[/caption]
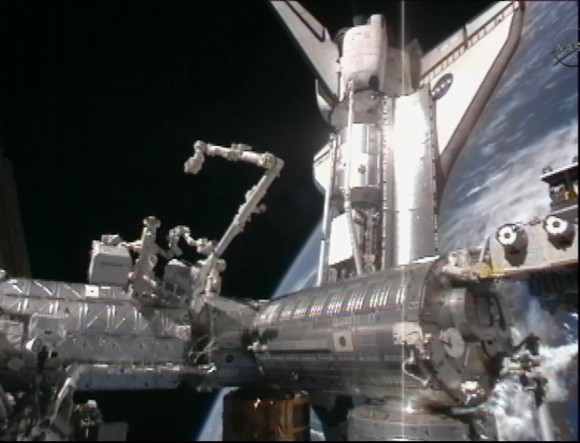
The international partners have decided against an historic ‘fly-about’ of the International Space Station, which would have provided one-of-a-kind images of the nearly completed ISS with space shuttle Discovery and an assortment of vehicles from the different participating space agencies docked to the station.
“This morning, our Russian colleagues, after doing their own independent review processes … have determined that they are not in position to recommend doing the fly about, because this particular vehicle is what they consider a new vehicle, the Series 700 vehicle, which is in its maiden flight,” said Kenneth Todd, a manager for Mission Integration and Operations at NASA, speaking at a mission briefing this morning.
The Russians felt they didn’t have the time or opportunity to fully understand, review and work through all the risks of the request of flying the Soyuz around the ISS, an idea which was presented only recently, and after the new Soyuz had already launched to orbit.
“From a MMT perspective, we knew it was critical for all partners to go through their processes,” Todd said. “It wasn’t necessarily what we were hoping to get back, but at the same point I applaud the Russians for doing the right thing, for not disregarding their own processes and making sure they do their own due diligence the way they should. I accepted the recommendation.”
Mission Control in Houston radioed up to ISS commander Scott Kelly and STS-133 Commander Steve Lindsey that the possible Soyuz fly about was a no-go, even though mission managers had already approved an extra day extension of the shuttle mission.
“We’ll now use that extra day for transfer work between the PMM (Permanent Multipurpose Module) and the ISS, to leave the station and crew in the best possible shape when Discovery undocks.” said Capcom Stan Love. “The fly about will not happen during this flight.”
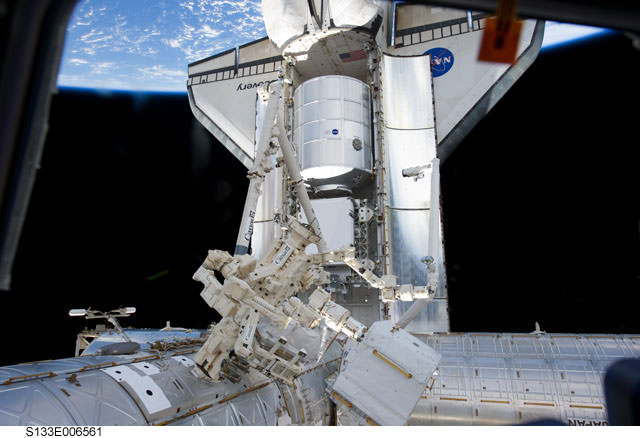
The fly-about –- only proposed about two weeks ago — would have had cosmonauts Alexander Kaleri and Oleg Skripochka along with Kelly to undock from the Russian Poisk module in the Soyuz TMA-01M spacecraft, back away from the ISS so they could show the ISS in its nearly completed configuration, with the shuttle attached, along with the Russian Progress and Soyuz, the European ATV and the Japanese HTV-1.
Todd said the images would not only be historic from an aesthetic perspective, but also provide valuable engineering views and data.
“There are multiple reasons this was going to be a good thing, to do this photo documentation,” he said. “Everytime we do one of these things we learn a lot, and we get a lot of good data about our ability to do this type of function, not just on our side but on the Russian side. I don’t see our review of this as wasted time or effort, and if we ever need to do this in the future, we will have to assess that at the time.”
Todd added that they should be able to get most of the images and data they were hoping for when the shuttle undocks and departs from the ISS next week – save for the historic aspect of having a shuttle docked to the station, along with all the other visiting vehicles.

Earlier today, the crews of STS-133 and the space station successfully installed the Leonardo Permanent Multipurpose Module, essentially storage space (a “float-in” closet – which has also been referred to as a potential Man-cave) which includes supplies. Also tucked inside is Robonaut-2, the first human-like robot to serve on board the space station.
Discovery’s landing is currently set for 11:36 am EST on Tuesday, March 8, 2011.