Some proponents of human missions to Mars say we have the technology today to send people to the Red Planet. But do we? Rob Manning of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory discusses the intricacies of entry, descent and landing and what needs to be done to make humans on Mars a reality.
There’s no comfort in the statistics for missions to Mars. To date over 60% of the missions have failed. The scientists and engineers of these undertakings use phrases like “Six Minutes of Terror,” and “The Great Galactic Ghoul” to illustrate their experiences, evidence of the anxiety that’s evoked by sending a robotic spacecraft to Mars — even among those who have devoted their careers to the task. But mention sending a human mission to land on the Red Planet, with payloads several factors larger than an unmanned spacecraft and the trepidation among that same group grows even larger. Why?
Nobody knows how to do it.
Surprised? Most people are, says Rob Manning the Chief Engineer for the Mars Exploration Directorate and presently the only person who has led teams to land three robotic spacecraft successfully on the surface of Mars.
“It turns out that most people aren’t aware of this problem and very few have worried about the details of how you get something very heavy safely to the surface of Mars,” said Manning.
He believes many people immediately come to the conclusion that landing humans on Mars should be easy. After all, humans have landed successfully on the Moon and we can land our human-carrying vehicles from space to Earth. And since Mars falls between the Earth and the Moon in size, and also in the amount of atmosphere it has then the middle ground of Mars should be easy. “There’s the mindset that we should just be able to connect the dots in between,” said Manning.
But as of now, the dots will need to connect across a large abyss.
“We know what the problems are. I like to blame the god of war,” quipped Manning. “This planet is not friendly or conducive for landing.”
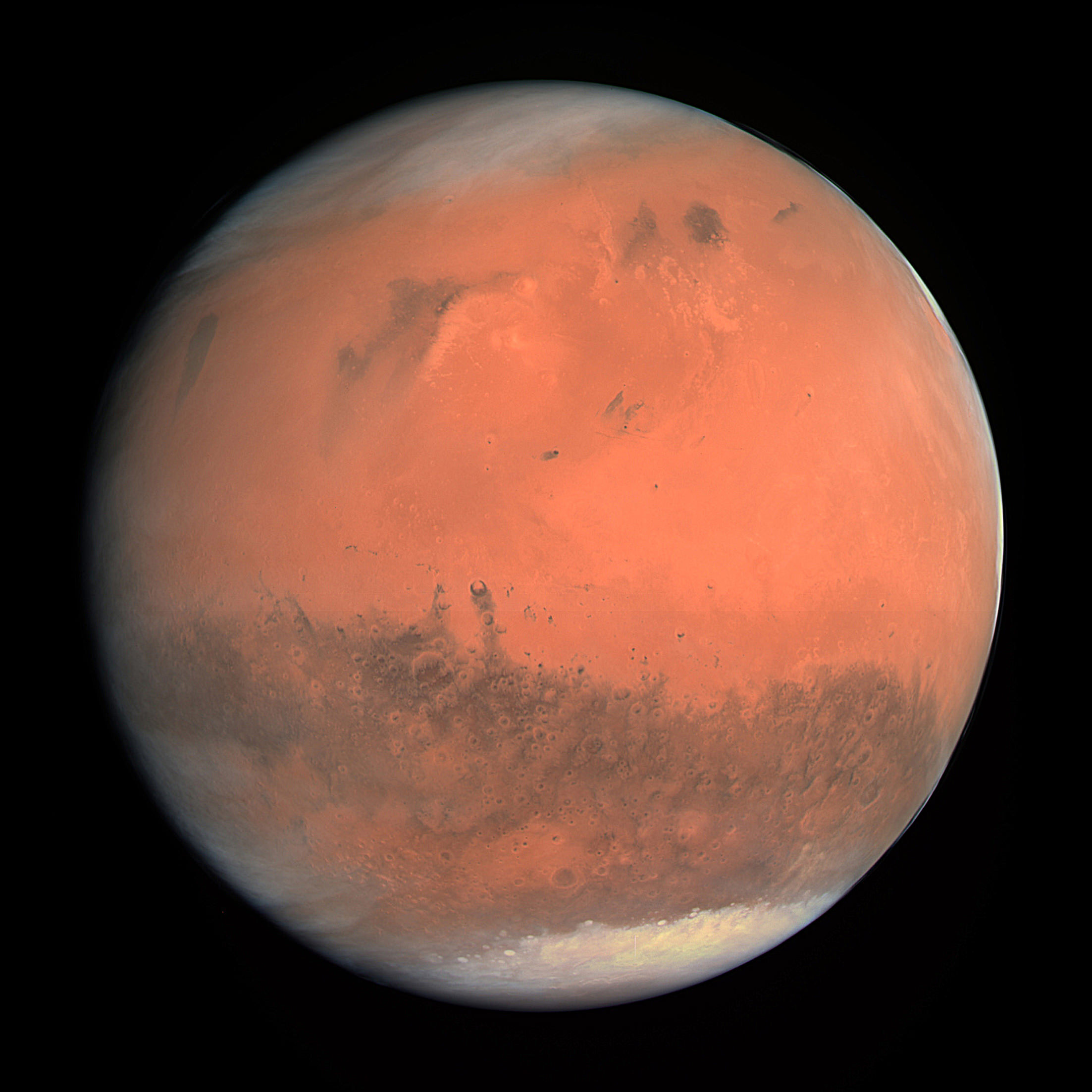
The real problem is the combination of Mars’ atmosphere and the size of spacecraft needed for human missions. So far, our robotic spacecraft have been small enough to enable at least some success in reaching the surface safely. But while the Apollo lunar lander weighed approximately 10 metric tons, a human mission to Mars will require three to six times that mass, given the restraints of staying on the planet for a year. Landing a payload that heavy on Mars is currently impossible, using our existing capabilities. “There’s too much atmosphere on Mars to land heavy vehicles like we do on the moon, using propulsive technology completely,” said Manning, “and there’s too little atmosphere to land like we do on Earth. So, it’s in this ugly, grey zone.”
But what about airbags, parachutes, or thrusters that have been used on the previous successful robotic Mars missions, or a lifting body vehicle similar to the space shuttle?
None of those will work, either on their own or in combination, to land payloads of one metric ton and beyond on Mars. This problem affects not only human missions to the Red Planet, but also larger robotic missions such as a sample return. “Unfortunately, that’s where we are,” said Manning. “Until we come up with a whole new trick, a whole new system, landing humans on Mars will be an ugly and scary proposition.”
Road Mapping
In 2004 NASA organized a Road Mapping session to discuss the current capabilities and future problems of landing humans on Mars. Manning co-chaired this event along with Apollo 17 astronaut Harrison Schmitt and Claude Graves, who has since passed away, from the Johnson Space Center. Approximately 50 other people from across NASA, academia and industry attended the session. “At that time the ability to explain these problems in a coherent way was not as good,” said Manning. “The entry, descent and landing process is actually made up of people from many different disciplines. Very few people really understood, especially for large scale systems, what all of the issues were. At the Road Mapping session we were able to put them all down and talk about them.”
The major conclusion that came from the session was that no one has yet figured out how to safely get large masses from speeds of entry and orbit down to the surface of Mars. “We call it the Supersonic Transition Problem,” said Manning. “Unique to Mars, there is a velocity-altitude gap below Mach 5. The gap is between the delivery capability of large entry systems at Mars and the capability of super-and sub-sonic decelerator technologies to get below the speed of sound.”
Plainly put, with our current capabilities, a large, heavy vehicle, streaking through Mars’ thin, volatile atmosphere only has about ninety seconds to slow from Mach 5 to under Mach 1, change and re-orient itself from a being a spacecraft to a lander, deploy parachutes to slow down further, then use thrusters to translate to the landing site and finally, gently touch down.
No Airbags
When this problem is first presented to people, the most offered solution, Manning says, is to use airbags, since they have been so successful for the missions that he has been involved with; the Pathfinder rover, Sojourner and the two Mars Exploration Rovers (MER), Spirit and Opportunity.
But engineers feel they have reached the capacity of airbags with MER. “It’s not just the mass or the volume of the airbags, or the size of the airbags themselves, but it’s the mass of the beast inside the airbags,” Manning said. “This is about as big as we can take that particular design.”
In addition, an airbag landing subjects the payload to forces between 10-20 G’s. While robots can withstand such force, humans can’t. This doesn’t mean airbags will never be used again, only that airbag landings can’t be used for something human or heavy.
Even the 2009 Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) rover, weighing 775 kilograms (versus MER at 175.4 kilograms each) requires an entirely new landing architecture. Too massive for airbags, the small-car sized rover will use a landing system dubbed the Sky Crane. “Even though some people laugh when they first see it, my personal view is that the Sky Crane is actually the most elegant system we’ve come up with yet, and the simplest,” said Manning. MSL will use a combination of a rocket-guided entry with a heat shield, a parachute, then thrusters to slow the vehicle even more, followed by a crane-like system that lowers the rover on a cable for a soft landing directly on its wheels. Depending on the success of the Sky Crane with MSL, it’s likely that this system can be scaled for larger payloads, but probably not the size needed to land humans on Mars.
Atmospheric Anxiety and Parachute Problems
“The great thing about Earth,” said Manning “is the atmosphere.” Returning to Earth and entering the atmosphere at speeds between 7-10 kilometers per second, the space shuttle, Apollo and Soyuz capsules and the proposed Crew Exploration Vehicle (CEV) will all decelerate to less than Mach 1 at about twenty kilometers above the ground just by skimming through Earth’s luxuriously thick atmosphere and using a heat shield. To reach slower speeds needed for landing, either a parachute is deployed, or in the case of the space shuttle, drag and lift allow the remainder of the speed to bleed away.
But Mars’ atmosphere is only one per cent as dense as Earth’s. For comparison, Mars atmosphere at its thickest is equivalent to Earth’s atmosphere at about 35 kilometers above the surface The air is so thin that a heavy vehicle like a CEV will basically plummet to the surface; there’s not enough air resistance to slow it down sufficiently. Parachutes can only be opened at speeds less than Mach 2, and a heavy spacecraft on Mars would never go that slow by using just a heat shield. “And there are no parachutes that you could use to slow this vehicle down,” said Manning. “That’s it. You can’t land a CEV on Mars unless you don’t mind it being a crater on the surface.”
That’s not good news for the Vision for Space Exploration. Would a higher lift vehicle like the space shuttle save the day? “Well, on Mars, when you use a very high lift to weight to drag ratio like the shuttle,” said Manning, “in order to get good deceleration and use the lift properly, you’d need to cut low into the atmosphere. You’d still be going at Mach 2 or 3 fairly close to the ground. If you had a good control system you could spread out your deceleration to lengthen the time you are in the air. You’d eventually slow down to under Mach 2 to open a parachute, but you’d be too close to the ground and even an ultra large supersonic parachute would not save you.”
Supersonic parachute experts have concluded that to sufficiently slow a large shuttle-type vehicle on Mars and reach the ground at reasonable speeds would require a parachute one hundred meters in diameter.
“That’s a good fraction of the Rose Bowl. That’s huge,” said Manning. “We believe there’s no way to make a 100-meter parachute that can be opened safely supersonically, not to mention the time it takes to inflate something that large. You’d be on the ground before it was fully inflated. It would not be a good outcome.”
Heat Shields and Thrusters
It’s not that Mars’ atmosphere is useless. Manning explained that with robotic spacecraft, 99% of the kinetic energy of an incoming vehicle is taken away using a heat shield in the atmosphere. “It’s not inconceivable that we can design larger, lighter heat shields,” he said, “but the problem is that right now the heat shield diameter for a human-capable spacecraft overwhelms any possibility of launching that vehicle from Earth.” Manning added that it would almost be better if Mars were like the moon, with no atmosphere at all.
If that were the case, an Apollo-type lunar lander with thrusters could be used. “But that would cause another problem,” said Manning, “in that for every kilogram of stuff in orbit, it takes twice as much fuel to get to the surface of Mars as the moon. Everything is twice as bad since Mars is about twice as big as the moon.” That would entail a large amount of fuel, perhaps over 6 times the payload mass in fuel, to get human-sized payloads to the surface, all of which would have to be brought along from Earth. Even on a fictitious air-less Mars that is not an option.
But using current thruster technology in Mars’ real, existing atmosphere poses aerodynamic problems. “Rocket plumes are notoriously unstable, dynamic, chaotic systems,” said Manning. “Basically flying into the plume at supersonics speeds, the rocket plume is acting like a nose cone; a nose cone that’s moving around in front of you against very high dynamic pressure. Even though the atmospheric density is very low, because the velocity is so high, the forces are really huge.”
Manning likened theses forces to a Category Five hurricane. This would cause extreme stress, with shaking and twisting that would likely destroy the vehicle. Therefore using propulsive technology alone is not an option.
Using thrusters in combination with a heat shield and parachute also poses challenges. Assuming the vehicle has used some technique to slow to under Mach 1, using propulsion just in last stages of descent to gradually adjust the lander’s trajectory would enable the vehicle to arrive very precisely at the desired landing site. “We’re looking at firing thrusters less than 1 kilometer above the ground. Your parachute has been discarded, and you see that you are perhaps 5 kilometers south of where you want to land,” said Manning. “So now you need the ability to turn the vehicle over sideways to try to get to your landing spot. But this may be an expensive option, adding a large tax in fuel to get to the desired landing rendezvous point.”
Additionally, on the moon, with no atmosphere or weather, there is nothing pushing against the vehicle, taking it off target, and a la Neil Armstrong on Apollo 11, the pilot can “fly out the uncertainties” as Manning called it, to reach a suitable or desired landing site. On Mars, however, the large variations in the density of the atmosphere coupled with high and unpredictable winds conspire to push vehicles off course. “We need to have ways to fight those forces or ways to make up for any mis-targeting using the propulsion system,” said Manning. “Right now, we don’t have that ability and we’re a long way from making it happen.”
Supersonic Decelerators
The best hope on the horizon for making the human enterprise on Mars possible is a new type of supersonic decelerator that’s only on the drawing board. A few companies are developing a new inflatable supersonic decelerator called a Hypercone.
Imagine a huge donut with a skin across its surface that girdles the vehicle and inflates very quickly with gas rockets (like air bags) to create a conical shape. This would inflate about 10 kilometers above the ground while the vehicle is traveling at Mach 4 or 5, after peak heating. The Hypercone would act as an aerodynamic anchor to slow the vehicle to Mach 1.
Glen Brown, Chief Engineer at Vertigo, Inc. in Lake Elsinore, California was also a participant in the Mars Road Mapping session. Brown says Vertigo has been doing extensive analysis of the Hypercone, including sizing and mass estimates for landers from four to sixty metric tons. “A high pressure inflatable structure in the form a of a torus is a logical way to support a membrane in a conical shape, which is stable and has high drag at high Mach numbers,” Brown said, adding that the structure would likely be made of a coated fabric such as silicon-Vectran matrix materials. Vertigo is currently competing for funding from NASA for further research, as the next step, deployment in a supersonic wind tunnel, is quite expensive.
The structure would need to be about thirty to forty meters in diameter. The problem here is that large, flexible structures are notoriously difficult to control. At this point in time there are also several other unknowns of developing and using a Hypercone.
One train of thought is that if the Hypercone can get the vehicle under Mach 1, then subsonic parachutes could be used, much like the ones employed by Apollo, or that the CEV is projected to use to land on Earth. However, it takes time for the parachutes to inflate, and subsequently there would only be a matter of seconds of use, allowing time to shed the parachutes before converting to a propulsive system.
“You’d also need to use thrusters,” said Manning. “You’re falling 10 times faster because the density of Mars’ atmosphere is 100 times less than Earth’s. That means that you can’t just land with parachutes and touch the ground. You’d break people’s bones, if not the hardware. So you need to transition from a parachute system to an Apollo-like lunar legged lander sometime before you get to the ground.”
Manning believes that those who are immersed in these matters, like himself, see the various problems fighting each other. “It’s hard to get your brain around all these problems because all the pieces connect in complex ways,” he said. “It’s very hard to see the right answer in your mind’s eye.”
The additional issues of creating new lightweight but strong shapes and structures, with the ability to come apart and transform from one stage to another at just the right time means developing a rapid-fire Rube Goldberg-like contraption.
“The honest truth of the matter,” said Manning, “is that we don’t have a standard canonical form, a standard configuration of systems that allows us to get to the ground, with the right size that balances the forces, the loads, the people, and allows us to do all the transformation that needs to be done in the very small amount of time that we have to land.”
Other Options and Issues
Another alternative discussed at the 2004 Mars Road Mapping session was the space elevator.
“Mars is really begging for a space elevator,” said Manning. “I think it has great potential. That would solve a lot of problems, and Mars would be an excellent platform to try it.” But Manning admitted that the technology needed to suspend a space elevator has not yet been invented. The issues with space elevator technology may be vast, even compared with the challenges of landing.
Despite these known obstacles, there are few at NASA currently spending any quality time working on any of the issues of landing humans on Mars.
Manning explained, “NASA does not yet have the resources to solve this problem and also develop the CEV, complete the International Space Station and do the lunar landing systems development at the same time. But NASA knows that this is on its plate of things to do in the future and is just beginning to get a handle on the needed technology developments. I try to go out of my way to tell this story because I’m encouraging young aeronautical engineering students, particularly graduate students, to start working on this problem on their own. There is no doubt in my mind that with their help, we can figure out how to make reliable human-scale landing systems work on Mars.”
While there is much interest throughout NASA and the space sector to try to tackle these issues in the ensuing years, technology also needs a few more years to catch up to our dreams of landing humans on Mars.
And this story, like all good engineering stories, will inevitably read like a good detective novel with technical twist and turns, scientific intrigue, and high adventure on another world.



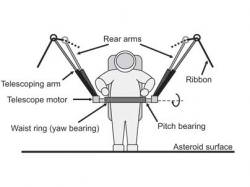





 Current spacesuit designs can weigh up to 136 kg (300 pounds), and are so restrictive to movement, that astronauts will spend the majority of their energy just working against the suit to bend it. A fabric-based design would be much more flexible and give astronauts a freedom of movement. Another advantage is safety. Even the slightest tear on a spacesuit will compromise its atmosphere, while a fabric suit can be easily patched up. To deal with the temperature extremes, astronauts could just put on and take off specially designed clothing.
Current spacesuit designs can weigh up to 136 kg (300 pounds), and are so restrictive to movement, that astronauts will spend the majority of their energy just working against the suit to bend it. A fabric-based design would be much more flexible and give astronauts a freedom of movement. Another advantage is safety. Even the slightest tear on a spacesuit will compromise its atmosphere, while a fabric suit can be easily patched up. To deal with the temperature extremes, astronauts could just put on and take off specially designed clothing.