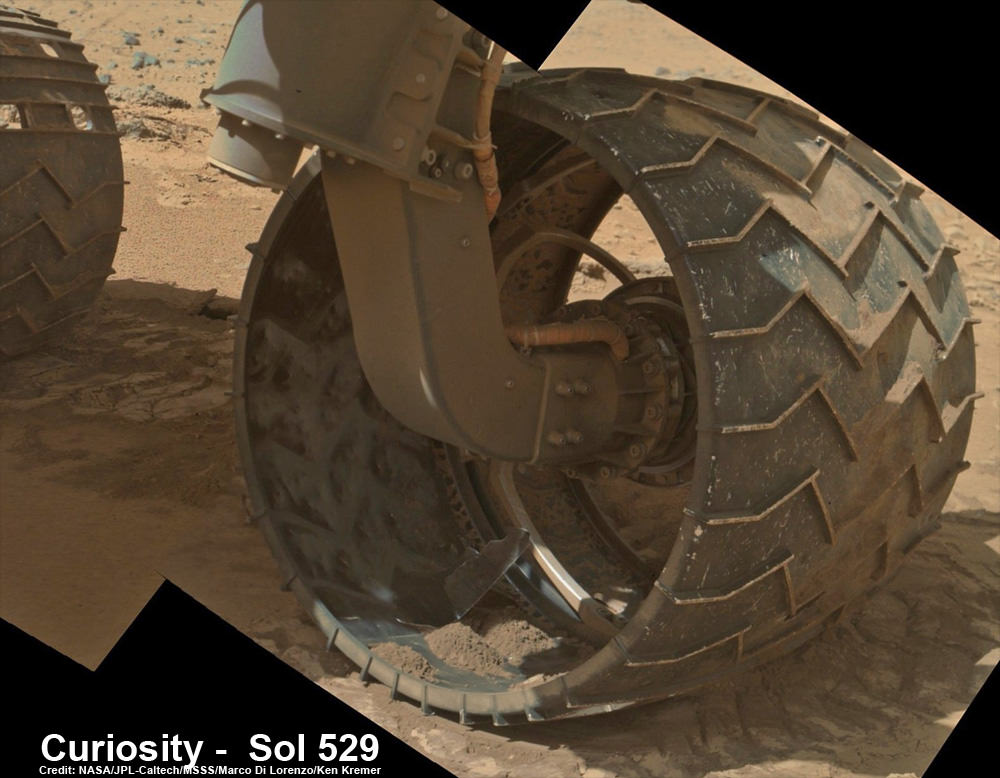
Up close photomosaic view shows lengthy tear in rover Curiosity’s left front wheel caused by recent driving over sharp edged Martian rocks on the months long trek to Mount Sharp. The team is evaluating an alternate, smoother way forward to next science target. Raw images taken by the MAHLI camera on Curiosity’s arm on Jan. 31, 2014 (Sol 529) were assembled to show some recent damage to several of its six wheels.
Credit: NASA / JPL / MSSS / Marco Di Lorenzo / Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com
See below complete 6 wheel mosaic and ‘Dingo Gap’ dune alternate route mosaic plus 3-D view[/caption]
Continuing wheel damage from hoards of sharp edged Martian rocks are forcing engineers to seek a smoother pathway forward – potentially through a treacherous dune field – for NASA’s Curiosity rover on the jagged rock strewn road to Mount Sharp, her primary science destination.
Ever since rover engineers noticed holes and tears to the robots six aluminum wheels this past fall and winter 2013, the team has been photographing the wheels much more frequently and carefully assessing their condition. See our mosaics above and below.
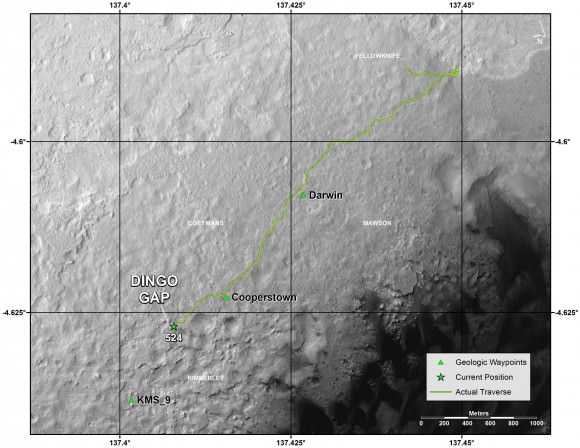
Curiosity’s handlers are now considering diverting the SUV-sized robot to an alternate path crossing into a dune field and the valley beyond that entails traversing through much smoother Martian terrain to reach a highly desirable and nearby science destination called “KMS-9.”
Newly received images taken by the robot only on Friday, Jan. 31, reveal a very significant ragged looking puncture at least 2 to 3 inches (5 to 8 cm) in length and a inch or so (3 cm) wide that’s bent back to the inside of the left front wheel.

This photomosaic from Curiosity’s Navigation Camera (Navcam) taken at the edge of the entrance to the Dingo Gap shows a 3 foot (1 meter) tall dune and valley terrain beyond to the west, all dramatically back dropped by eroded rim of Gale Crater. View from the rover’s current position on Sol 528 (Jan. 30, 2014). The rover team may decide soon whether Curiosity will bridge the dune gap as a smoother path to next science destination. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com
See NASA’s 3-D view of Dingo Gap below
Unfortunately, the fields of rough Red Planet rocks have not been a blessing to the 1 ton behemoth.
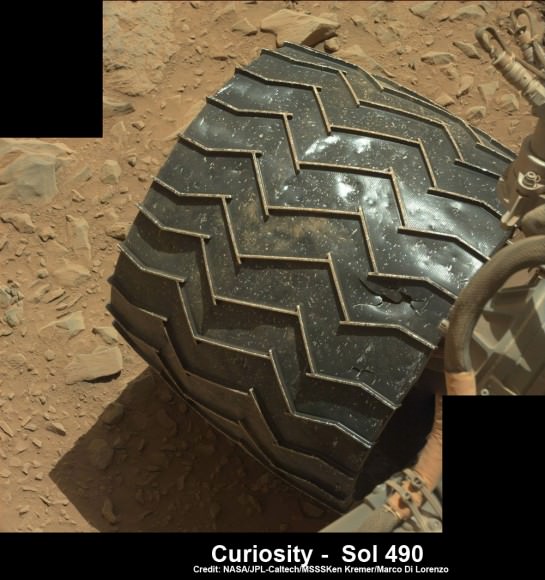
See our new underbelly mosaic view of Curiosity’s holy wheels (above and below) snapped on Jan. 31, (Sol 529), that’s aimed at the interior and which vividly shows the extent of the injury to the 20 inch diameter wheel.

The rate of wheel damage has picked up dramatically as the driving pace accelerated across the rugged, rock filled Martian terrain over the past six months and put over 4.89 kilometers (3.04 mi.) on the odometer to date since the nailbiting August 2012 landing.
The mega robot is now standing at the edge of the dune field by the picturesque entrance known as the “Dingo Gap” after driving another 865 feet (264.7 meters) during January 2014.
You can see the increased damage resulting from the past months drive by comparing the new Sol 529 view with our underbelly mosaic from Sol 490 in December 2013.

However, the dune cutting across “Dingo Gap” measures about 3 feet (1 meter) in height.
Look at this 3-D “Dingo Gap” mosaic view from NASA and you can judge for yourself the choices the team faces.
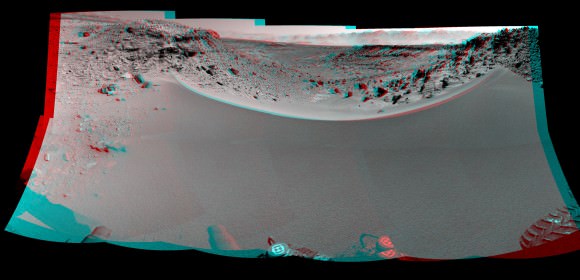
This stereo mosaic of images from the Navigation Camera (Navcam) on Curiosity shows the terrain to the west from the rover’s position on Sol 528 (Jan. 30, 2014). The scene appears three dimensional when viewed through red-blue glasses with the red lens on the left. The view was taken just after Curiosity had arrived at the eastern edge of a location called “Dingo Gap.” A dune across the gap is about 3 feet (1 meter) high in the middle and tapered at south (left) and north (right) ends onto low scarps on either side of the gap. The rover team is evaluating possible driving routes on the other side before a decision whether the cross the gap. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
So the team is evaluating whether that’s safe to bridge because they don’t want to get stuck in a hidden sand trap like the one that ultimately led to Spirit’s demise a few years back.
“The decision hasn’t been made yet, but it is prudent to go check,” said Jim Erickson of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif., project manager for Curiosity, in a NASA statement.

“We’ll take a peek over the dune into the valley immediately to the west to see whether the terrain looks as good as the analysis of orbital images implies,” Erickson added, based on orbital images snapped by the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) circling overhead.
The team is also testing an array of different driving techniques to minimize the accumulation of wheel punctures, such as driving backwards or using only four of the six wheels to reduce the force of the wheels pushing against jagged rocks.
The “Dingo Gap” could offer a safer gateway to “KMS-9” along the journey of the rovers southwestwardly route to breathtaking foothills of Mount Sharp.

Dingo Gap lies between two low scarps and that is tapered off at both sides to the north and south.
KMS-9 is a potentially science rich target where the team hopes to conduct the first rock drilling operations since departing the Yellowknife Bay quadrant in July 2013.
The candidate drilling site lies only about half a mile (800 meters) away as the martian crow flies and features geology that’s appealing to the science team. But the roving routes under consideration are all much farther in actual distance.
“At KMS-9, we see three terrain types exposed and a relatively dust-free surface,” said science team collaborator Katie Stack of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena.
Curiosity has already accomplished her primary goal of discovering a habitable zone on Mars that could support Martian microbes if they ever existed.
NASA’s rover Curiosity uncovered evidence that an ancient Martian lake had the right chemical ingredients, including clay minerals that could have sustained microbial life forms for long periods of time – and that these habitable conditions persisted on the Red Planet until a more recent epoch than previously thought.
As a result, the science team has shifted the missions focus to include the search for organic molecules – the building blocks of life as we know it – which may be preserved in the sedimentary rock layers of Mount Sharp.
“Really what we’re doing is turning the corner from a mission that is dedicated to the search for habitable environments to a mission that is now dedicated to the search for that subset of habitable environments which also preserves organic carbon,” Curiosity Principal Investigator John Grotzinger, of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, said recently at the Dec. 2013 annual meeting of the American Geophysical Union (AGU).
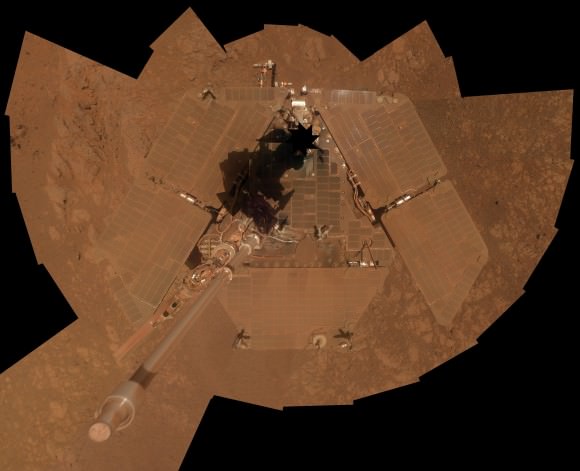
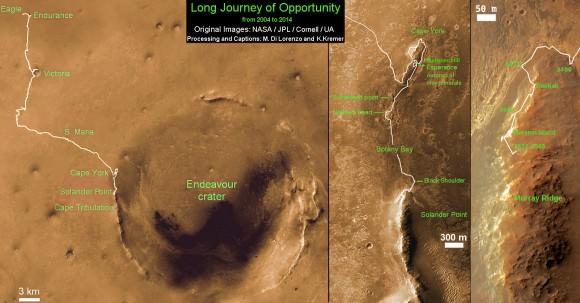
Meanwhile, NASA’s Opportunity rover is exploring clay mineral outcrops by the summit of Solander Point on the opposite side of the Mars at the start of her 2nd Decade investigating the Red Planets mysteries.
Read my new story about the Top 10 Decade 1 discoveries of Spirit and Opportunity – here.
And a pair of new orbiters are streaking to the Red Planet to fortify Earth’s invasion fleet- NASA’s MAVEN and India’s MOM.
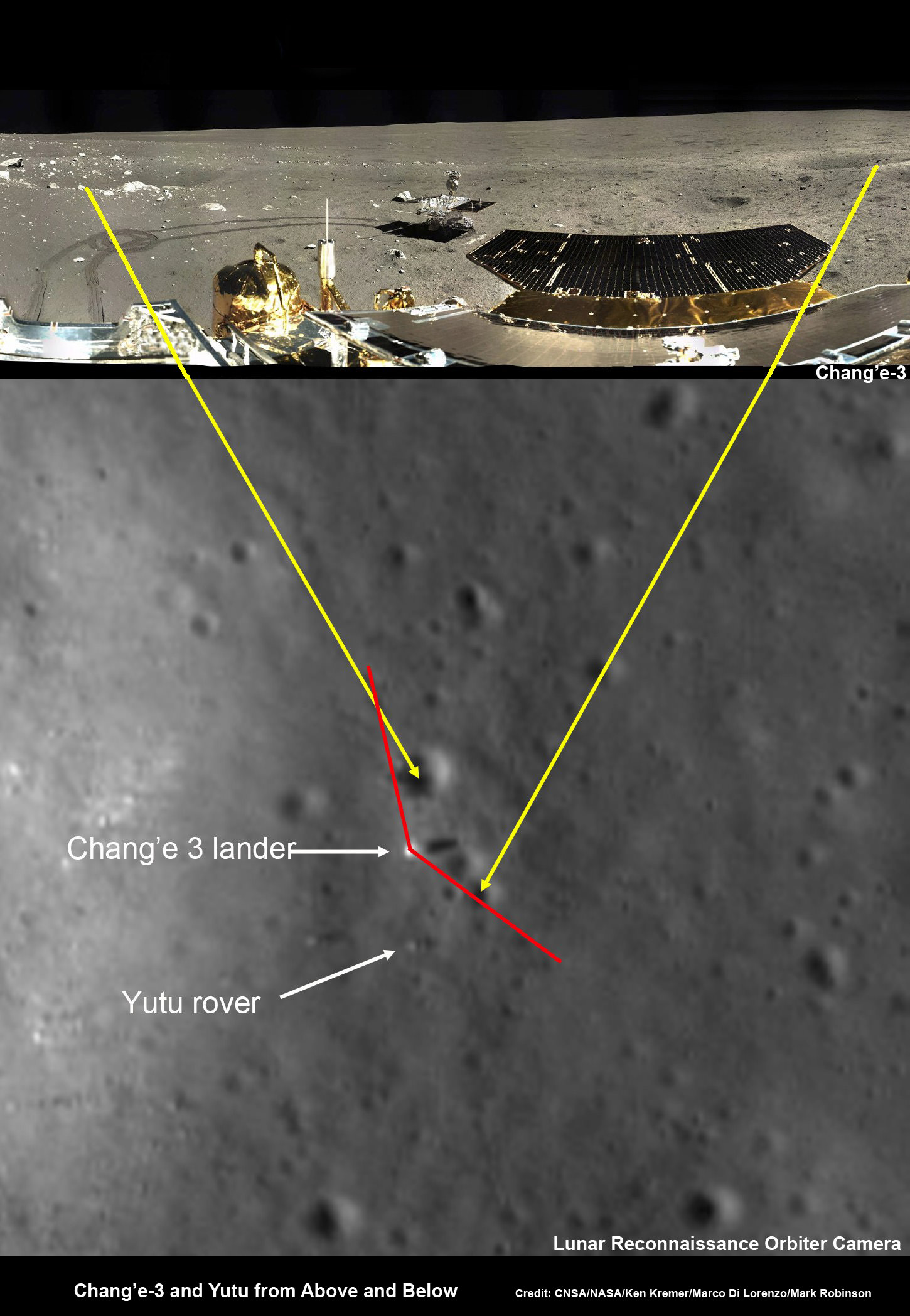
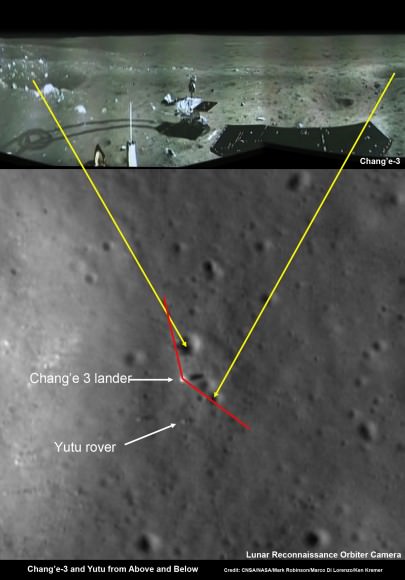
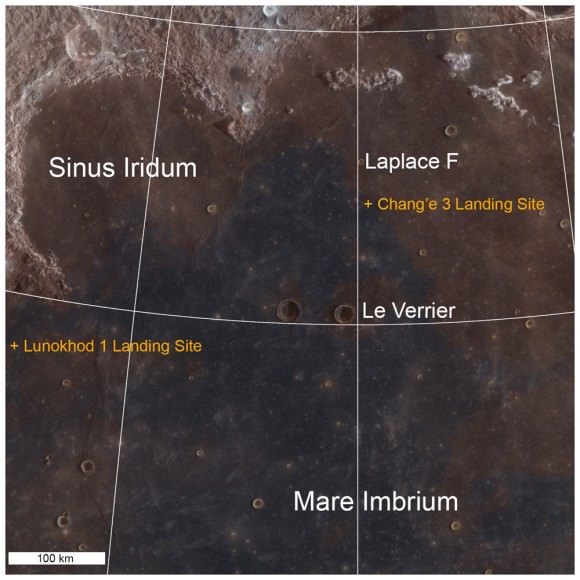
Finally, China’s new Yutu moon rover is hibernating through her 2nd lunar night as we await word of her fate next weekend, around Feb 8 or 9.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Curiosity, Opportunity, Chang’e-3, SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, LADEE, MAVEN, MOM and Mars news.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech













![MER10-SpiritAndOpportunity_ByTheNumbers[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/MER10-SpiritAndOpportunity_ByTheNumbers1-580x423.jpg)