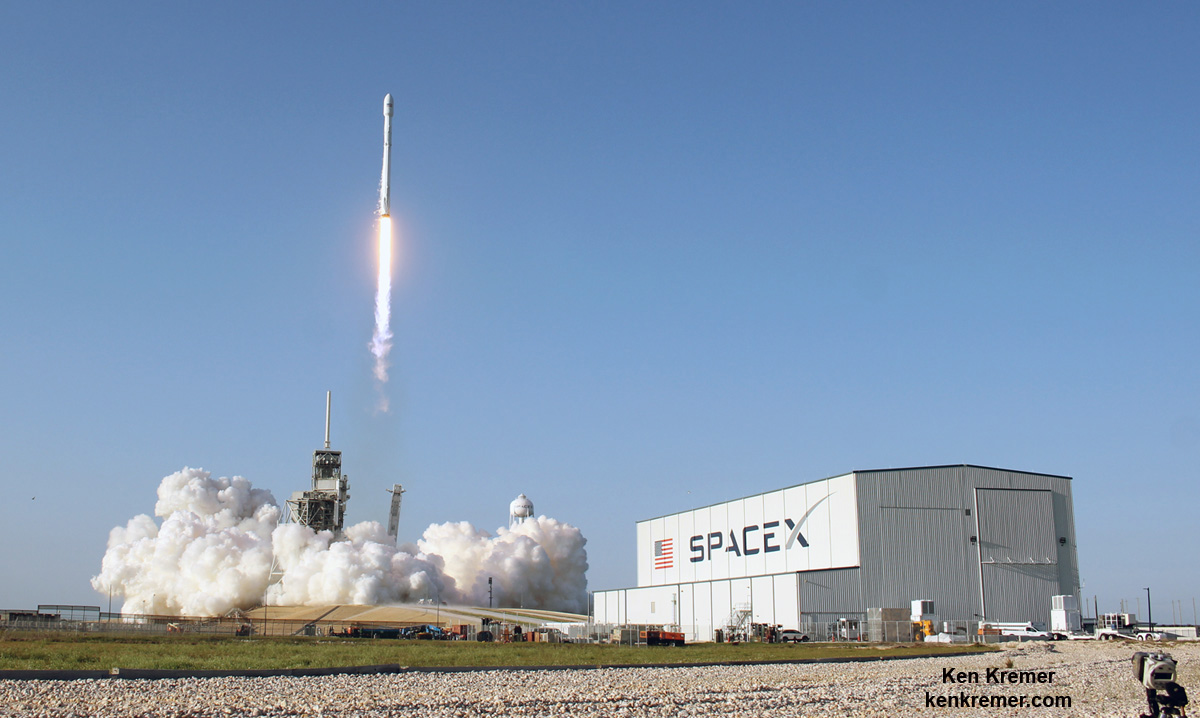
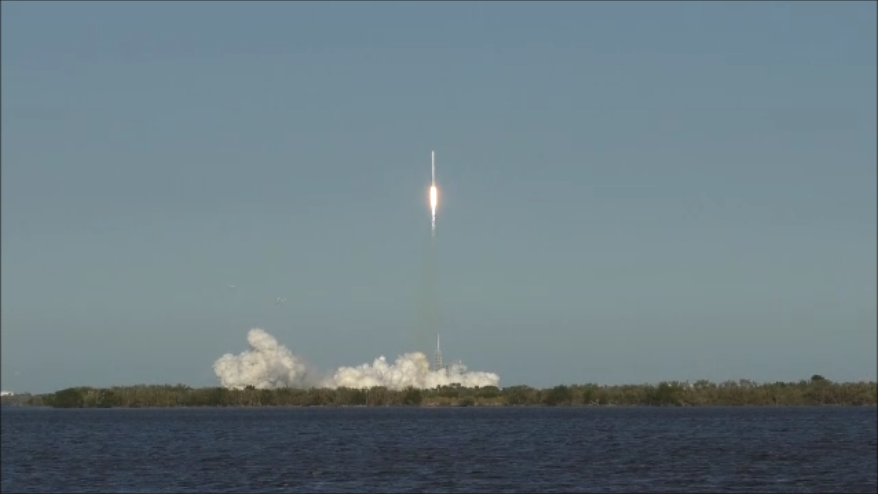
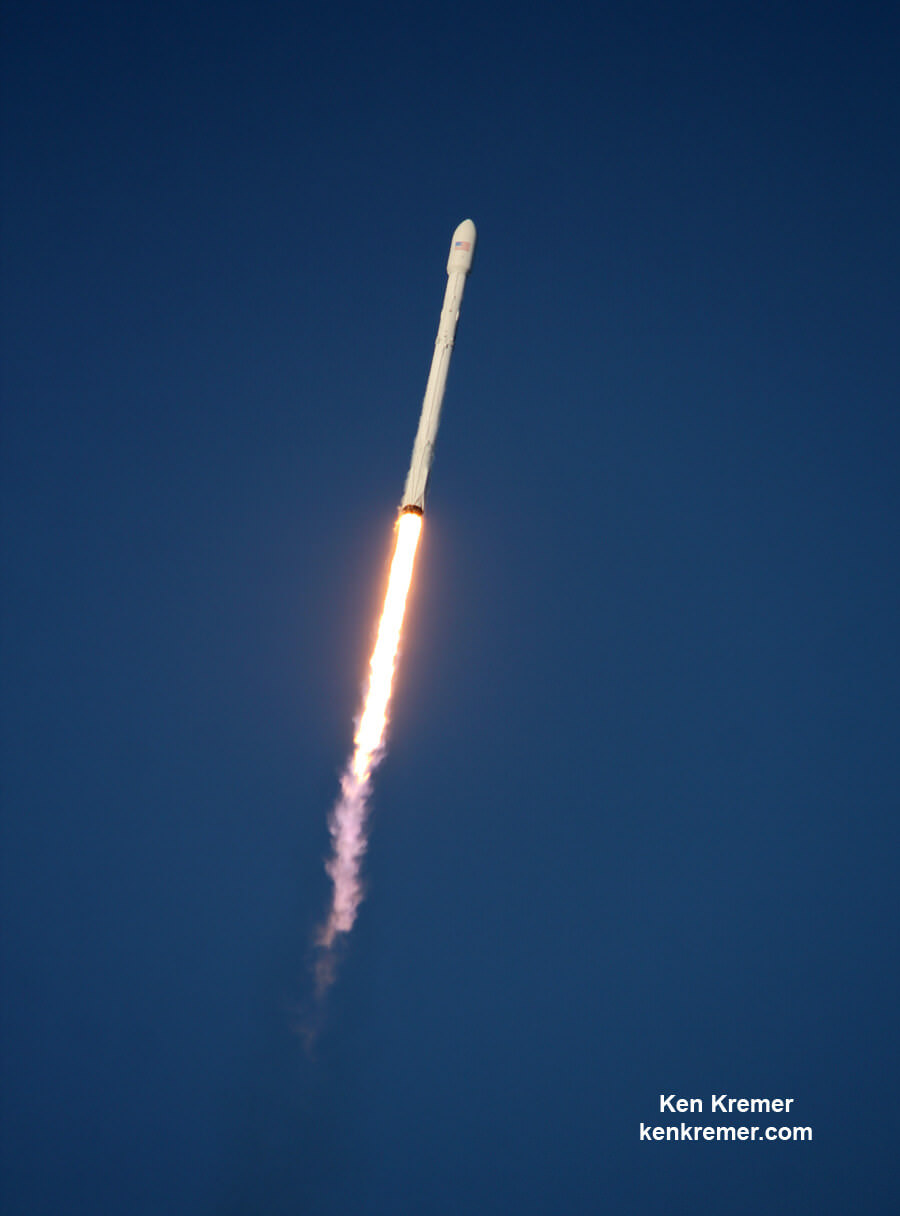
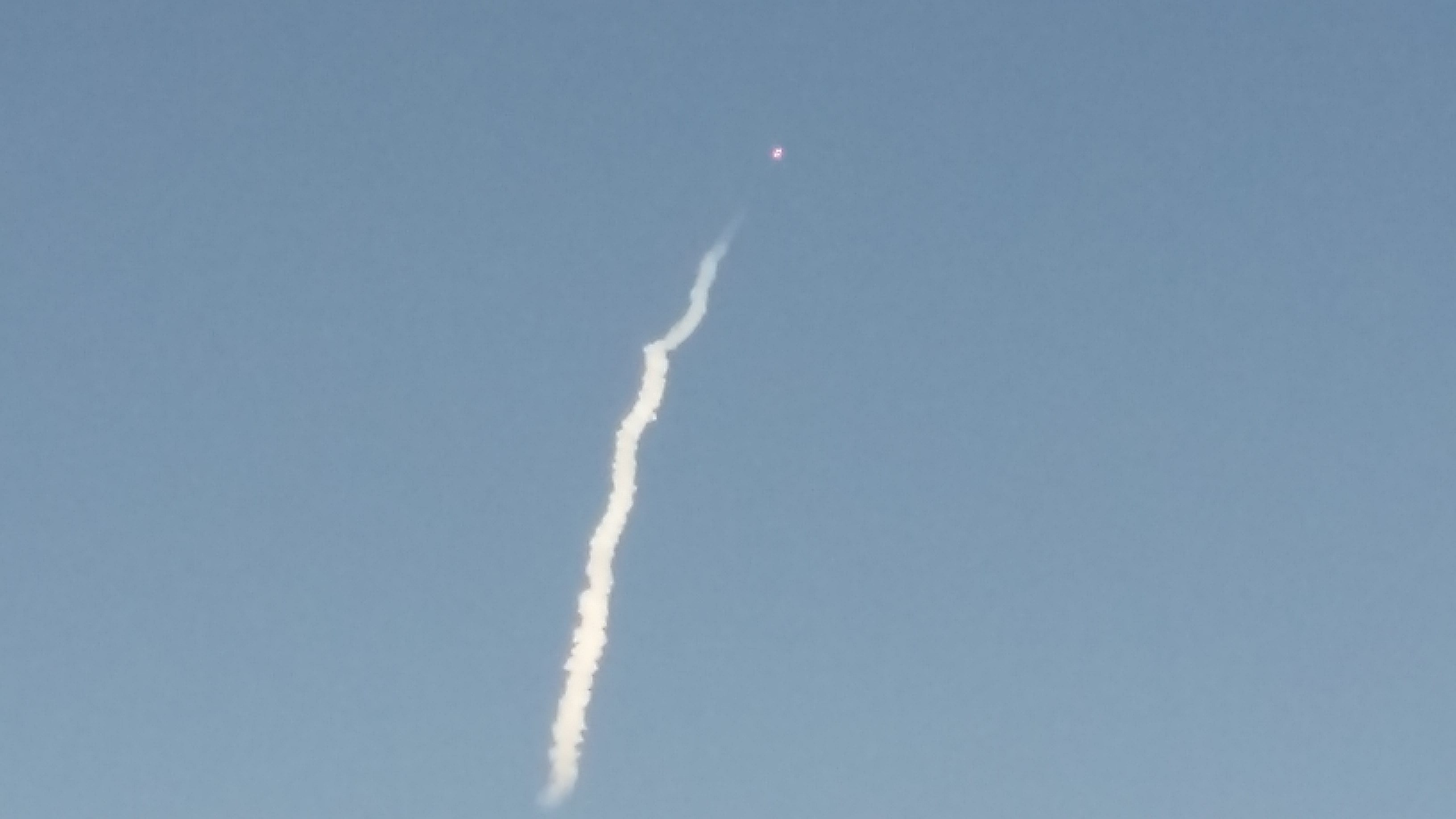
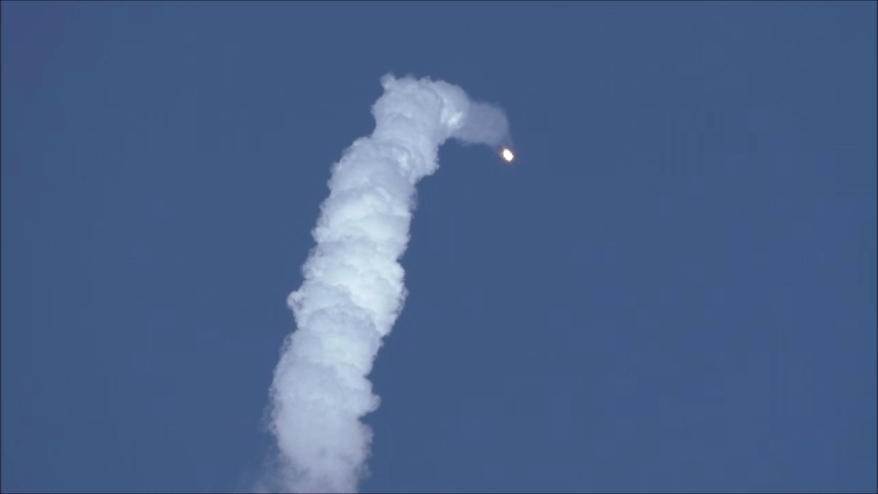
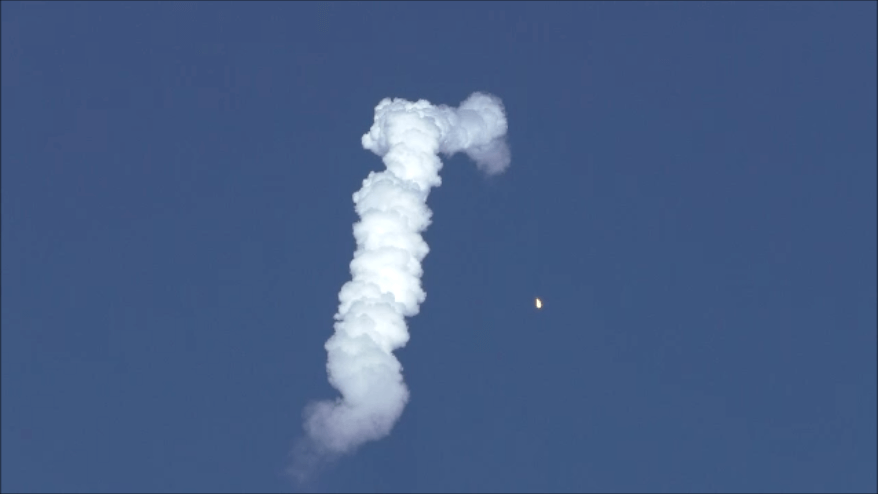
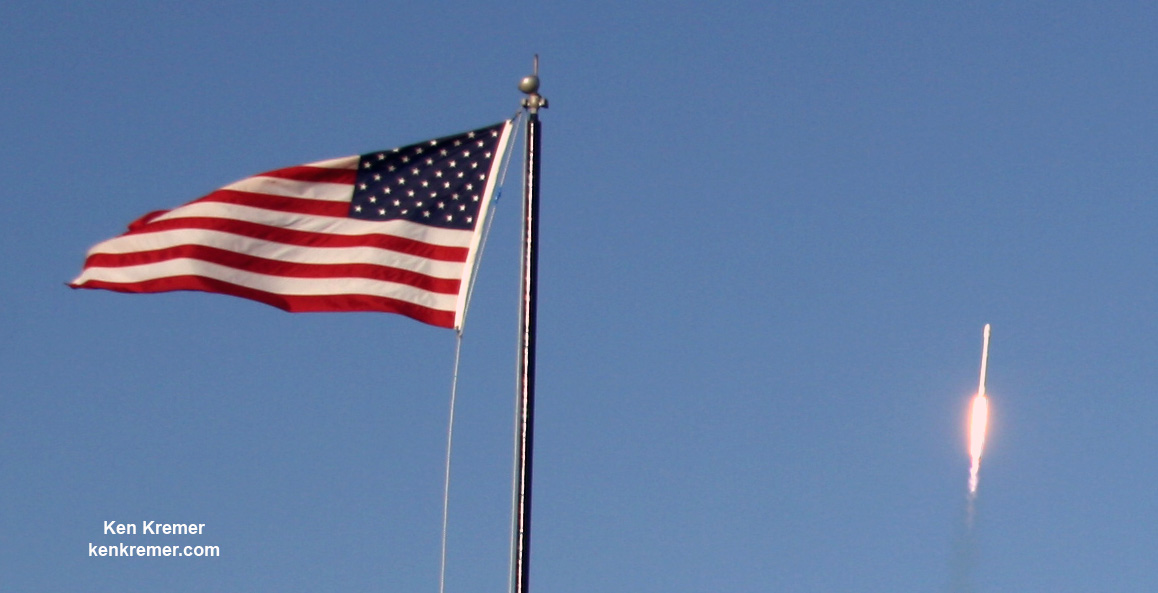
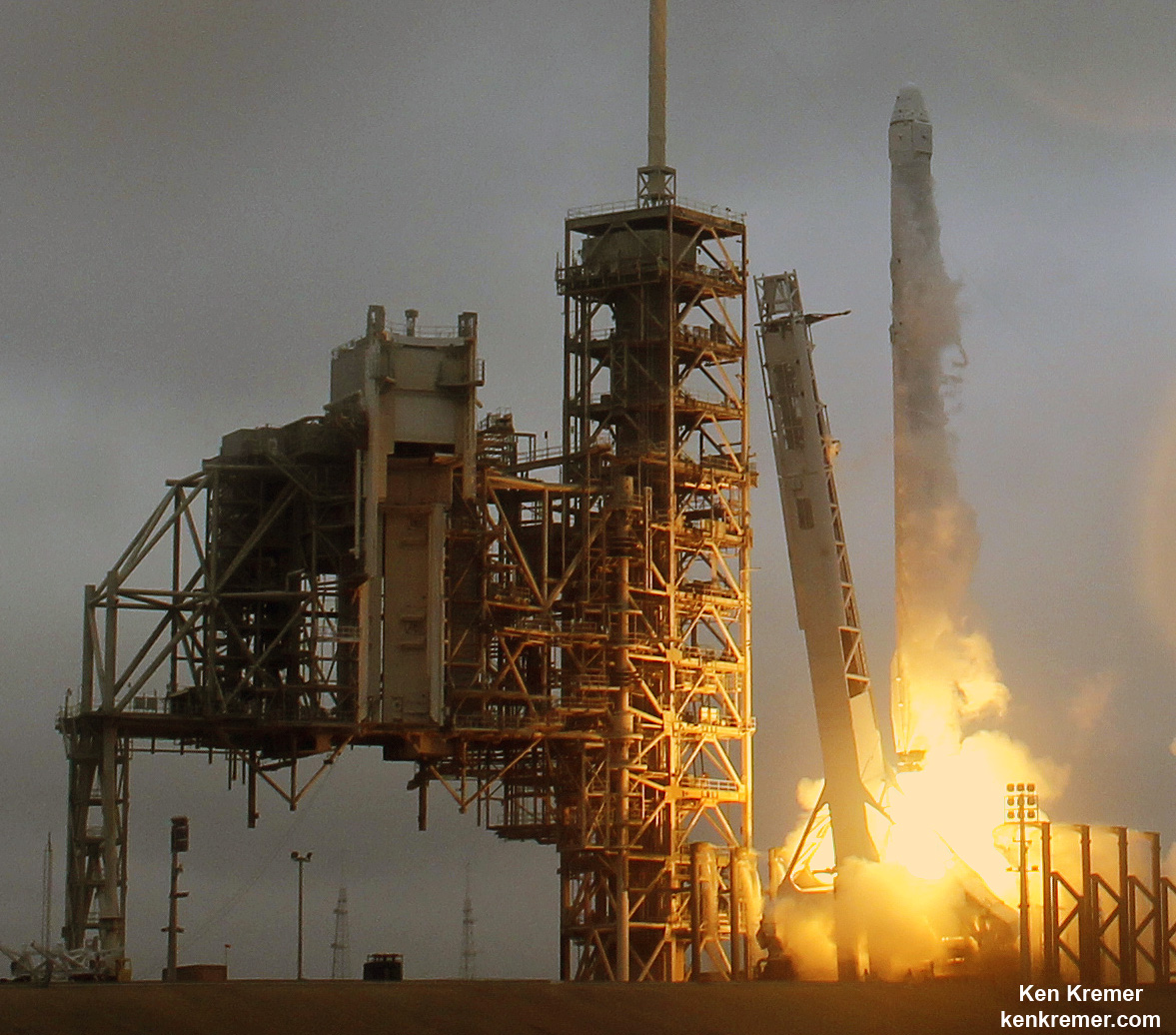
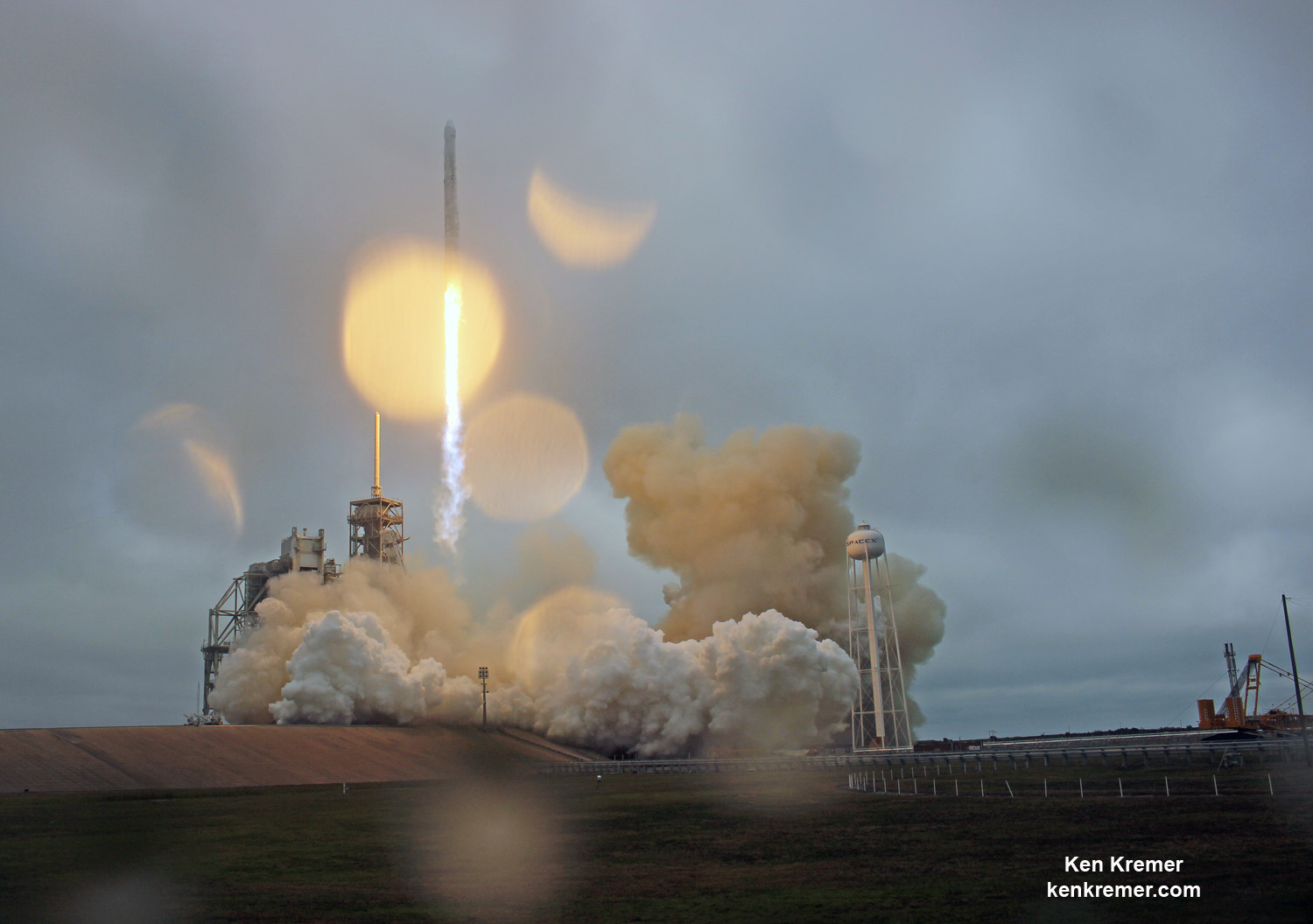
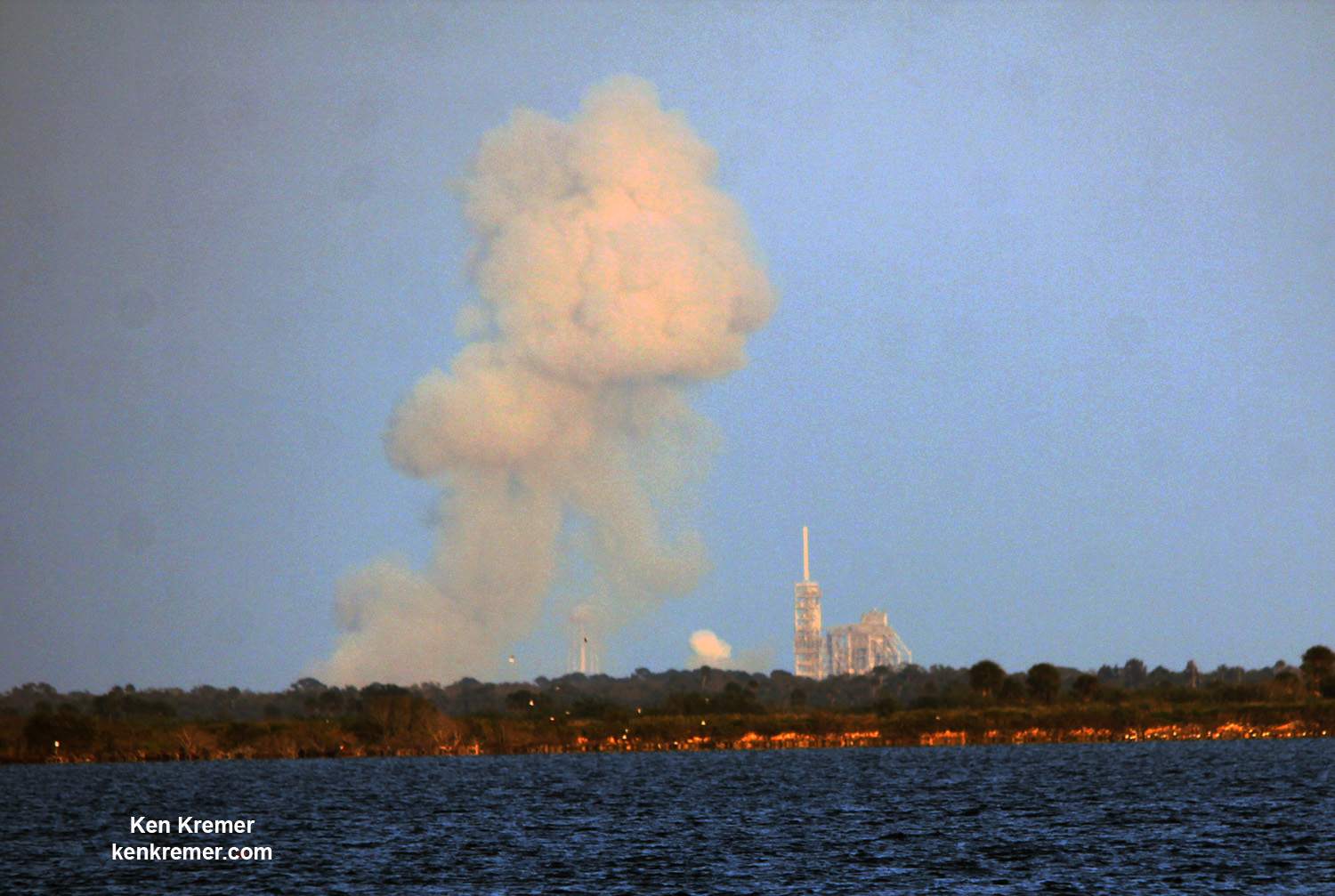
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FL – SpaceX CEO Elon Musk’s Billion dollar bet on rocket recycling paid off beautifully when the world’s first ever reflown rocket booster – a SpaceX Falcon 9 – roared off NASA’s historic pad 39A at the Kennedy Space Center and successfully delivered the next generation SES-10 TV satellite to orbit and simultaneously shot revolutionary shock waves reverberating forever across the rocket industry worldwide.
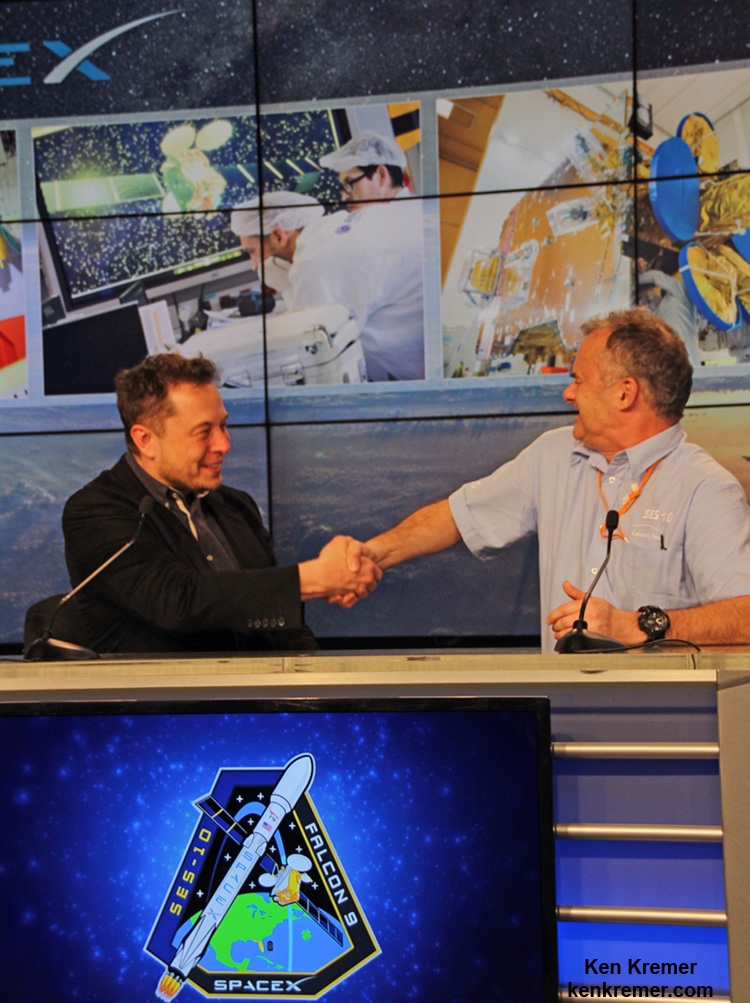
“This is a huge revolution in spaceflight,” billionaire SpaceX CEO and Chief Designer Elon Musk told reporters at the post launch briefing at the Kennedy Space Center press site, barely an hour after liftoff.
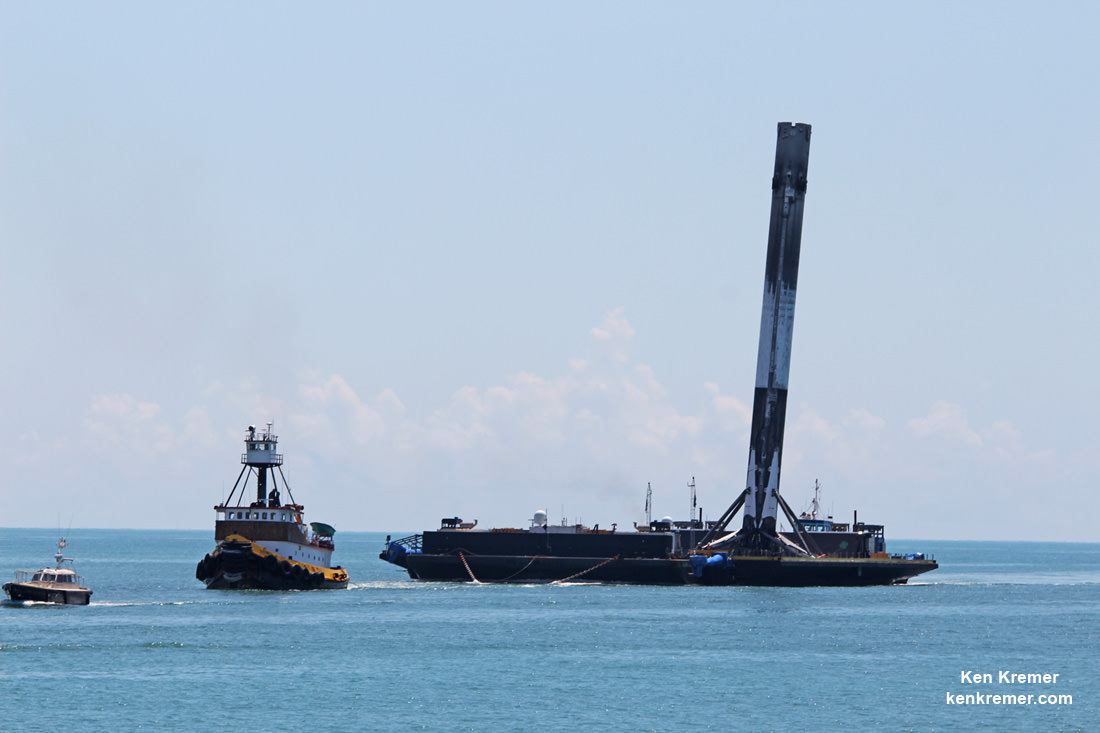
And as if the relaunch of a ‘Flight-Proven’ booster was not enough, SpaceX engineers deftly maneuvered the Falcon 9 first stage to a second successful pinpoint landing on a miniscule droneship at sea.
The stunning events were captured by journalists and tourists gathered from around the globe to witness history in the making with their own eyeballs.
Check out this expanding gallery of eyepopping photos and videos from several space journalist colleagues and friends and myself – for views you won’t see elsewhere.
Click back as the gallery grows !

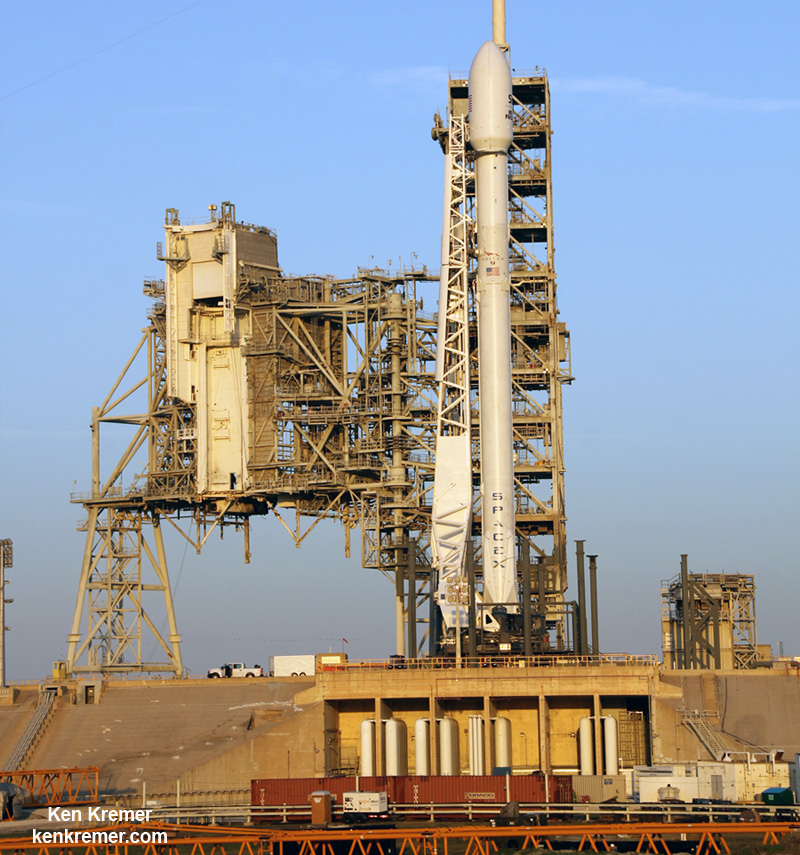
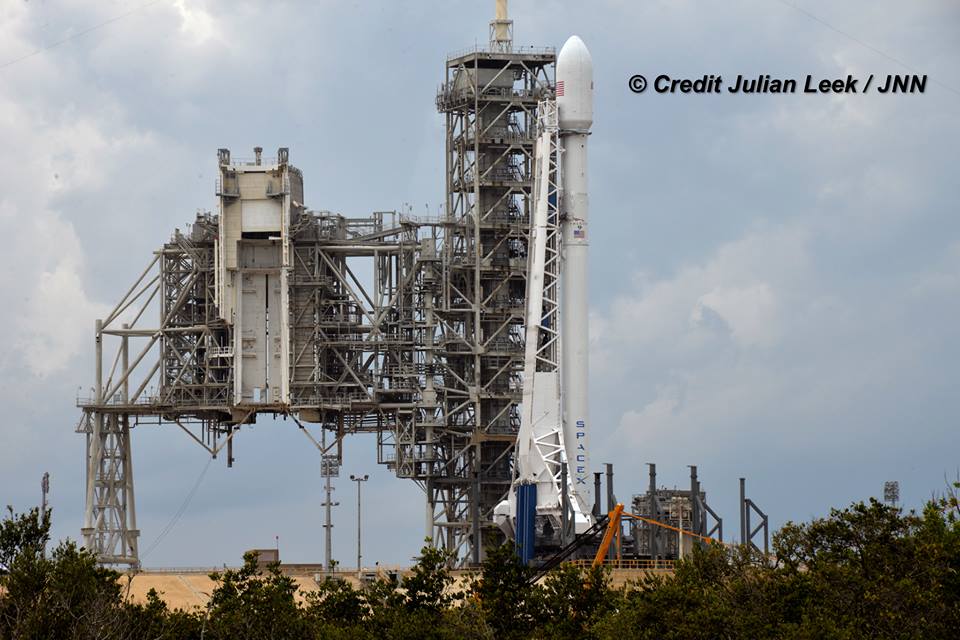
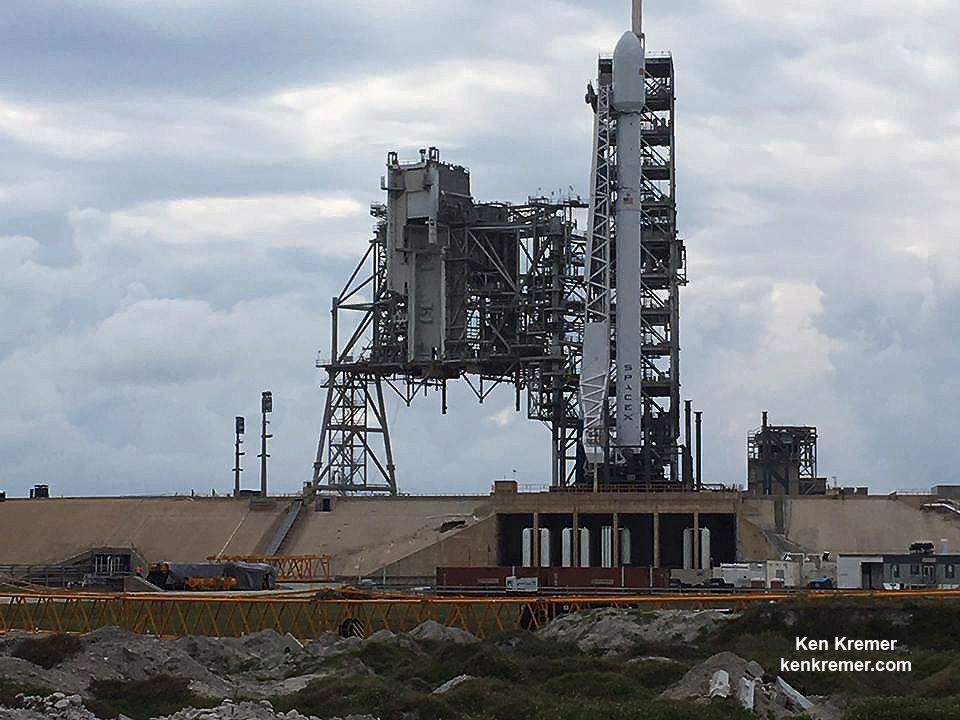
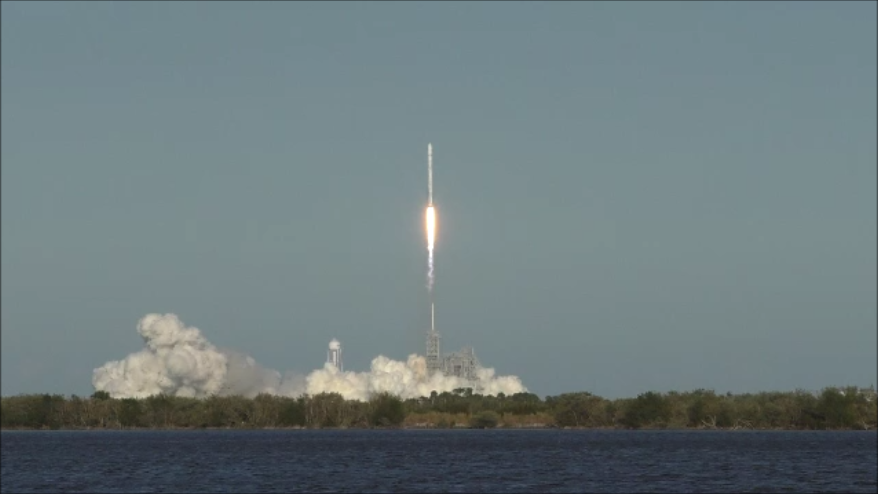
The milestone SpaceX mission to refly the first ever ‘used rocket’ blasted off right on time at the opening of the dinnertime launch window on Thursday, March 30, at 6:27 p.m. EDT.
The used two stage 229-foot-tall (70-meter) rocket carried the SES-10 telecommunications payload to orbit using a ‘Flight-Proven’ Falcon 9 rocket from seaside Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida.
Musk said SpaceX invested about a billion dollars of his firm’s own funds and 15 years of hard won effort to accomplish the unprecedented feat that many experts deemed virtually unattainable or outright impossible.
“This represents the culmination of 15 years of work at SpaceX to be able to refly a rocket booster,” Musk elaborated.
“It’s really a great day, not just for SpaceX, but for the space industry as a whole, proving something can be done that many people said was impossible.”
But SES Chief Technology Officer (CTO) Martin Martin Halliwell had faith in SpaceX from the beginning and unabashedly discounted the risk – based on his in depth knowledge.
‘We had a team embedded with SpaceX all along the way,” SES CTO Haliwell said at the post launch briefing.
Furthermore Halliwell was instrumental in signing up telecom giant SES as the paying customer who had complete confidence in placing his firm’s expensive SES-10 communication satellite atop SpaceX’s history making used and now successfully reflown booster.
“There have been naysayers,” Halliwell told reporters at a prelaunch press briefing on March 28. “I can tell you there was a chief engineer of another launch provider — I will not say the name — who told me, categorically to my face, you will never land a first stage booster. It is impossible. If you do it then it will be completely wrecked.”
“We are confident in this booster,” Halliwell told me at the prelaunch briefing.
“There is not a huge risk,” Halliwell stated emphatically. “In this particular case we know that the reusability capability is built into the design of the Falcon 9 vehicle.”
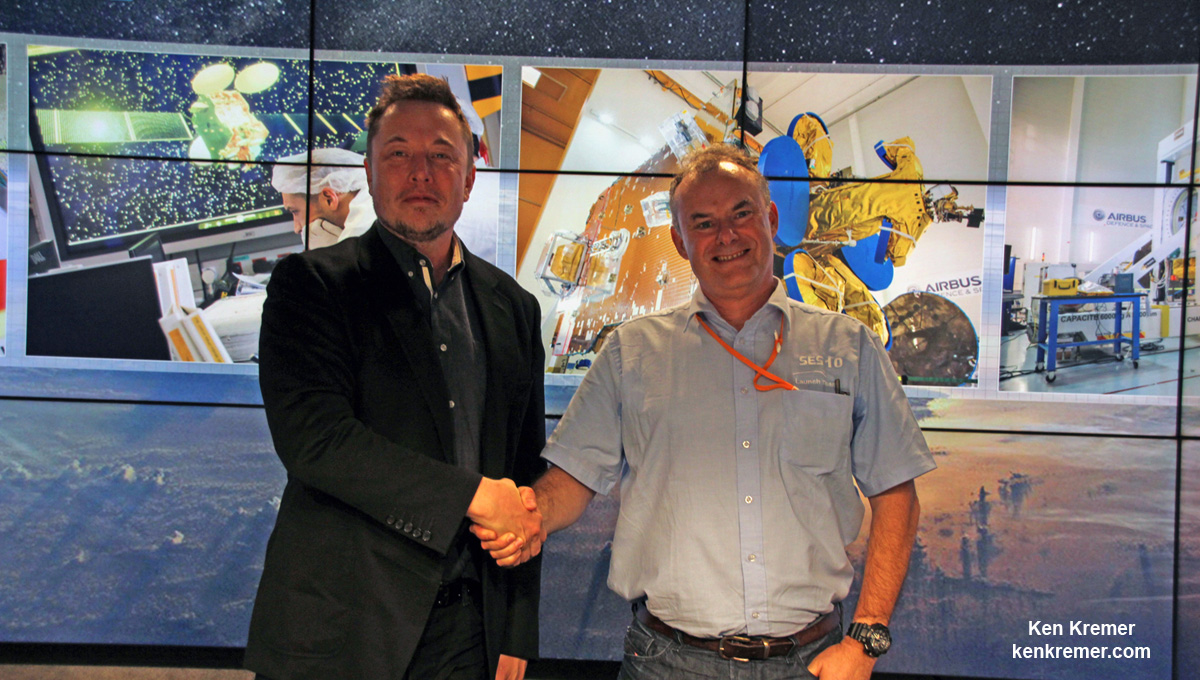

“You’ve got to decouple the emotion from the engineering,” Halliwell elaborated on Thursday’s launch. “The engineering team that Elon has working for him is really second to none. He asks very simple profound questions. And he gets very good answers. The proof is in the pudding.”

“This will rock the space industry,” said Halliwell at the post launch media briefing. “And SpaceX already has!”
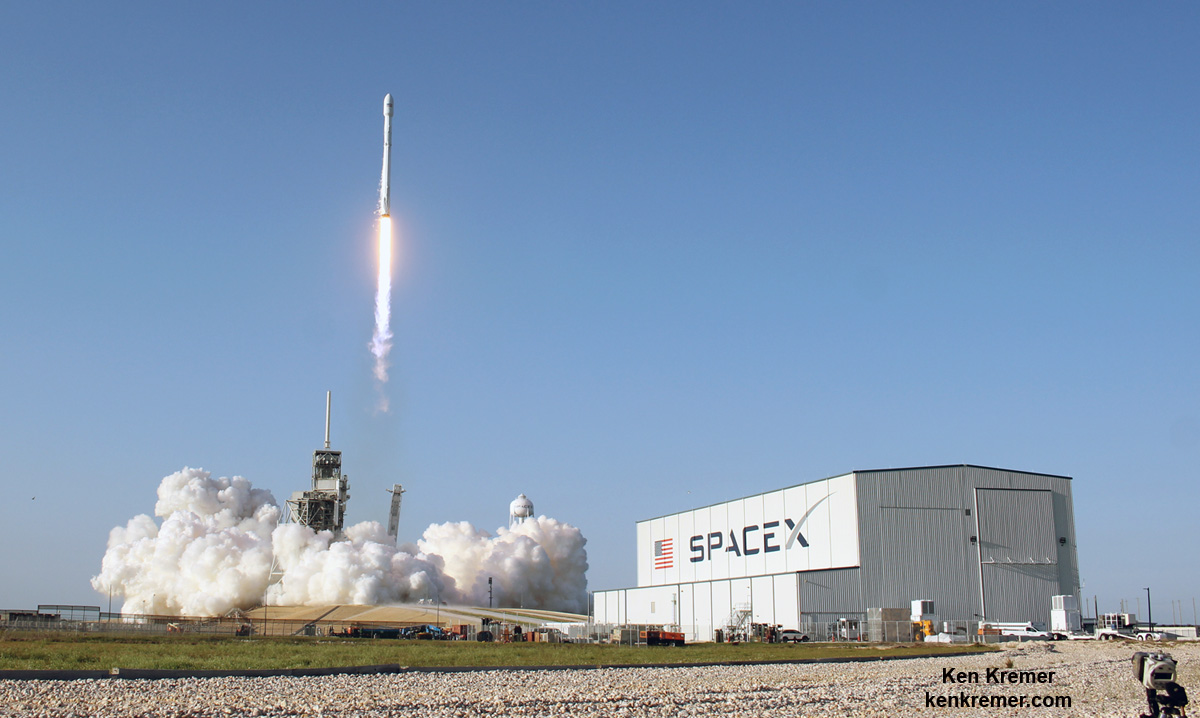

The recycled Falcon delivered the nearly six ton SES-10 satellite to geostationary transfer orbit where it will provide significantly improved TV, voice, data and maratime service to over 37 million customers across Central and South America.
This recycled Falcon 9 first stage booster first launched in April 2016 for NASA on the SpaceX Dragon CRS-8 resupply mission to the International Space Station (ISS) under contract for the space agency.
Furthermore, after the 156 foot tall first stage booster completed its primary mission task, SpaceX engineers successfully guided it to a second landing on the tiny OCISLY drone ship for a soft touchdown some eight and a half minutes after liftoff.
OCISLY had left Port Canaveral several days ahead of the March 30 launch and was prepositioned in the Atlantic Ocean some 400 miles (600 km) off the US East coast, just waiting for the boosters 2nd history making approach and pinpoint propulsive soft landing.
It thus became the first booster in history to launch twice and land twice.

Watch for Ken’s continuing coverage direct from onsite at the Kennedy Space Center press site and Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.