[/caption]
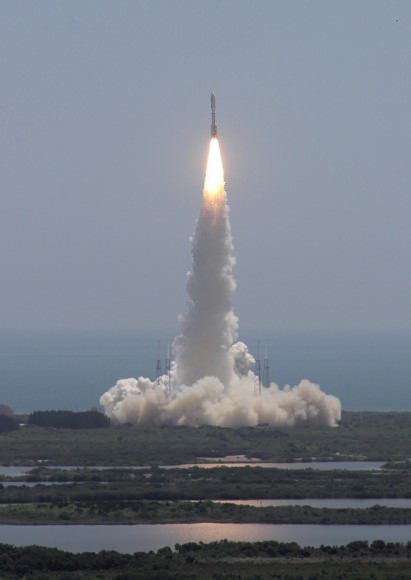
NASA’s powerful lunar mapping duo of GRAIL spacecraft are now poised for liftoff in just one weeks time on Thursday, Sept. 8.
Mission managers held a Flight Readiness Review on Wednesday (Aug.31) and gave a tentative approval to begin fueling the Delta II rockets second stage on Sept. 2 and 3 after evaluating all issues related to the rocket, launch pad and payloads.
Launch preparations are proceeding on schedule towards an early morning lift off from the seaside Space Launch Complex 17B (SLC-17B) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida. There are two instantaneous launch windows at 8:37:06 a.m. and 9:16:12 a.m. EDT lasting one second each.
“Launch vehicle and spacecraft closeouts will begin on Tuesday, and the Launch Readiness Review is also scheduled for Tuesday morning,” NASA KSC spokesman George Diller told Universe Today.
“This morning’s launch countdown dress rehearsal went fine.”
“Delta II 2nd stage fueling has been rescheduled for Friday and Saturday [Sept. 2 and 3]. Last evening a software error was found in the launch processing system data base. ULA (United Launch Alliance) decided they would like to look for any additional errors before the fueling begins. There is no impact to the launch date and currently no work is scheduled on Sunday or on Labor Day,” said Diller.
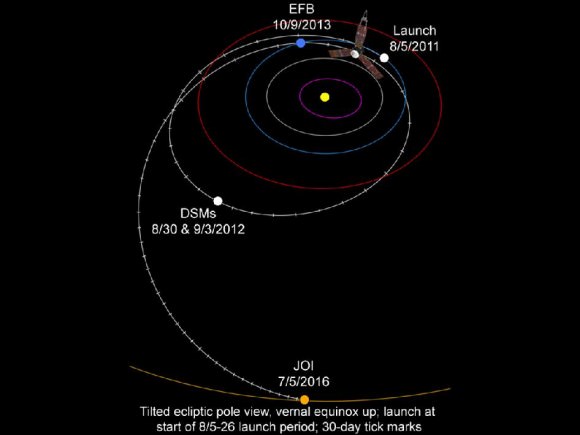
The launch period extends through Oct. 19, with liftoff occurring approximately four minutes earlier each day in case of a delay. The flight plan was designed to avoid a pair of lunar eclipses occurring on December 10th, 2011 and June 4th 2012 which would interfere with the missions operations and science.
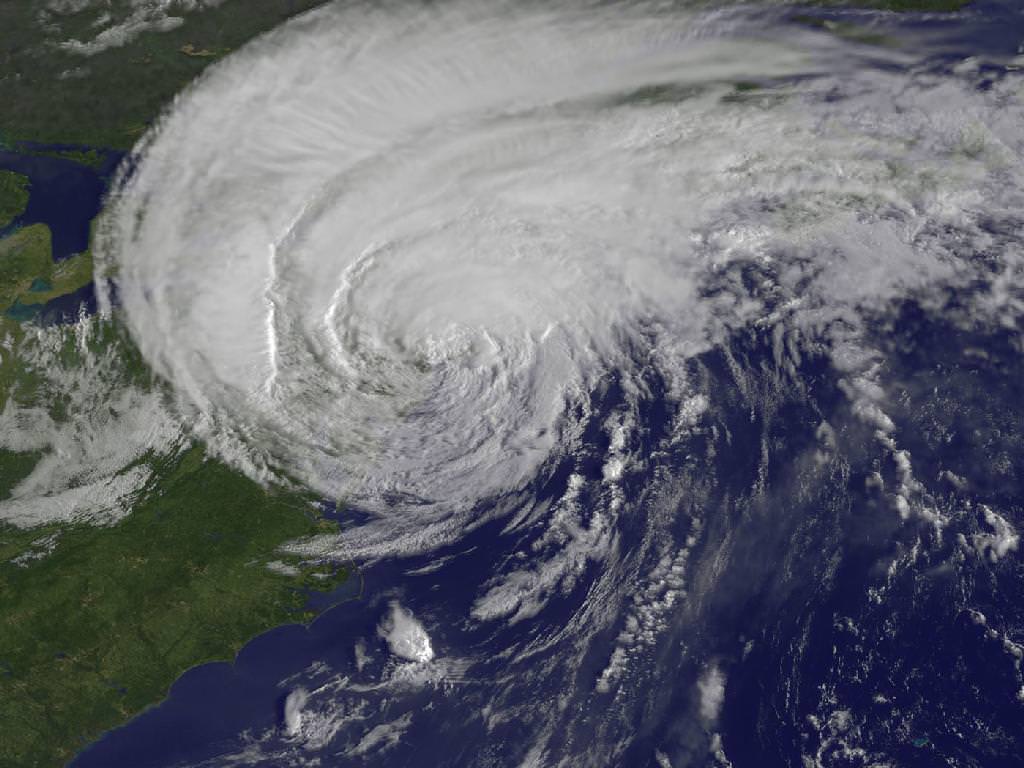
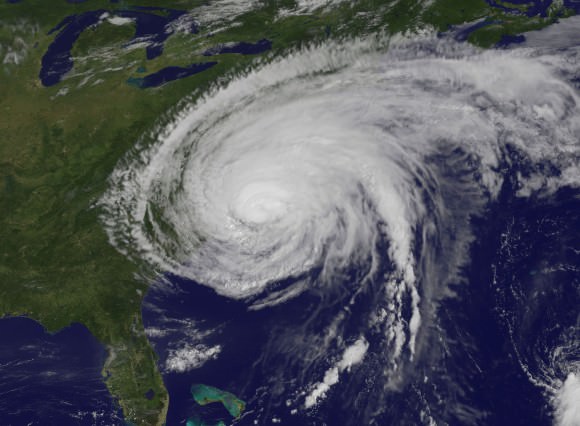
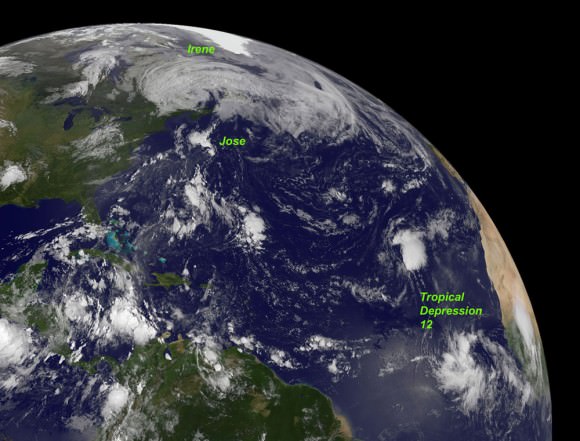
The team is keeping a close watch on the weather as the season’s next Atlantic Ocean storm heads westwards. Katia has just been upgraded to Hurricane status and follows closely on the heels of the continuing vast destruction, misery and deaths caused by Hurricane Irene earlier this week.
“The preliminary weather forecast is favorable for launch day as long as the wind remains out of the west as is currently forecast for that time of the morning,” Diller told me.

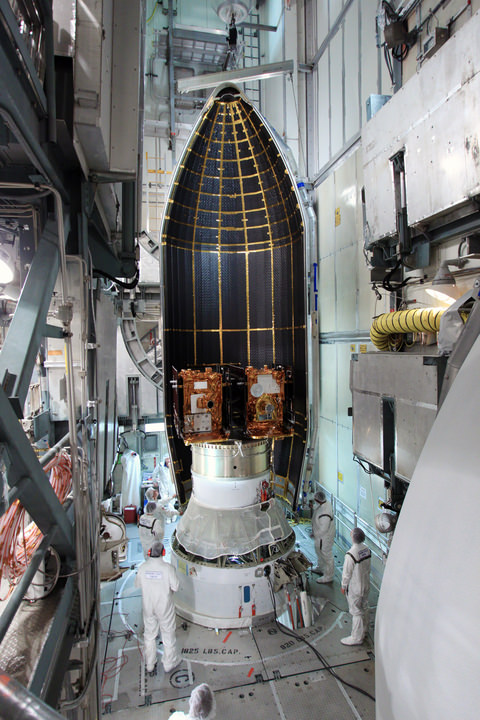
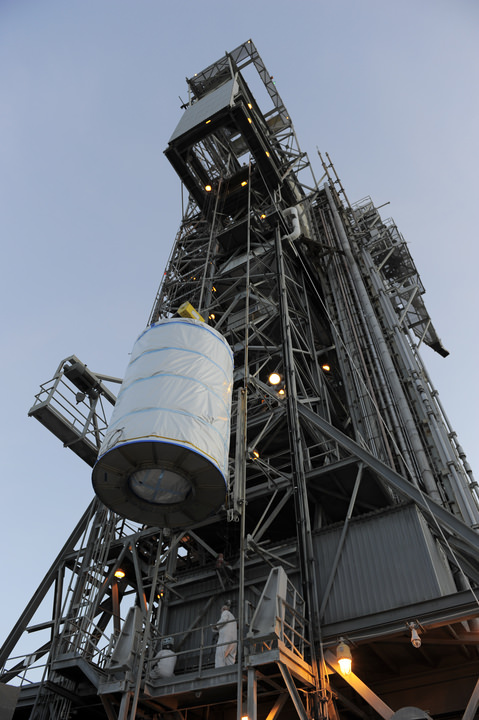
The twin probes known as GRAIL-A and GRAIL-B (Gravity Recovery and Interior Laboratory) were encapsulated inside the clamshell like payload fairing on Aug. 23 The nearly identical spacecraft are mounted side by side and sit atop the Centaur upper stage.
The fairing shields the spacecraft from aerodynamic pressures, friction and extreme heating for the first few minutes of flight during ascent through the Earth atmosphere.
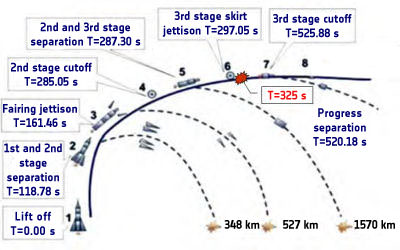
This Delta II Heavy booster rocket is the most powerful version of the Delta II family built by ULA. The booster’s first stage is augmented with larger diameter solid rocket motors.
GRAIL was processed for launch inside at the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. See my GRAIL spacecraft photos from inside the Astrotech clean room facilities here.
“The GRAIL spacecraft inside the handling can departed Astrotech and arrived at the launch pad, SLC-17B on Aug. 18” said Tim Dunn, NASA’s Delta II Launch Director in an interview with Universe Today. “The spacecraft was then hoisted by crane onto the Delta II launch vehicle and the spacecraft mate operation was flawlessly executed by the combined ULA and NASA Delta II Team.”
An Integrated Systems Test (IST) of the mated booster and payload was completed on Aug. 22

The dynamic duo will orbit the moon in a tandam formation just 50 kilometers above the lunar surface with an average separation of 200 km. During the 90 day science phase the goal is to determine the structure of the lunar interior from crust to core and to advance understanding of the thermal evolution of the moon.
GRAIL-A & GRAIL-B will measure the lunar gravity field with unprecedented resolution up to 100 times improvement on the near side and 1000 times improvement for the far side.
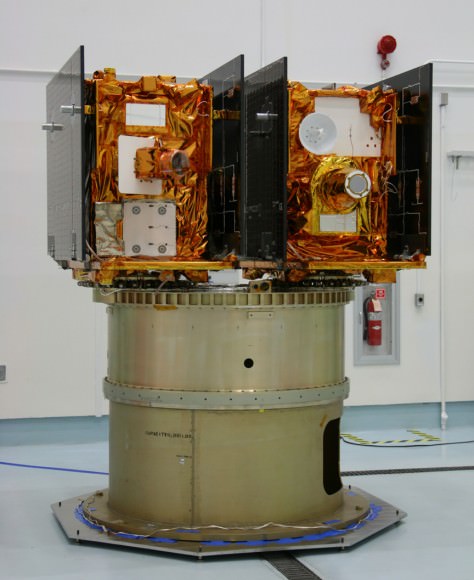

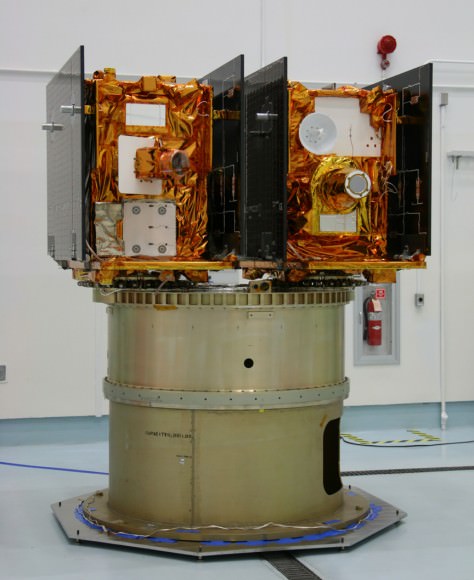
GRAIL B (left) and GRAIL A (right) spacecraft are mounted side by side on top of a payload adapter inside the clean room at Astrotech Space Operations facility. The spacecraft await lunar launch on Sept. 8, 2011. Credit: Ken Kremer
Read Ken’s continuing features about GRAIL
GRAIL Lunar Twins Mated to Delta Rocket at Launch Pad
GRAIL Twins ready for NASA Science Expedition to the Moon: Photo Gallery