Nearly twelve hours after the threat of a leak of toxic ammonia forced the crew into a middle of the night evacuation from the US side of the International Space Station this morning (Jan. 14) and a hatch closure, top level managers from the partner space agencies gave the all clear and allowed the astronauts and cosmonauts to reopen access to the American portion of the orbiting outpost.
The six person crew hailing from the US, Italy and Russia were allowed to open the sealed hatch to the U.S. segment later this afternoon after it was determined that the ammonia leak was quite fortunately a false alarm.
No ammonia leak was actually detected. But the crew and mission control had to shut down some non essential station systems on the US segment in the interim.
All the Expedition 42 crew members were safe and in good health and never in danger, reported NASA.
The station crews and mission control teams must constantly be prepared and train for the unexpected and how to deal with potential emergencies, such as today’s threat of a serious chemical leak.
After a thorough review of the situation by the International Space Station mission management team, the crew were given the OK by flight controllers to head back.
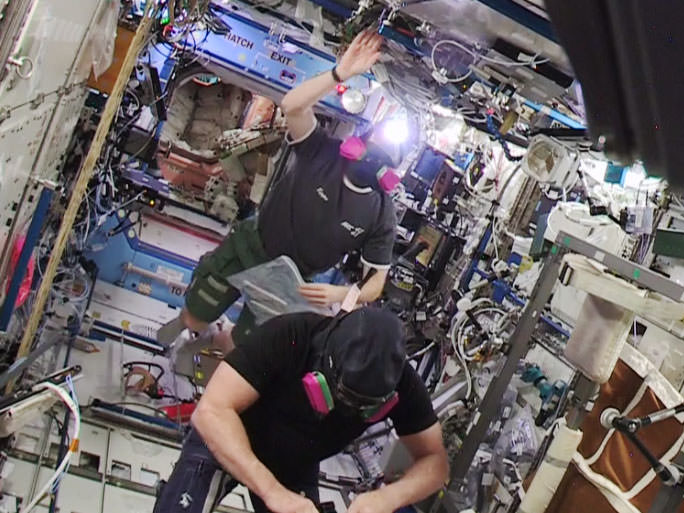
They returned inside at 3:05 p.m. EST. Taking no chances, they wore protective masks and sampled the cabin atmosphere and reported no indications of any ammonia.
Fears that a leak had been detected resulted from the sounding of an alarm at around 4 a.m. EST.
The alarm forced Expedition 42 station commander Barry Wilmore and Flight Engineer Terry Virts of NASA and Flight Engineer Samantha Cristoforetti of the European Space Agency to don protective gas masks and move quickly into the Russian segment, sealing the hatch behind them to the US segment.
Inside the Russian segment, they joined the remainder of Expedition 42, namely cosmonauts Aleksandr Samokutyayev, Yelena Serova, and Anton Shkaplerov from Russia, also living and working aboard the ISS and rounding out the crew of four men and two women.

“The alarm is part of the environmental systems software on the station designed to monitor the cabin’s atmosphere. At the same time, the station’s protection software shut down one of two redundant cooling loops (Thermal Control System Loop B),” NASA said in an update.
Ammonia is a toxic substance used as a coolant in the stations complex cooling system that is an essential requirement to continued operation of the station.
Ammonia is a gas at room temperature that is extremely dangerous to inhale or when it comes in contact with skin, eyes and internal organs.
Precautions must be taken if a leak is feared in a confined space such as the ISS. It has about the same habitable volume as a four bedroom house.
As a professional chemist, I’ve worked frequently with ammonia in research and development labs and manufacturing plants and know the dangers firsthand. It can cause severe burns and irritations and worse.
There have been prior ammonia leaks aboard the ISS facility that forced a partial evacuation similar to today’s incident.
The ISS has been continuously occupied by humans for 15 years.
In the case of a life threatening emergency, the crew can rapidly abandon the station aboard the two docked Russian Soyuz capsules. They hold three persons each and serve as lifeboats.
Fortunately, the perceived ammonia leak this morning was not real and apparently was caused by a false alarm.
“This morning’s alarm is suspected to have been caused by a transient error message in one of the station’s computer relay systems, called a multiplexer-demultiplexer. A subsequent action to turn that relay box off and back on cleared the error message and the relay box is reported by flight controllers to be in good operating condition,” according to a NASA statement.
“Meanwhile, flight controllers are continuing to analyze data in an effort to determine what triggered the alarm that set today’s actions in motion.”
“Work to reactivate cooling loop B on the station will continue throughout the night and into the day Thursday. The crew members are expected to resume a normal complement of research activities on Thursday as well.”
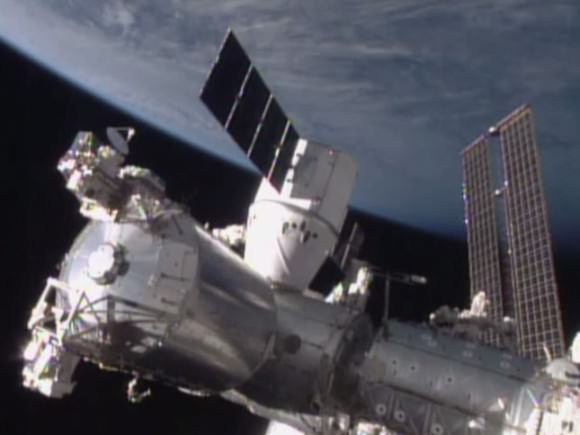

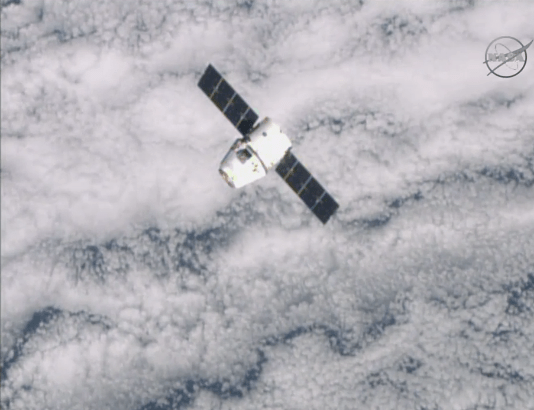
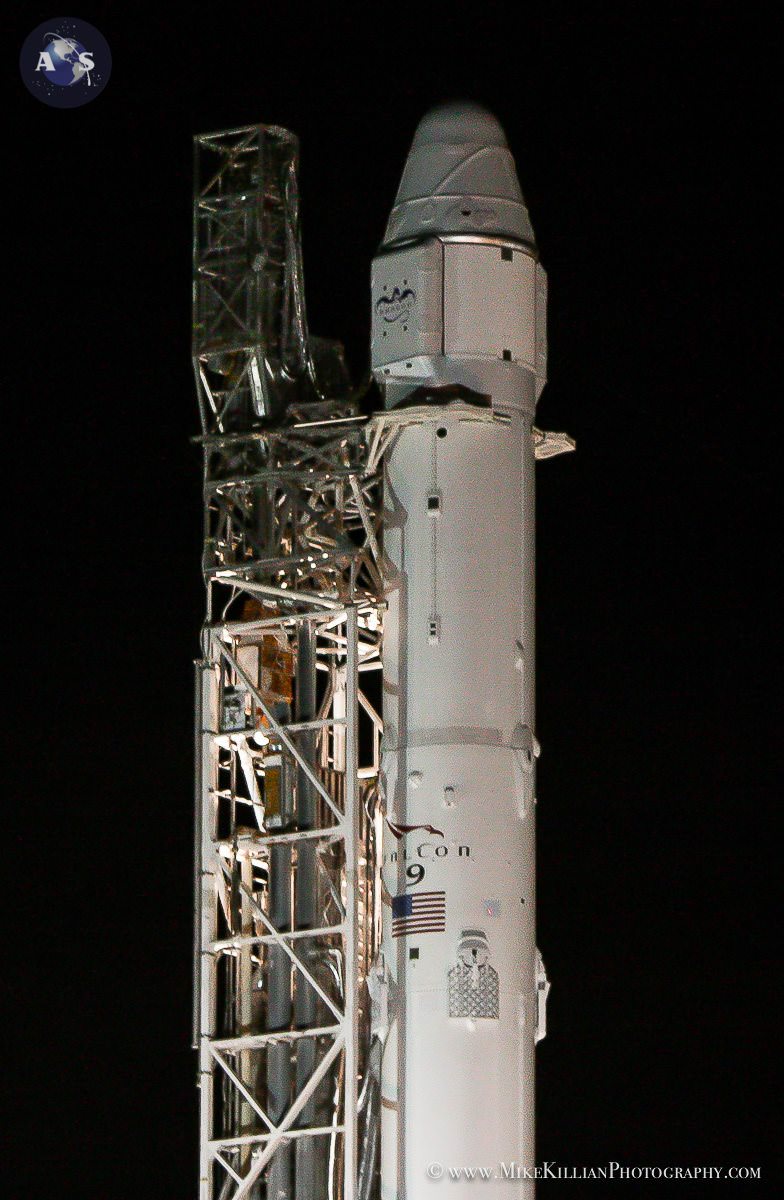
The evacuation came just two days after a commercial SpaceX Dragon cargo freighter successfully rendezvoused and berthed at the station on Monday, Jan. 12.
The crew had just opened the hatch to Dragon and begun unloading the goodies stored aboard.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.