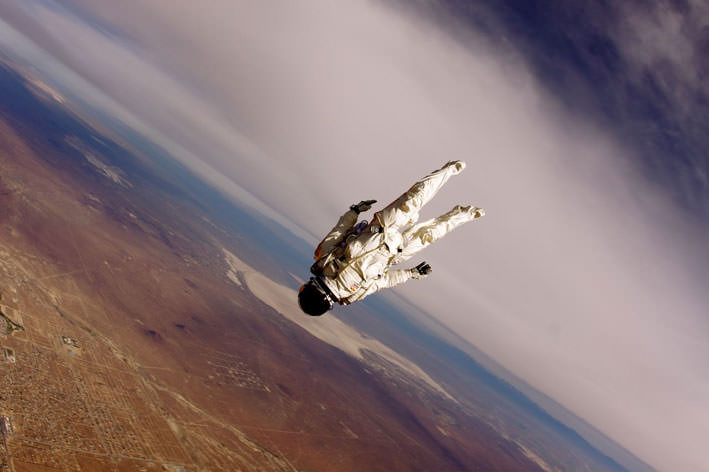
Want to know what it is like to bail out in near space and freefall 37 km (23 miles) to Earth? You’re about to find out. While no date has been announced yet for Felix Baumgartner’s attempt at breaking the speed of sound during freefall, when it does occur, everyone will be able to watch. The Red Bull Stratos mission team announced today there will be a live television broadcast and online stream of the activities. In-flight cameras will be mounted on the capsule that brings him to 36,500 meters (120,000 feet) altitude via stratospheric balloon, as well as on Baumgartner’s space suit. If successful, this will be the first time in history a freefalling human body will reach supersonic speeds.
[/caption]
There will also be microphones inside the capsule and inside Baumgartner’s helmet. Those on the capsule will record sound only as long as there is air to carry the soundwaves. When Baumgartner depressurizes the capsule (just before he jumps), those ambient microphones in the capsule will stop picking up sound, but his helmet mic should keep working.
The final launch date, location and live stream details will be announced in the coming weeks on www.redbullstratos.com, on Twitter (@RedBullStratos), and on Facebook.
The current record-holder, USAF Col. (Ret.) Joe Kittinger jumped from 102,800 feet 50 years ago this month. He did not break the speed of sound, although he probably came close. There have been several attempts to surpass Kittinger’s record, but none have succeeded, and people have given their lives for the quest. There are some movies and images from Kittinger’s jump, and his team used spring-wound motion picture cameras warmed by hot-water bottles to document his freefall. Red Bull Stratos will use high-definition video cameras and ultra-high-definition 4K digital cinematography cameras. The challenge will be keeping them cool in an environment where the air is too thin to wick away their heat.
The footage is being taken by FlightLine Films, who will be making a documentary about the jump, so it’s not clear how much will be live on the webcast, although the press release by Red Bull Stratos says the camers will “provide viewers of the worldwide broadcast with perspectives of the capsule, the skyscape and Baumgartner himself.”
And of course there is the main reason to record everything that happens in the jump: for the benefit of scientific research.
We’ll provide an update on the date of the Baumgartner’s jump when it is announced.
Read our preview article on Baumgartner’s record-breaking attempt.