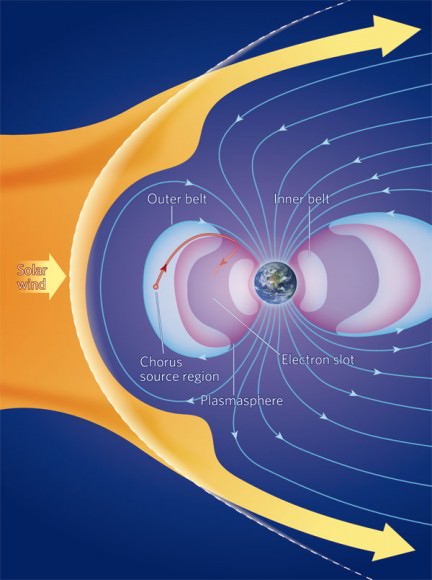
Video Caption: EVE rediscovered the Van Allen Radiation Belt. These EVE data highlight where the energetic protons are in the inner Van Allen radiation belt. The red dots indicate the highest concentration of protons (lower altitude), and the blue-violet dots represents very little detection of particles (higher altitude of GEO). Visualization by Chris Jeppesen.
Following several precise propulsion burns to circularize its orbit, NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) has arrived “On Station” and multiple tasks critical to check out of the science instruments are in progress this week, according to Dean Pesnell. Pesnell is the SDO project scientist from NASA’s Goddard Spaceflight Center which built the spacecraft and manages the nearly $1 Billion mission for NASA.
“We reached our final orbit on March 16, 2010”, Pesnell told me in an interview. “The SDO spacecraft is working great and all systems are behaving as expected”. SDO was launched on Feb. 11, 2010 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station aboard an Atlas V rocket.
[/caption]
The revolutionary science mission has been dubbed the “crown jewel” of NASA’s Solar Exploration research fleet, joining the twin STEREO spacecraft and SOHO. SDO is equipped with three science instruments (HMI, AIA, and EVE) to explore the Sun and its complex interior mechanisms in unprecedented detail.
Although the doors to the solar science payload will be opened starting just today (March 24), SDO has already managed to transmit its “first data”, Pesnell explained. This bonus science data from Earth’s radiation belt was unexpected he said. The first solar light data will come after the science instruments are fully activated.
“The amount of proton data was not expected as we were not supposed to spend as much time in the belts as we did. By spending a few extra days in the inner belt the MEGS-P radiometer was able to measure a more complete picture of the radiation belt. It may be the only measurement of the proton fluxes in the inner radiation belt during the extremely low solar activity of the current solar minimum,” added Pesnell.
Check out of the science payload is moving ahead swiftly as planned. “The SDO instruments are working through their initial steps to turning them completely on”, Pesnell explained. A key activity was to “bake out” the instruments to remove any remaining harmful contaminants that could threaten to degrade the quality of the science data.
“CCD decontamination heaters had been turned on for several weeks to allow the instruments to outgas any residual contamination”, according to Pesnell. “During the first 40 days of the mission the instruments kept their CCDs hot with heaters. This prevents water vapor from condensing onto the surfaces of the CCDs while forcing water vapor out of the interior of the instruments. Two instruments, HMI and EVE, have turned off their decontamination heaters while AIA will turn them off next week. Those heaters are being turned off to allow the CCD’s to cool to their normal operating temperatures of about minus 100 C”.
“HMI will open their payload door Wednesday and begin checking out the instrument. EVE is cooling their CCDs getting ready to open their doors on Thursday. AIA will open their doors on Saturday”.
Pesnell mentioned that the SDO team expects to show off the initial data at a telecom in mid-April. “The science data should start to flow in early May, fully calibrated data will show up later. We will discuss the data at the SPD/AAS meeting in Miami, FL at the end of May”.
SDO will collect a staggering 1.5 terabytes of data per day, equivalent to 380 full length movies per day on a 24/7 basis. “The data will be continuously beamed back to newly built receivers on Earth. We have no onboard recorders since nothing is available to handle such a huge data volume,” said Pesnell. “SDO will transmit 50 times more science data than any other mission in NASA history”.
Test data have already been transmitted via the spacecraft antenna to the receiving station on the ground in New Mexico, confirming that the vital communications systems are operating perfectly.
SDO’s measurements of the Sun’s interior, magnetic field and hot plasma of the solar corona will allow scientists to determine how violent solar events are created which then cause ‘space weather’ that ultimately affects every aspect of life here on Earth. The goal is create better predictions of ‘space weather’ in order to provide early warning to valuable satellites and astronauts operating in space, and to prevent disruption to navigation systems and failures in the power grid.
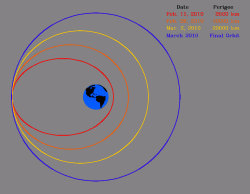
“SDO is in an inclined geosynchronous orbit at the longitude of New Mexico. The inclination of 28 degrees is the natural orbit when launched from Kennedy Space Center. Changing the inclination of an orbit requires a lot of fuel, so this orbit was less expensive than a geostationary orbit,” said Pesnell. This orbit will keep the observatory in constant view of the two newly constructed 18-meter dishes around the clock so that not a single bit of data should be lost.
Nancy Atkinson and Ken Kremer covered the Feb 11, 2010 SDO launch on site at KSC for Universe Today
Read SDO launch report by Nancy Atkinson here.
Read earlier SDO reports by Ken Kremer below, including from on site at the Atlas launch pad
NASA Sun Probe rolled to Pad; 10 hours to Blast off
NASA’s Solar Crown Jewel Bolted atop Atlas Rocket
NASA advanced Solar Observatory nearing February launch; will send IMAX like movies daily
Learn more at the NASA SDO Website