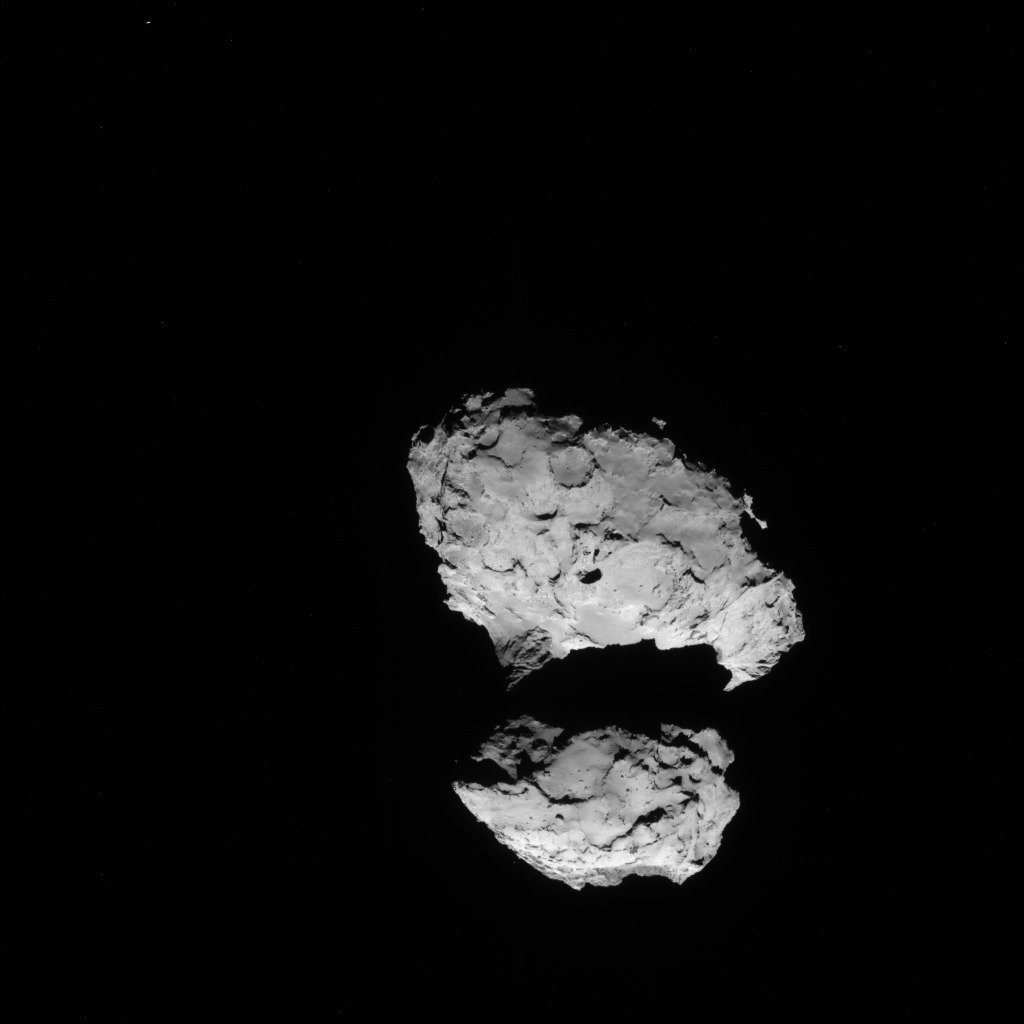
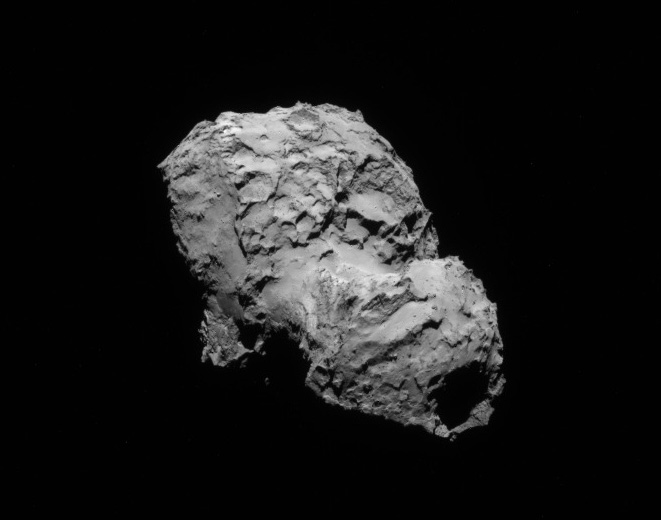
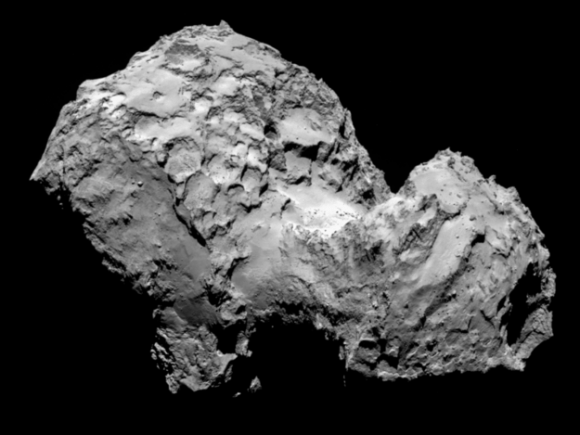
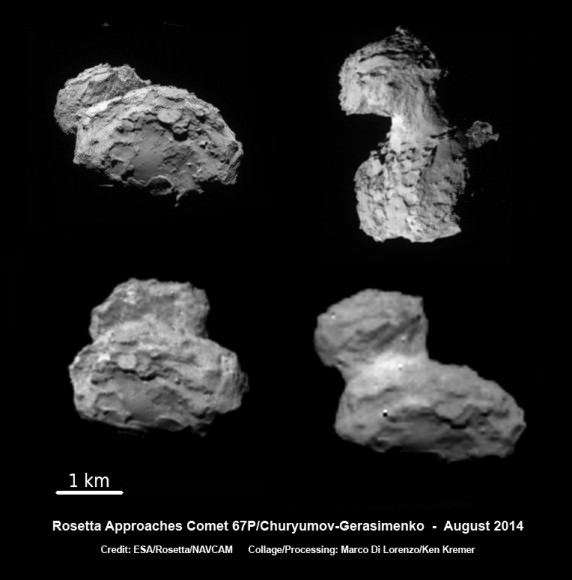
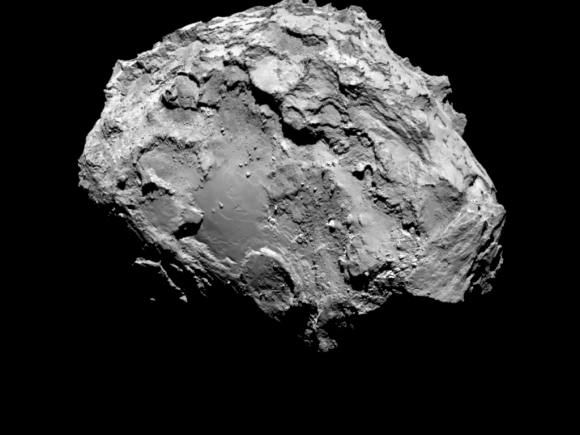
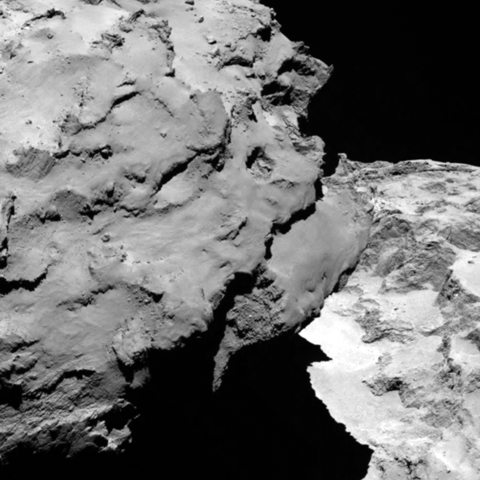
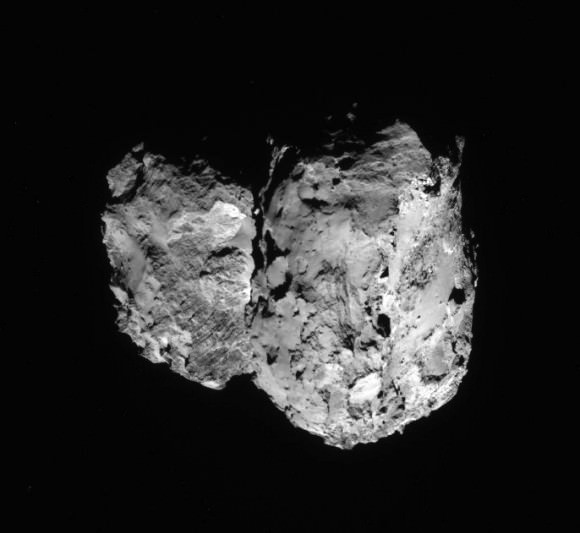
With the historic arrival of the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Rosetta spacecraft at destination Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko flawlessly accomplished on August 6, 2014 after a decade long journey, ground breaking up close science at this bizarre world has begun while the team diligently and simultaneously searches for a landing site for the attached Philae comet lander.
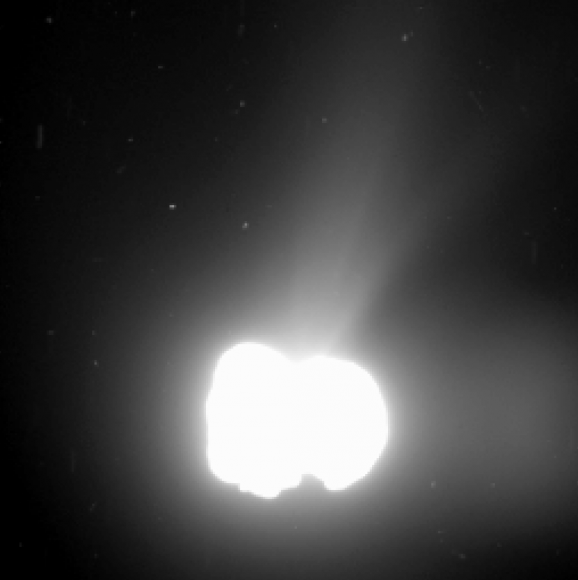
Rosetta started collecting cometary dust from the coma encircling the comet’s nucleus with the onboard COSIMA instrument on Sunday, August 10, 2014 as the spacecraft orbits around and ahead of the icy wanderer from a distance of approximately 100 kilometers (62 miles). See coma image below.
Hopes are high that unprecedented science discoveries await at this alien world described as a “Scientific Disneyland,” by Mark McCaughrean, senior scientific adviser to ESA’s Science Directorate, during ESA’s live arrival day webcast. “It’s just astonishing.”
COSIMA stands for Cometary Secondary Ion Mass Analyser and is one of Rosetta’s suite of 11 state-of-the-art science instruments with a combined mass of 165 kg.
Its purpose is to conduct the first “in situ” analysis of the grains of dust particles emitted from the comets nucleus and determine their physical and chemical characteristics, including whether they are organic or inorganic – in essence what is cometary dust material made of and how it differs from the surface composition.
COSIMA will collect the coma dust using 24 specially designed ‘target holders’ – the first of which was opened to study the comets environment on Aug. 10. Since the comet is not especially active right now, the team plans to keep the target holder open for at least a month and check the progress of any particle collections on a weekly basis.
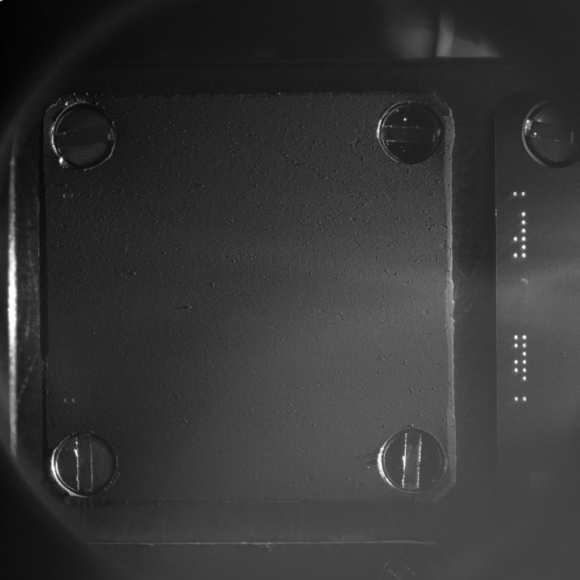
In fact the team says the coma environment “is still comparable to a high-quality cleanroom”at this time.
But everyone expects that to change radically as Rosetta continues escorting Comet 67P as it loops around the sun, getting closer and warming the surface every day and until reaching perihelion in August 2015.
COSIMA is managed by the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (Max-Planck-Institut für Sonnensystemforschung ) in Katlenburg-Lindau, Germany, with Principal Investigator Martin Hilchenbach.
There are also substantial contributions from the Institut d’Astrophysique Spatiale in France, Finnish Meteorological Institute, Osterreichisches Forschungszentrum Seibersdorf and more.
The target holders measure about one square centimeter and were developed by the Universität der Bundeswehr in Germany.
Each of these targets measures one square centimeter and is comprised of a gold plate covered with a thin 30 µm layer of gold nanoparticles (“gold black”) which the team says should “decelerate and capture cometary dust particles impacting with velocities of ~100 m/s.”
The target will be illuminated by a pair of LED’s to find the dust particles. The particles will be analyzed by COSIMA’s built in mass spectrometer after being located on the target holder by the French supplied COSISCOPE microscopic camera and ionized by a beam of indium ions.

The team expects any grains found on the first target to be analyzed by mid-September 2014.
“COSIMA uses the method of Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry. They will be fired at with a beam of Indium ions. This will spark individual ions (we say secondary ions) from their surfaces, which will then be analysed with COSIMA’s mass spectrometer,” according to a description from the COSIMA team.
The mass spec has the capability to analyze the elemental composition in an atomic mass range of 1 to 4000 atomic mass units, determine isotopic abundances of some key elements, characterize organic components and functional groups, and conduct mineralic and petrographic characterization of the inorganic phases, all of which will inform as as never before about solar system chemistry.
Comets are leftover remnants from the formation of the solar system. Scientists believe they delivered a vast quantity of water to Earth. They may have also seeded Earth with organic molecules – the building blocks of life as we know it.
Any finding of organic molecules and their identification by COSIMA will be a major discovery for Rosetta and ESA and inform us about the origin of life on Earth.
Data obtained so far from Rosetta’s VIRTIS instrument indicates the comets surface is too hot to be covered in ice and must instead have a dark, dusty crust.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.
…….
Read my Rosetta series here:
What’s Ahead for Rosetta – ‘Finding a Landing Strip’ on Bizarre Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko
Rosetta on Final Approach to Historic Comet Rendezvous – Watch Live Here
Rosetta Probe Swoops Closer to Comet Destination than ISS is to Earth and Reveals Exquisite Views
Rosetta Orbiter less than 500 Kilometers from Comet 67P Following Penultimate Trajectory Burn
Rosetta Closing in on Comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko after Decade Long Chase