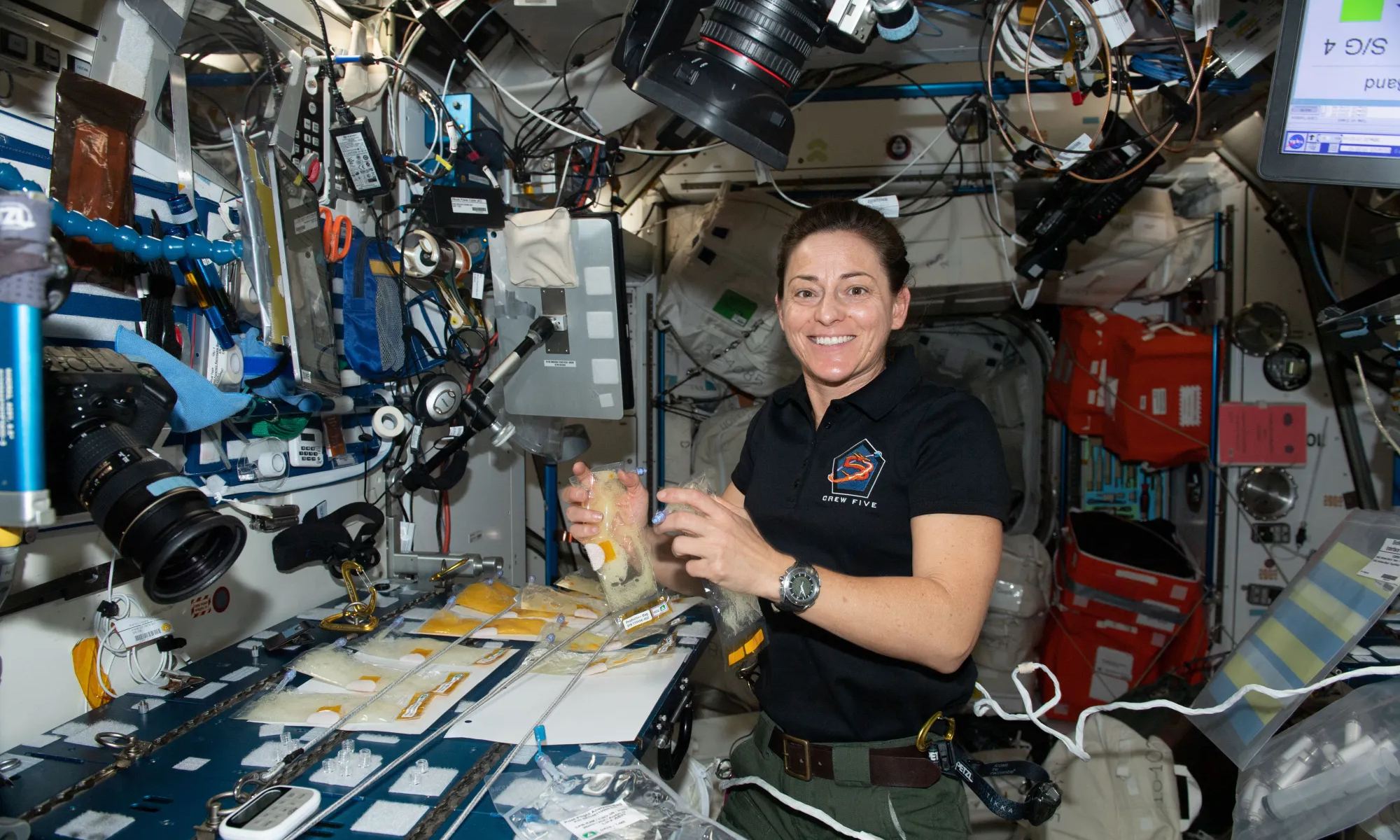
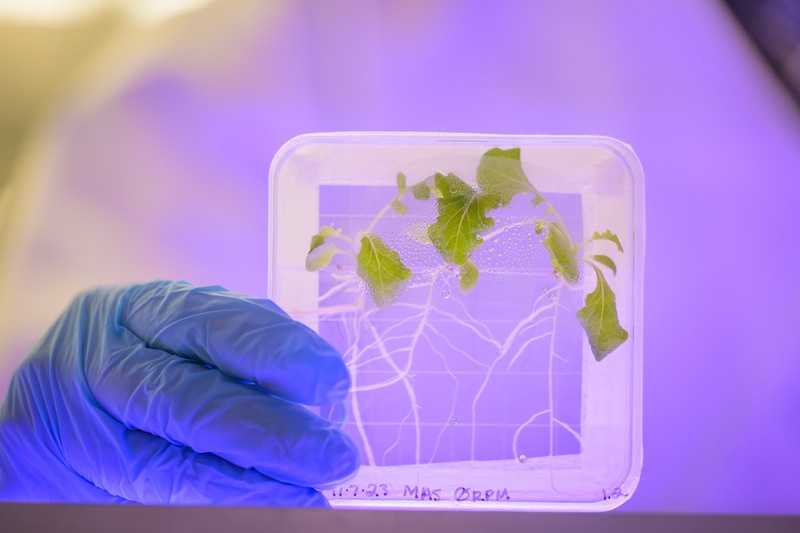
Astronauts on board the International Space Station are often visited by supply ships from Earth with food among other things. Take a trip to Mars or other and the distances are much greater making it impractical to send fresh supplies. The prepackaged food used by NASA loses nutritional value over time so NASA is looking at ways astronauts can produce nutrients. They are exploring genetic engineering techniques that can create microbes with minimal resource usage.
Continue reading “Astronaut Food Will Lose Nutrients on Long-Duration Missions. NASA is Working on a Fix”Astronaut Food Will Lose Nutrients on Long-Duration Missions. NASA is Working on a Fix