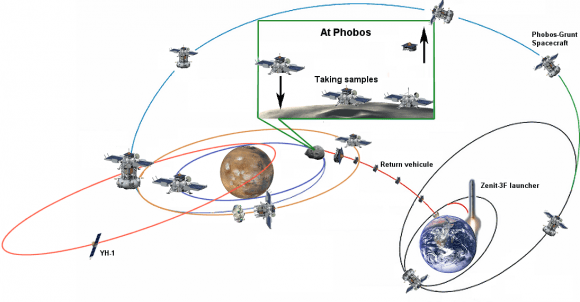
[/caption]
Solar sails, much like anti-matter and ion engines appear at first glance to only exist in science fiction. Many technologies from science fiction however, become science fact.
In the example of solar sails, perfecting the technology would allow spacecraft to travel through our solar system using very little fuel.
NASA has been making strides with solar sail technology. Using the NanoSail-D mission, NASA continues to gather valuable data on how well solar sails perform in space. The Planetary Society will also be testing solar sail technology with their LightSail-1 project sometime next year.
How will NASA (and others) test solar sail technology, and develop it into a common, reliable technology?
The second of three recently announced technology demonstrations, The Solar Sail Demonstration, will test the deployment of a solar sail in space along with testing attitude control. The solar sail will also execute a navigation sequence with mission-capable accuracy.
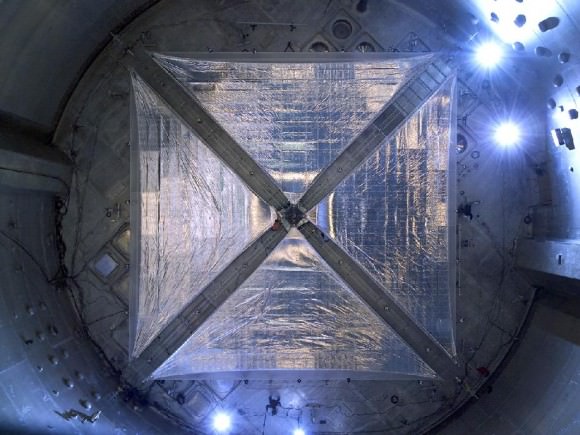
In order to make science fiction into reality, NASA engineers are testing solar sails that could one day provide the propulsion for deep space missions. Spacecraft using solar sails would travel in our solar system in a similar manner to a sailboat through water, except spacecraft using solar sails would rely on sunlight instead of wind. A spacecraft propelled by a solar sail would use the sail to capture photons emitted from the Sun. Over time, the buildup of the solar photons provides enough thrust for a small spacecraft to travel in space.
NASA’s solar sail demonstration mission will deploy and operate a sail area 7 times larger than ever flown in space. The technology used in the demonstration will be applicable to many future space missions, including use in space weather warning systems to provide timely and accurate warnings of solar flare activity. The solar sail demonstration is a collaborative effort between The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), NASA and contractor L’Garde Inc.
NASA lists several capabilities solar sails have to offer, such as:
As an example, the GeoStorm project considers locating solar storm warning satellites at pseudo Lagrange points three times further from the Earth by using the solar sail to cancel some solar gravitational pull, thus increasing warning time from ~15 minutes to ~45 minutes.
Providing a satellite with a persistent view of northern or southern latitudes, i.e., a “pole-sitter” project. This allows the observational advantages of today’s geosynchronous satellites for orbits with view angles of the northern and southern high-latitudes.
If you’d like to learn more about solar sails, Caltech has a nice “Solar Sailing 101” page at: http://www.ugcs.caltech.edu/~diedrich/solarsails/intro/intro.html