[/caption]
Note: To celebrate the 40th anniversary of the Apollo 13 mission, for 13 days, Universe Today will feature “13 Things That Saved Apollo 13,” discussing different turning points of the mission with NASA engineer Jerry Woodfill.
Going to the Moon was big. It was a giant stride in doing what had once been thought impossible. Initially many scientists and engineers had big plans for huge rockets akin to the ships imagined in science fiction: one piece vehicles that took off from Earth, landed intact bottom down on the Moon and had the ability to launch again from the lunar surface. But other rocket engineers had different ideas, and this caused some big arguments. The method of going to the Moon that eventually won out used — in part — a little lunar lander. This decision ended up being instrumental in saving the crew of Apollo 13. And that was big.
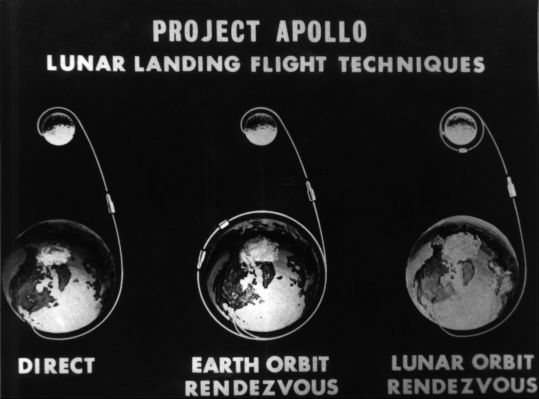
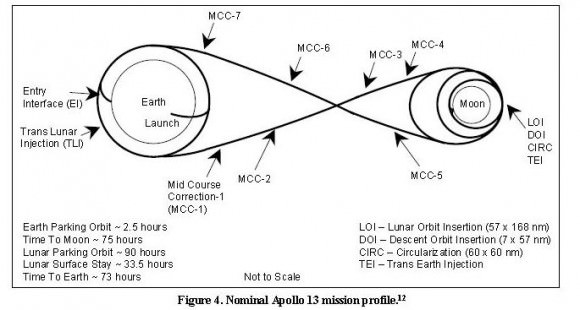
There were three different methods to choose from in reaching the Moon. One, called the Direct Ascent Mode, would have used the big Flash Gordon-like enormous rocket – which was known as a Nova class rocket –to fly straight to the Moon, land and return. Second, the Earth Orbital Rendezvous technique called for two not-quite-as big Saturn V boosters to launch and rendezvous in Earth orbit. In this mode, one rocket would carry a single Apollo vehicle and its crew, and the other, more fuel, which would be transferred to Apollo in Earth orbit, and then the spacecraft would head off to the Moon. The third option was Lunar Orbit Rendezvous which used only one three-stage Saturn V booster, and split the Apollo vehicle into two separate vehicles – a combined Command and Service Module (CSM), and a Lunar Module (LM).
Those familiar with NASA history know that Lunar Orbit Rendezvous was the final choice.
But this mode wasn’t an obvious choice, said NASA engineer Jerry Woodfill.
“At first, Werner Von Braun wanted to use the Nova class rocket Direct Ascent approach, and so did President Kennedy’s science advisor, ” Woodfill said. “But a group at Langley Research Center led by Dr. John Houbolt came up with the Lunar Orbit Rendezvous design. And most everyone ignored them at first.”

But Houbolt insisted the one-rocket system was not feasible. In a NASA interview Houbolt said, “It can not be done. I said you must include rendezvous in your thinking — to simplify, to manage your energy much better.”
Houbolt said it turned into a two-and-a-half year fight to convince people, but he and his team had the facts and figures to back up their claims.
Woodfill said one of his colleagues, former NASA engineer Bob Lacy was part of the discussions on which plan to use. “He said it was unbelievable,” Woodfill recalled. “They were debating in a meeting room at Langley about the best way to go to the Moon. One side was for sending a single vehicle requiring a huge booster to get it there. The other group wanted a two spaceship method. No one seemed agreeable to the other side’s approach. Tempers were starting to flare. To ease the situation someone said, ‘Let’s flip a coin to settle the score.’ Can you believe that?”
No one flipped a coin, but the story demonstrates the intensity of the debate.
In the race to get to the Moon, the Soviet Union had embraced the Nova rocket concept. “The Soviets pressed forward with the direct assent approach to use a Nova class booster,” said Woodfill. “Designated N-1, it clustered 30 engines on its first stage. The design achieved a Herculean thrust of 10-12 millions pounds. Additionally, this uncomplicated direct ascent launch would be less complex was thought to take less time to accomplish. Designing, building, testing and launching two separate spaceships might not win the race to the Moon.”
Woodfill said the Nova rocket may have proved to be the best choice except for the failure of just one of those 30 engines at launch. “This would unbalance the entire assemblage,” Woodfill said.
And twice in 1969 – one occurring just weeks before the scheduled launch of Apollo 11 — the Soviet N-1 booster exploded at liftoff. The huge rocket proved to be too complicated, while the Lunar Orbit Rendezvous method had a simple elegance that was also more economical.

In November 1961, Houbolt boldly wrote a letter to NASA associate administrator Robert C. Seamans, “Do we want to go to the Moon or not?” he wrote. “Why is Nova, with its ponderous size simply just accepted, and why is a much less grandiose scheme involving rendezvous ostracized or put on the defensive? I fully realize that contacting you in this manner is somewhat unorthodox,” Houbolt admitted, “but the issues at stake are crucial enough to us all that an unusual course is warranted.”
The bold move paid off, and Seamans saw to it that NASA took a closer look at Houbolt’s design, and surprisingly, it soon became the favored approach – after a little debate..
Houbolt’s design separated the spacecraft into two specialized vehicles. This allowed the spacecraft to take advantage of the Moon’s low gravity. The lunar lander could be made quite small and lightweight, reducing bulk, fuel, and thrust requirements.
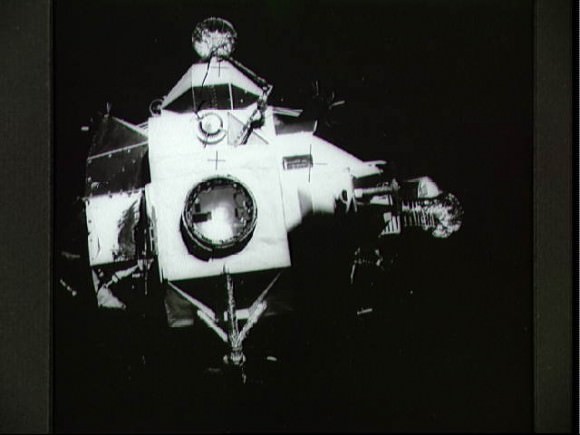
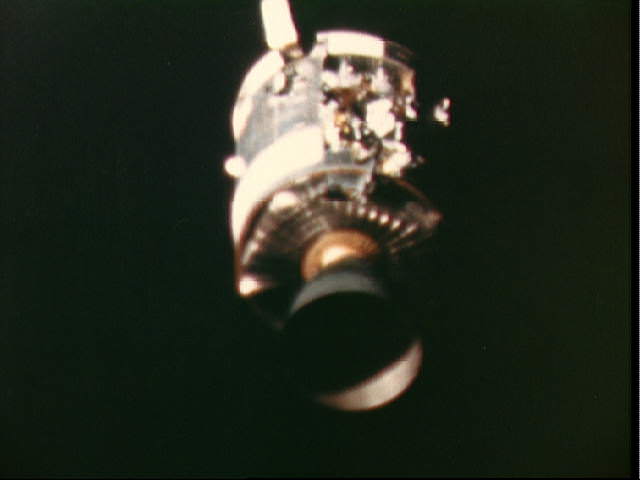
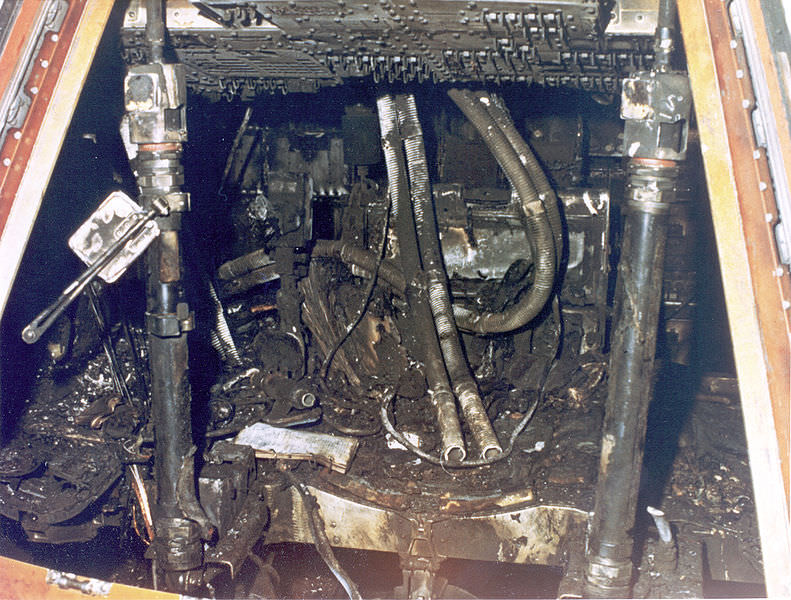
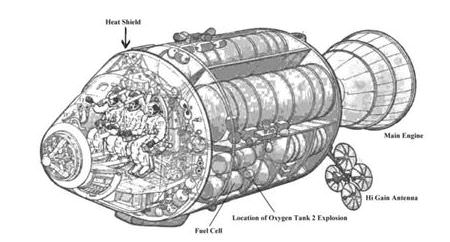
When the oxygen tank in Apollo 13’s Service Module exploded, the Lunar Module “Aquarius” played an unexpected role in saving the lives of the three astronauts, serving as a lifeboat to return the astronauts safely back to Earth. Additionally, its descent stage engine was used for propulsion, and its batteries supplied power for the trip home while recharging the Command Module’s batteries critical for re-entry. And with ingenuity of Mission Control the LM’s life support system – which was originally designed to support two astronauts for 45 hours, — was stretched to support three astronauts for 90 hours.
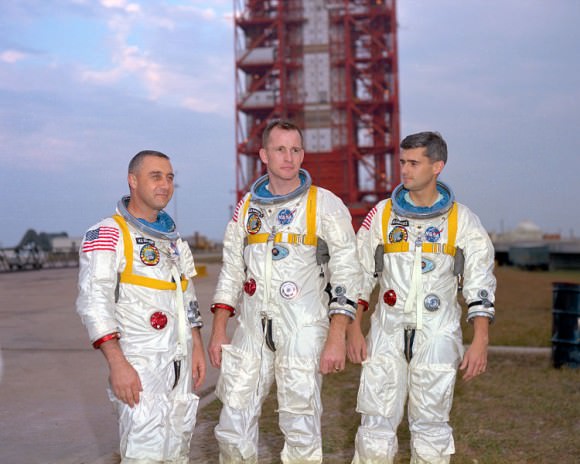
Imagine, Woodfill said, if Apollo 13 had been a single vehicle employing the Direct Ascent approach. “After the explosion and subsequent loss of the fuel cells, only those entry batteries would have been available to sustain life. Their life, even if all systems except life support, were turned off would be less than 24 hours. And Lovell, Swigert and Haise along with Apollo 13 would return to Earth on that “free-return-trajectory” being cremated in the fiery heat of reentry. But for the clever Lunar Orbit Rendezvous approach, Apollo 13 would have been a casket. Instead, its lunar lander became a wonderful lifeboat” Woodfill said.
Next: Part 13: Houston
Earlier articles from the “13 Things That Saved Apollo 13” series:
Part 2: The Hatch That Wouldn’t Close
Part 3: Charlie Duke’s Measles
Part 4: Using the LM for Propulsion
Part 5: Unexplained Shutdown of the Saturn V Center Engine
Part 6: Navigating by Earth’s Terminator
Part 8: The Command Module Wasn’t Severed
Part 12: Lunar Orbit Rendezvous
Part 13: The Mission Operations Team
Also:
Your Questions about Apollo 13 Answered by Jerry Woodfill (Part 1)
More Reader Questions about Apollo 13 Answered by Jerry Woodfill (part 2)
Final Round of Apollo 13 Questions Answered by Jerry Woodfill (part 3)
Never Before Published Images of Apollo 13’s Recovery
Listen to an interview of Jerry Woodfill on the 365 Days of Astronomy podcast.