Trekking Mars – NASA’s intrepid robot Curiosity is roving rapidly across the sandy ripples of the Red Planet in her quest to reach mysterious Mount Sharp and just drove outside her landing ellipse!
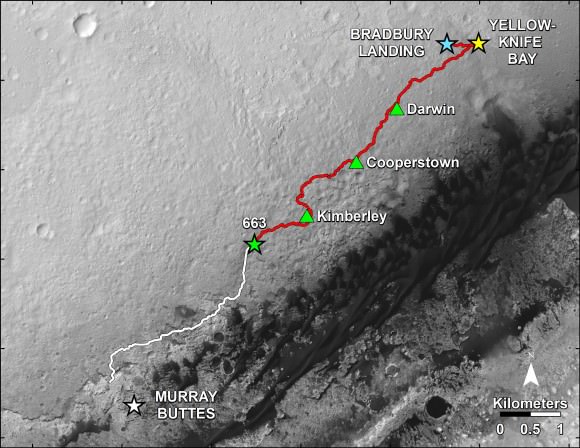
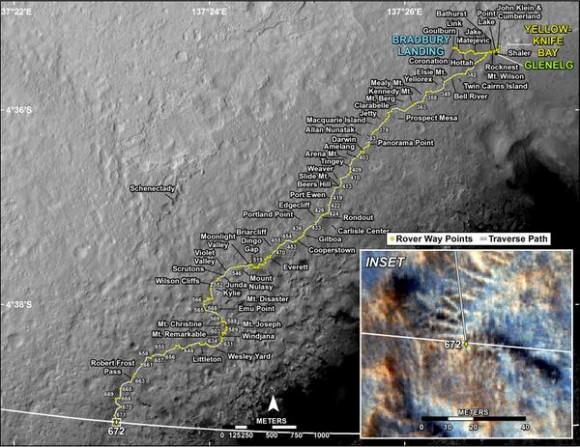
The six wheeled rover marked a major milestone on Sol 672, June 27, 2014, by traversing beyond her targeted landing ellipse for the first time since touchdown on Mars nearly two years ago on August 5, 2012.
“On yestersol’s drive [June 27], I left my landing ellipse—the 20×25 km area I targeted for landing,” Curiosity tweeted across interplanetary space.
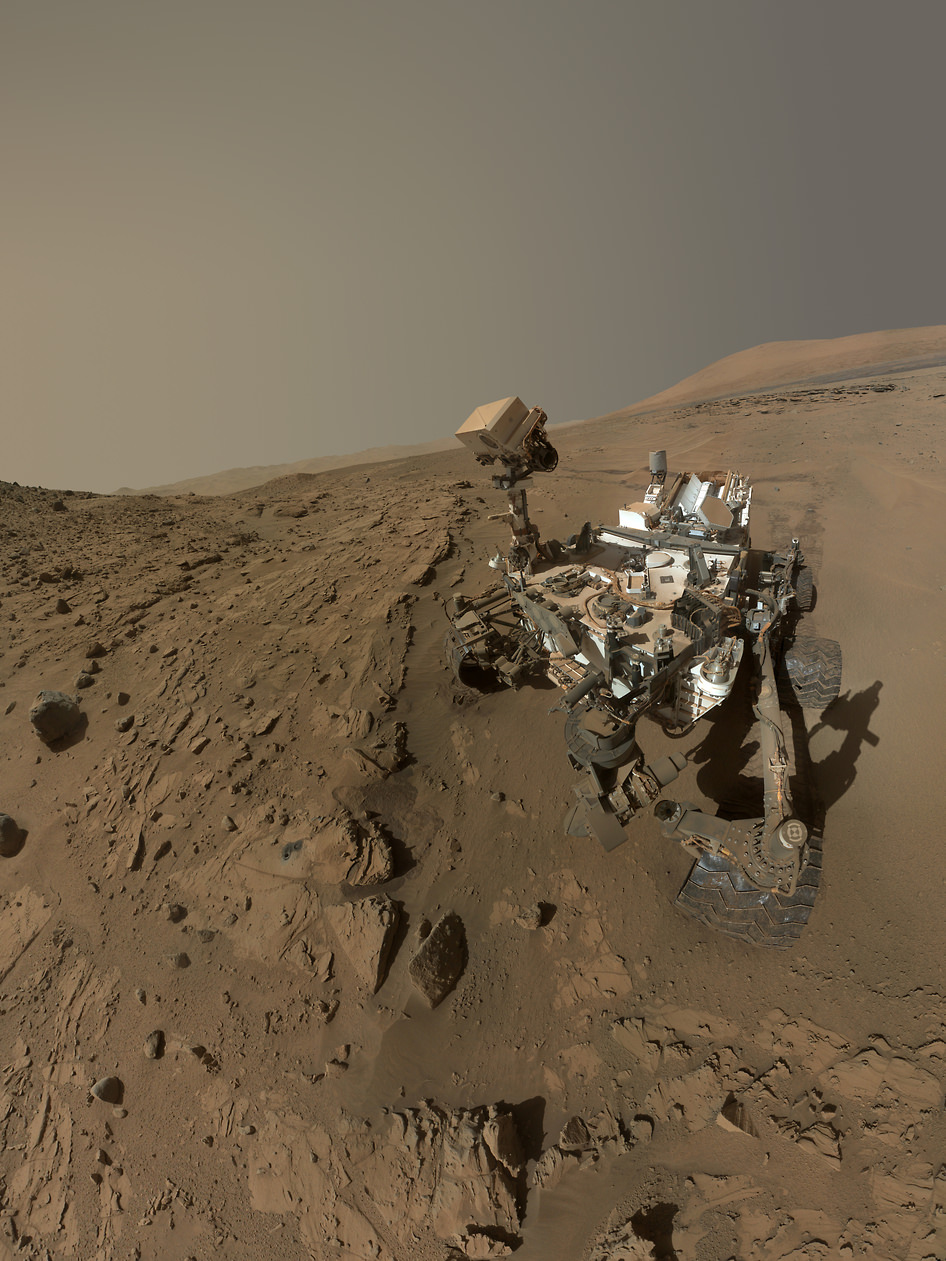
See our new Sol 672 photo mosaic above showing Curiosity’s glorious view marking this major achievement just days ago.
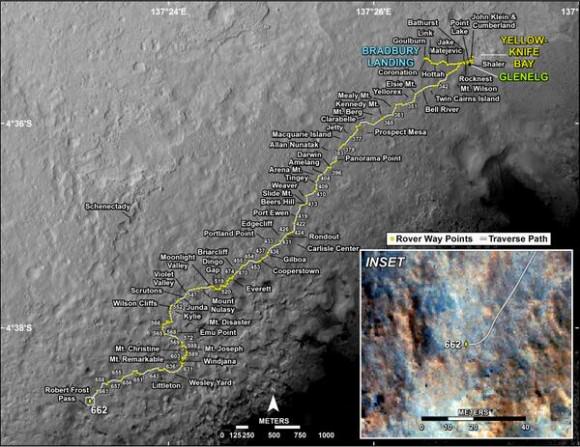
Since switching paths to smoother, sandier terrain with less sharp edged rocks, Curiosity continues rolling across the floor of her Gale Crater landing site, pausing occasionally for potentially dicey dunes.
“After traversing 82 meters the rover stopped because it determined that it was slipping too much,” wrote mission scientist Ken Herkenhoff in an update.
“Coincidentally, the rover stopped right on the landing ellipse, a major mission milestone!”

Curiosity treks to Mount Sharp in this photo mosaic view captured on Sol 669, June 24, 2014. Navcam camera raw images stitched and colorized. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer – kenkremer.com
“The vehicle was designed to be able to traverse far enough to drive out of the region defined by the uncertainty in the landing location, and has now achieved that laudable goal,” Herkenhoff confirmed.
The SUV sized rover automatically stopped when it encountered soft sand and sensed that it wasn’t making enough progress. It’s been programmed with this built in safety check to avoid being trapped in a quagmire of quicksand.
Earlier last week, Curiosity celebrated another milestone anniversary on June 24 (Sol 669) – 1 Martian Year on Mars!
A Martian year is equivalent to 687 Earth days, or nearly two Earth years.
See our Sol 669 photo mosaic marking 1 Mars Year on Mars – above.
During Year 1 on Mars, Earth’s emissary has already accomplished her primary objective of discovering a habitable zone on the Red Planet that contains the minerals necessary to support microbial life in the ancient past.
So there’s no stopping Curiosity on her way to Mount Sharp, which dominates the center of Gale Crater and reaches 3.4 miles (5.5 km) into the Martian sky – taller than Mount Rainier.
Driving, Driving, Driving – that’s Curiosity’s number one priority as she traverses across the surface of Gale Crater towards towering Mount Sharp on an expedition in search of the chemical ingredients of life that could support Martian microbes if they ever existed.
Curiosity still has about another 2.4 miles (3.9 kilometers) to go to reach the entry way at a gap in the dunes at the foothills of Mount Sharp sometime later this year.

To date, Curiosity’s odometer totals over 5.1 miles (8.4 kilometers) since landing inside Gale Crater on Mars in August 2012. She has taken over 162,000 images.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Curiosity, Opportunity, Orion, SpaceX, Boeing, Orbital Sciences, commercial space, MAVEN, MOM, Mars and more planetary and human spaceflight news.