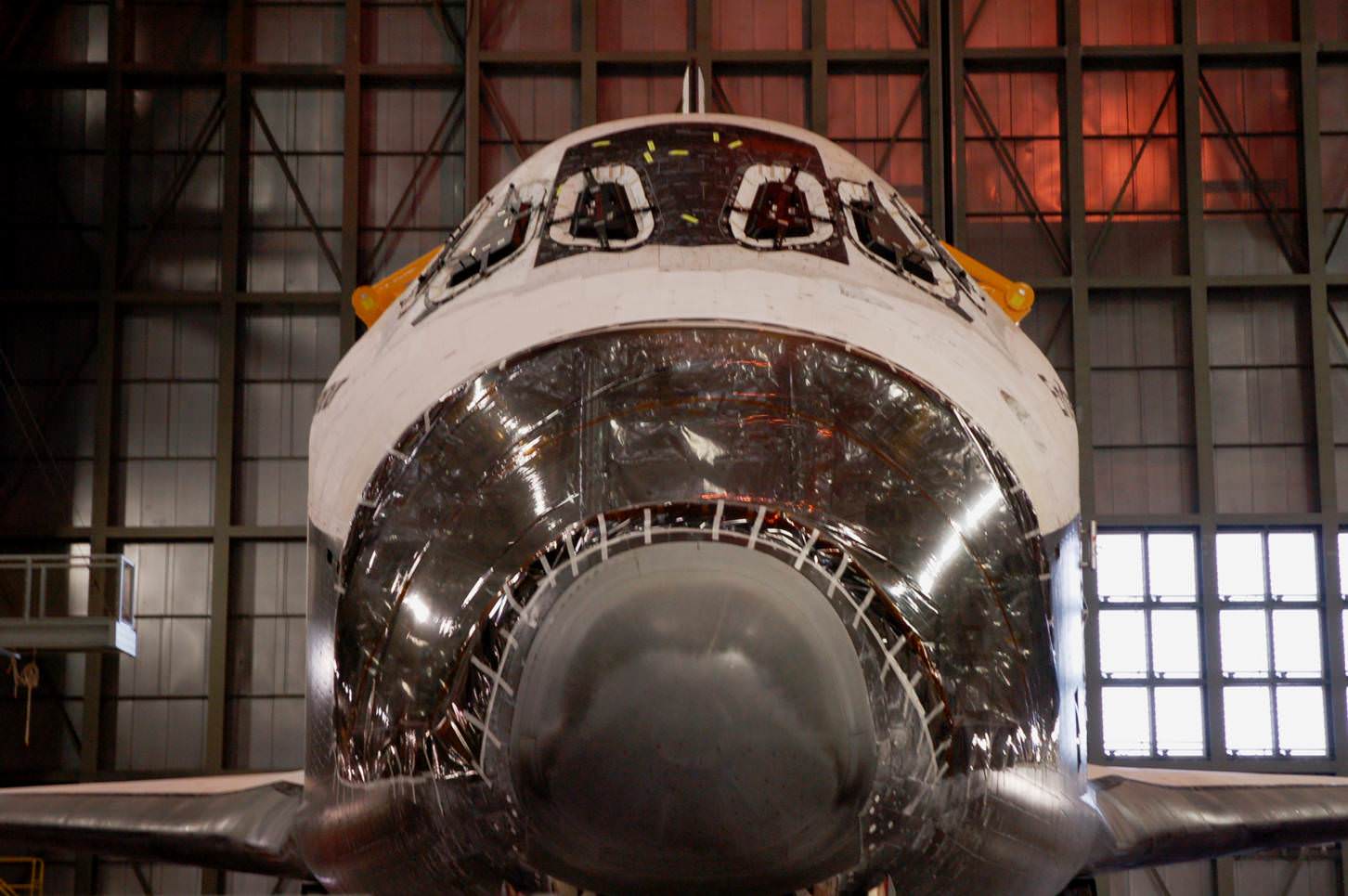
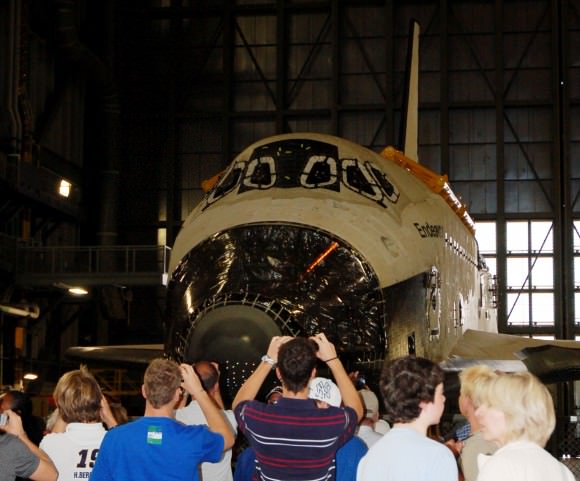
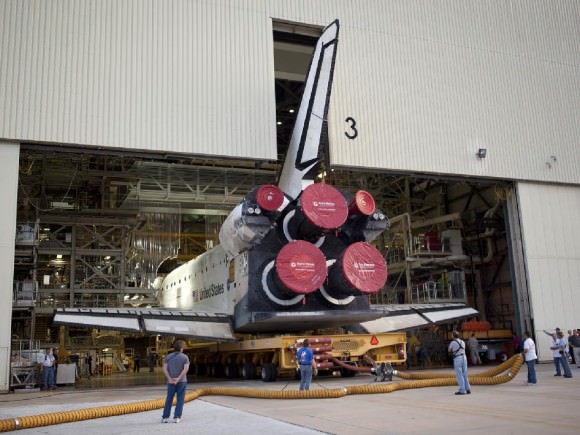
After years of meticulous design work and robotic construction by dedicated scientists and engineers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California and months of vigilant final assembly and preflight processing at the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Curiosity was finally moved the last few miles (km) she’ll ever travel on Earth – in the dead of night – to Space Launch Complex 41 at the Cape.

The robo behemoth was tucked inside her protective aeroshell Mars entry capsule and clamshell-like nose cone, gingerly loaded onto the payload transporter inside the PHSF and arrived – after a careful drive – at Pad 41 at about 4:35 a.m. EDT on Nov. 3. The move was delayed one day by high winds at the Cape.

Teams from rocket builder United Launch Alliance then hoisted MSL by crane on top of the Atlas V rocket already assembled inside the launch gantry known as the Vertical Integration Facility, or VIF, and bolted it to the venerable Centaur upper stage. Technicians also attached umbilicals for mechanical, electrical and gaseous connections.
Curiosity’s purpose is to search for evidence of habitats that could ever have supported microbial life on Mars and determine whether the ingredients of life exist on Mars today in the form of organic molecules – the building blocks of life.
We are all made of organic molecules – which is one of the essential requirements for the genesis of life along with water and an energy source. Mars harbors lots of water and is replete with energy sources, but confirmation of organics is what’s lacking.

The Atlas V will launch in the configuration known as Atlas 541. The 4 indicates a total of four solid rocket motors (SRM) are attached to the base of the first stage. The 5 indicates a five meter diameter payload fairing. The 1 indicates use of a single engine Centaur upper stage.
One of the last but critical jobs remaining at the pad is installation of Curiosity’s MMRTG (Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator) power source about a week before launch around Nov. 17. Technicians will install the MMRTG through small portholes on the side of the payload fairing and aeroshell.
The nuclear power source will significantly enhance the driving range, scientific capability and working lifetime of the six wheeled rover compared to other solar powered landed surface explorers like Pathfinder, Spirit, Opportunity, Phoenix and Phobos-Grunt.
The minivan sized rover measures three meters in length, roughly twice the size of the MER rovers; Spirit and Opportunity. MSL is equipped with 10 science instruments for a minimum two year expedition across Gale crater. The science payload weighs ten times more than any prior Mars rover mission.
The Atlas V rocket and Curiosity will roll out to the launch pad on Wednedsay, November 23, the day before Thanksgiving.
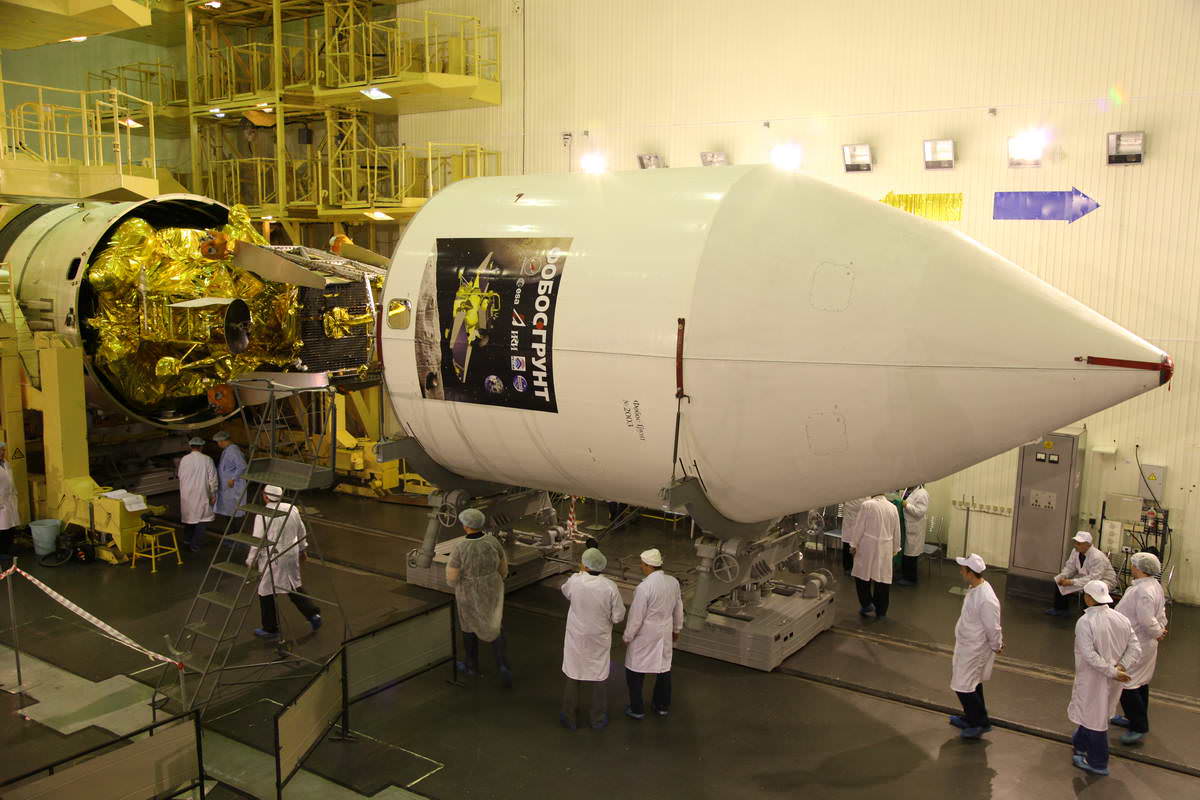
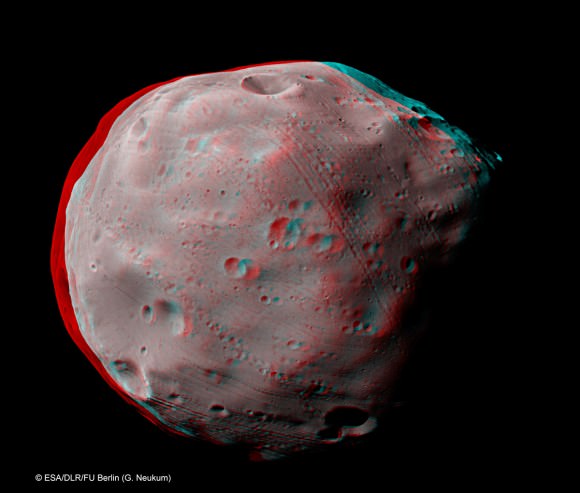
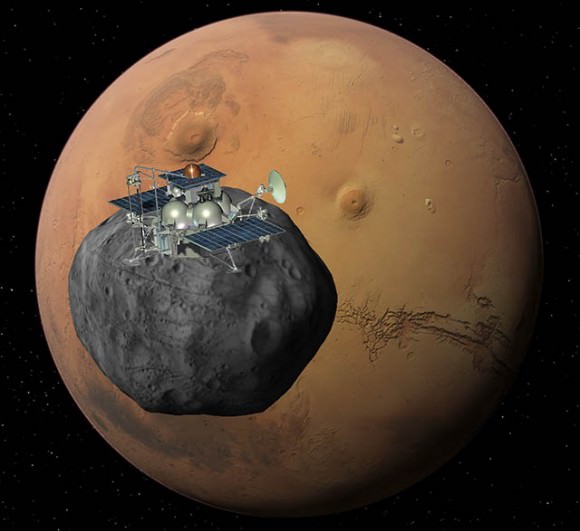
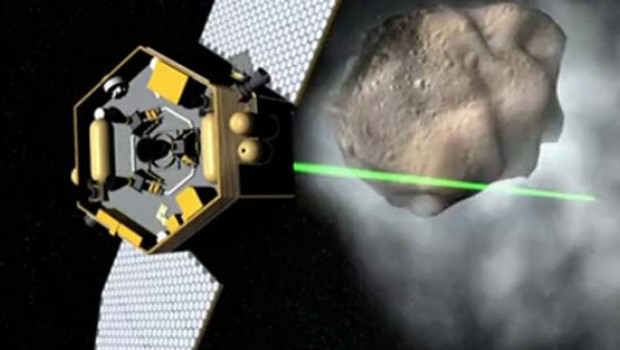
Meanwhile, Russia’s Phobos-Grunt mission to Mars and Phobos is on target to blast off on November 9, Moscow time [Nov 8, US time].
Read Ken’s continuing features about Curiosity starting here:
Closing the Clamshell on a Martian Curiosity
Curiosity Buttoned Up for Martian Voyage in Search of Life’s Ingredients
Assembling Curiosity’s Rocket to Mars
Encapsulating Curiosity for Martian Flight Test
Dramatic New NASA Animation Depicts Next Mars Rover in Action
Read Ken’s continuing features about Phobos-Grunt upcoming Nov 9 launch here:
Phobos-Grunt and Yinghuo-1 Encapsulated for Voyage to Mars and Phobos
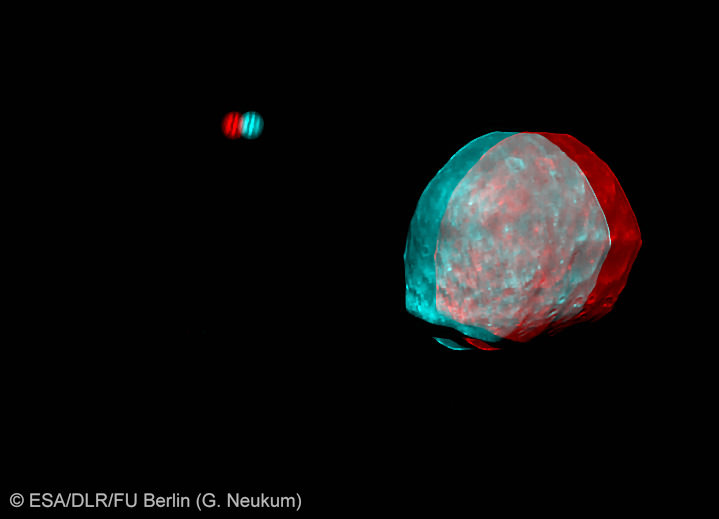
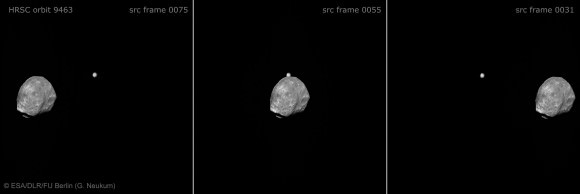
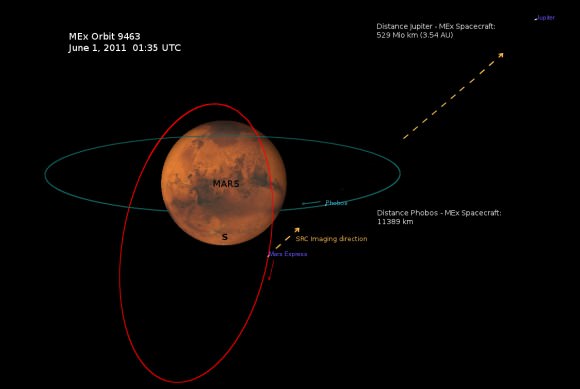
Phobos and Jupiter Conjunction in 3 D and Amazing Animation – Blastoff to Martian Moon near
Russia Fuels Phobos-Grunt and sets Mars Launch for November 9
Phobos-Grunt and Yinghou-1 Arrive at Baikonur Launch Site to tight Mars Deadline
Phobos-Grunt: The Mission Poster
Daring Russian Sample Return mission to Martian Moon Phobos aims for November Liftoff