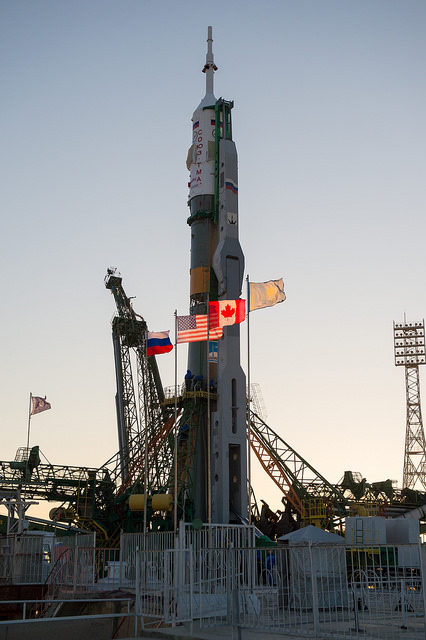
Want to know more about the Soyuz rocket? This new video from ESA is based on actual lessons for astronauts about the Soyuz rocket and describes the parts of the Soyuz, the stages and launch sequence. The info here was part of ESA Basic Training for the ESA astronaut class of 2009 (also known as the Shenanigans09).
Opportunity Mountain Goal Dead Ahead as Mars Orbiter Restarts Critical Targeting Hunt for Habitability Signs
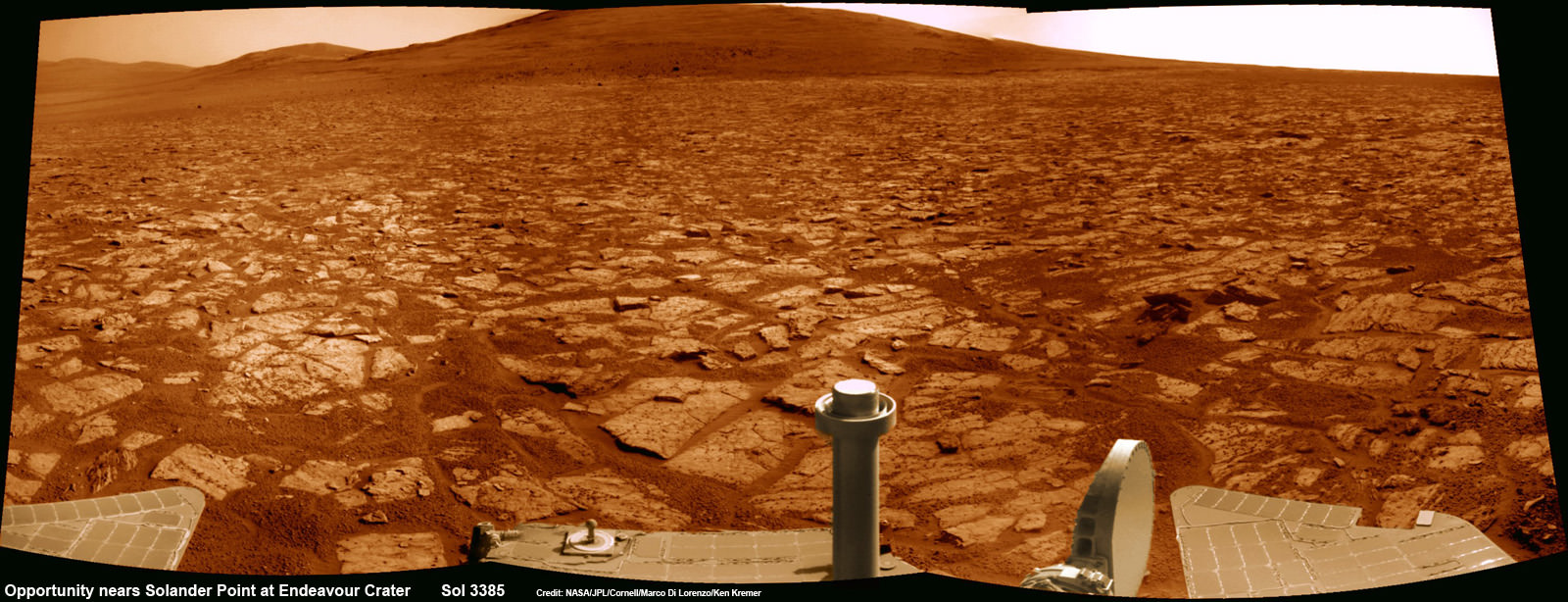

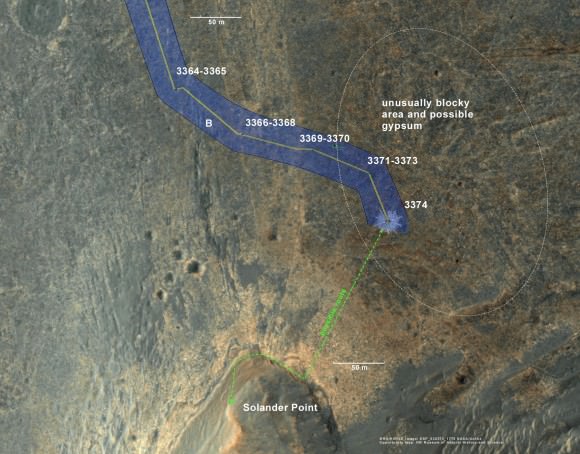
Opportunity rover’s 1st mountain climbing goal is dead ahead in this up close view of Solander Point at Endeavour Crater. Opportunity will ascend the mountain looking for clues indicative of a Martian habitable environment. This navcam panoramic mosaic was assembled from raw images taken on Sol 3385 (Aug 2, 2013).
Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer (kenkremer.com)[/caption]
NASA’s most powerful Mars orbiter has been given the green light today (Aug. 5) to capture new high resolution spectral scans that are absolutely crucial for directing the long lived Opportunity rover’s hunt for signatures of habitability atop the intriguing mountain she will soon ascend.
In a plan only recently approved by NASA, engineers are aiming the CRISM mineral mapping spectrometer aboard the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) circling overhead to collect high resolution survey scans of Solander Point – Opportunity’s 1st mountain climbing goal along the rim of huge Endeavour Crater.
“New CRISM observations centered over Solander Point will be acquired on Aug. 5, 2013,” Ray Arvidson told Universe Today exclusively. Arvidson is the mission’s deputy principal scientific investigator from Washington University in St. Louis, Mo.
NASA’s decade old rover Opportunity is about to make ‘landfall’ at the base of Solander Point, the Martian mountain she will scale in search of the chemical ingredients that could sustain Martian microbes.
So the new spectral data can’t come back to Earth soon enough.
And all this is taking place as NASA’s Curiosity rover celebrates her 1st Birthday on the Red Planet. Read that story – here.
Currently, the science team lacks the same quality of high resolution CRISM data from Solander Point that they had at a prior stop at Cape York. And that data was crucial because it allowed the rover to be precisely targeted – and thereby discover a habitable zone, Arvidson told me.
“CRISM collected lots of overlapping measurements at Cape York to sharpen the image resolution to 5 meters per pixel to find the phyllosilicate smectite [clay minerals] signatures at Matejivic Hill on Cape York.”
“We don’t have that at Solander Point. We only have 18 meters per pixel data. And at that resolution you can’t tell if the phyllosilicate smectite [clay minerals] outcrops are present.”
Today’s new survey from Mars orbit will vastly improve the spectral resolution – from 18 meters per pixel down to 5 meters per pixel.
“5 meter per pixel CRISM resolution is expected in the along-track direction over Solander Point by commanding the gimbaled optical system to oversample that much,” Arvidson explained.

The new CRISM spectral survey from Mars is essential to enable the science team to carefully study the alien, unexplored terrain in detail and locate the clay minerals and other water bearing minerals, even before the rover arrives.
Clay minerals form in neutral pH water conducive to life.
Opportunity would then be commanded to drive to preselected sites to conduct “ground truth” forays at Solander.
That’s just like was done at Cape York and the “Esperance” rock loaded with clay minerals that turned into one of the “Top 5 discoveries of the mission” according to Arvidson and Steve Squyres, Opportunity’s Science Principal Investigator of Cornell.
But it took some cajoling and inter team negotiations to convince everyone to move forward with the special but crucial CRISM imaging plan.
Since MRO is getting on in age – it launched in 2005 – NASA and the spacecraft managers have to carefully consider special requests such as this one which involves slewing the MRO spacecraft instruments and therefore entails some health risks to the vehicle.
“CRISM has been operating at Mars since 2006 and sometimes the optics on a gimble have actuators that get stuck a little bit and don’t sweep as fully as planned.”
Nevertheless, Arvidson told me a few weeks ago he was hopeful to get approval.
“I suspect I can talk the team into it.”
And eventually he did! And informed me for the readers of Universe Today.
The fact that the Opportunity scientists already scored a ‘Science Home Run’ with their prior CRISM targeting request at Cape York certainly aided their cause immensely.
The new approved CRISM measurements due to be captured today will give Opportunity the best chance to be targeted to the most promising mineral outcrops, and as quickly as possible.
“With the coordinated observations from CRISM and Opportunity we will go into Solander Point a lot smarter!”
“And we’ll have a pretty good idea of what to look for and where,” Arvidson told me.

Today marks Opportunity’s 3389th Sol or Martian day roving Mars. Merely 90 days were expected!
Having completed her investigation of the rocky crater plains, the rover continues to drive south.
Any day now Opportunity will drive onto the Bench surrounding Solander and start a new phase of the mission.
Since she basically arrived at Solander with plenty of power and ahead of schedule prior to the onset of the 6th Martian winter, the robot has some spare time to investigate the foothills before ascending the north facing slopes.
“We will be examining the bench and then working our way counterclockwise to reach the steep slopes associated with the Noachian outcrops that are part of the Endeavour rim,” Arvidson said.
Ken Kremer
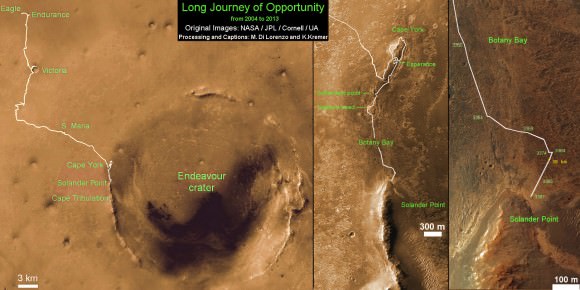
This map shows the entire path the rover has driven during more than 9 years and over 3387 Sols, or Martian days, since landing inside Eagle Crater on Jan 24, 2004 to current location near foothills of Solander Point at the western rim of Endeavour Crater. Opportunity discovered clay minerals at Esperance – indicative of a habitable zone. Credit: NASA/JPL/Cornell/ASU/Marco Di Lorenzo/Ken Kremer
Curiosity rover Celebrates 1 Year on Mars with Dramatic Discoveries
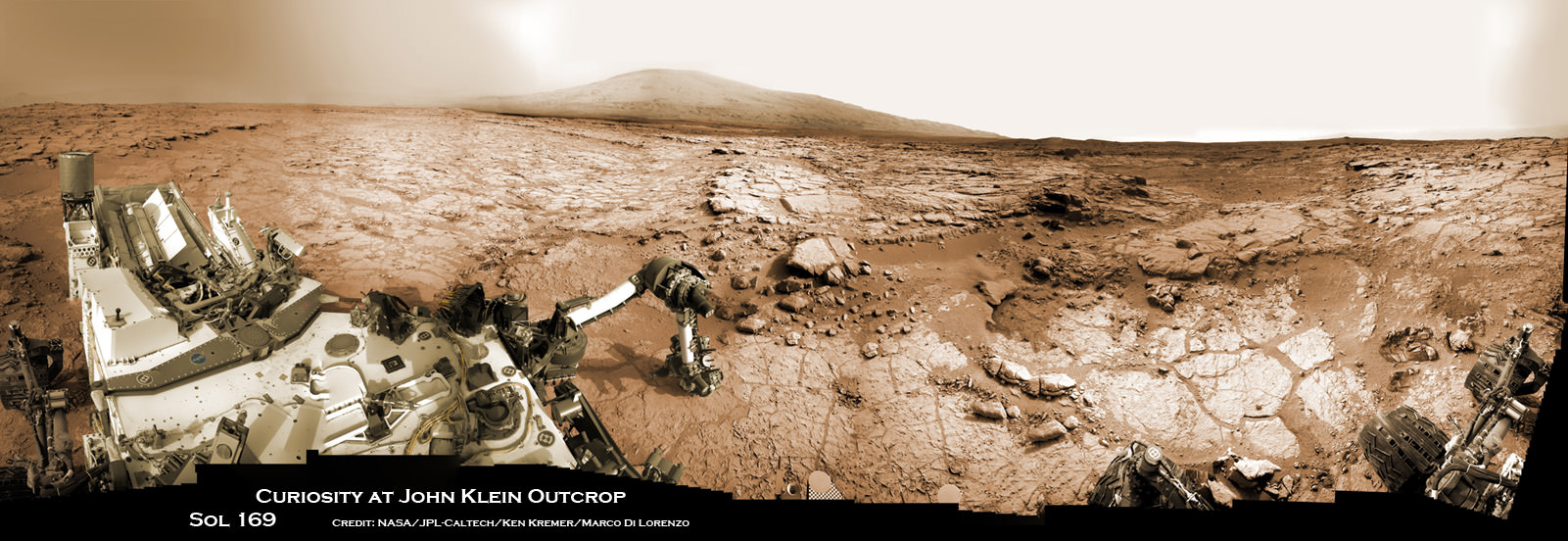

Curiosity accomplished Historic 1st drilling into Martian rock at John Klein outcrop on Feb 8, 2013 (Sol 182), shown in this context mosaic view of the Yellowknife Bay basin taken on Jan. 26 (Sol 169). The robotic arm is pressing down on the surface at John Klein outcrop of veined hydrated minerals – dramatically back dropped with her ultimate destination; Mount Sharp.
Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Ken Kremer/Marco Di Lorenzo
Story updated with further details[/caption]
NASA’s mega Mars rover Curiosity is celebrating 1 Year on the Red Planet since the dramatic landing on Aug. 6, 2012 by reveling in a string of groundbreaking science discoveries demonstrating that Mars could once have supported past life – thereby accomplishing her primary science goal – and with a promise that the best is yet to come!
“We now know Mars offered favorable conditions for microbial life billions of years ago,” said the mission’s project scientist, John Grotzinger of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena.
“Curiosity has landed in an ancient river or lake bed on Mars,” Jim Green, Director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division, told Universe Today.
Curiosity is now speeding onwards towards Mount Sharp, the huge 3.4 mile (5. 5 km) mountain dominating the center of her Gale Crater landing site – and which is the primary destination of the mission.
During Year 1, Curiosity has transmitted over 190 gigabits of data, captured more than 71,000 images, fired over 75,000 laser shots to investigate the composition of rocks and soil and drilled into two rocks for sample analysis by the pair of state-of-the-art miniaturized chemistry labs housed in her belly – SAM & CheMin.
“From the sophisticated instruments on Curiosity the data tells us that this region could have been habitable in Mars’ distant past,” Green told me.
“This is a major step forward in understanding the history and evolution of Mars.”
And just in the nick of time for her 1 year anniversary, the car sized robot just passed the 1 mile (1.6 kilometer) driving mark on Aug. 1, or Sol 351.
Mount Sharp still lies roughly 5 miles (8 kilometers) distant – as the Martian crow flies.
“We will be on a general heading of southwest to Mount Sharp,” Jim Erickson, Curiosity Project Manager of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), told Universe Today in an exclusive interview. See the NASA JPL route maps below.
“We have been going through various options of different planned routes.”
How long will the journey to Mount Sharp take?
“Perhaps about a year,” Erickson told me.
“We have put some new software – called autonav, or autonomous navigation – on the vehicle right after the conjunction period back in March 2013. This will increase our ability to drive.”
“We are trying to make that significantly faster by bringing the new autonav online. That will help. But how much it helps really depends on the terrain.”
So far the terrain has not been problematical.
“Things are going very well and we have a couple of drives under our belt,” said Erickson, since starting the long trek to Mount Sharp about a month ago.
The lower reaches of Mount Sharp are comprised of exposed geological layers of sedimentary materials that formed eons ago when Mars was warmer and wetter, and much more hospitable to microscopic life.
“It has been gratifying to succeed, but that has also whetted our appetites to learn more,” says Grotzinger. “We hope those enticing layers at Mount Sharp will preserve a broad diversity of other environmental conditions that could have affected habitability.”
Indeed, Curiosity’s breakthrough discovery that the surface of Mars possesses the key chemical ingredients required to sustain microbial life in a habitable zone, has emboldened NASA to start mapping out the future of Mars exploration.
NASA announced plans to start work on a follow on robotic explorer launching in 2020 and develop strategies for returning Martian samples to Earth and dispatching eventual human missions to Mars in the 2030’s using the new Orion capsule and SLS Heavy lift rocket.
“NASA’s Mars program is back on track with the 2016 InSight lander and the 2020 rover,” Jim Green, Director of NASA’s Planetary Science Division, told Universe Today in an interview.
“Successes of our Curiosity — that dramatic touchdown a year ago and the science findings since then — advance us toward further exploration, including sending humans to an asteroid and Mars,” said NASA Administrator Charles Bolden in a statement.
“Wheel tracks now, will lead to boot prints later.”
Following the hair-raising touchdown using with the never before used sky-crane descent thrusters, the science team directed the 1 ton robot to drive to a nearby area of interesting outcrops on the Gale crater floor – at a place called Glenelg and Yellowknife Bay.
Along the way, barely 5 weeks after landing, Curiosity found a spot laden with rounded pebbles at the Hottah outcrop of concretions that formed in an ancient stream bed where hip deep liquid water once flowed rather vigorously.
In February 2013, Curiosity conducted the historic first ever interplanetary drilling into Red Planet rocks at the ‘John Klein’ outcrop inside Yellowknife Bay that was shot through with hydrated mineral veins of gypsum.
The Yellowknife Bay basin looks like a dried up river bed.

Analysis of pulverized portions of the gray colored rocky powder cored from the interior of ‘John Klein’ revealed evidence for phyllosilicates clay minerals that typically form in pH neutral water. These starting findings on the crater floor were unexpected and revealed habitable environmental conditions on Mars – thus fulfilling the primary science goal of the mission.
See herein our context panoramic mosaic from Sol 169 showing the robotic arm touching and investigating the Martian soil and rocks at ‘John Klein’.
And if you take a visit to Washington, DC, you can see our panorama (assembled by Ken Kremer and Marco Di Lorenzo) on permanent display at a newly installed Solar System exhibit at the US National Mall in front of the Smithsonian National Air & Space Museum- details here.

“We have found a habitable environment [at John Klein] which is so benign and supportive of life that probably if this water was around, and you had been on the planet, you would have been able to drink it,” says Grotzinger, summing up the mission.

This past week she captured rare sky watching images of the diminutive Martian moons – Phobos and Deimos – together!
Meanwhile, Curiosity’s 10 year old sister rover Opportunity Is trundling merrily along and will arrive shortly at her own mountain climbing goal on the opposite of Mars.
And NASA’s next Mars orbiter called MAVEN (for Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution), has just arrived intact at the Kennedy Space Center after a cross country trip aboard a USAF C-17.
Technicians at Kennedy will complete final preparations for MAVEN’s blastoff to the Red Planet on Nov. 18 from the Florida Space Coast atop an Atlas V rocket.
On Tuesday, Aug 6, NASA will broadcast a half day of new programming on NASA TV commemorating the landing and discussing the science accomplished so far and what’s coming next.
And stay tuned for more astonishing discoveries during ‘Year 2’ on the Red Planet from our intrepid rover Curiosity – Starting Right Now !
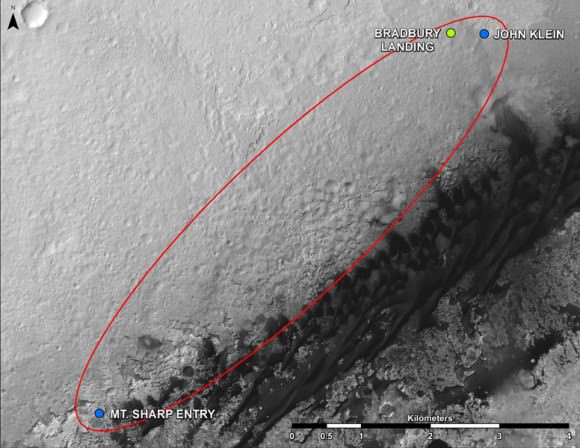

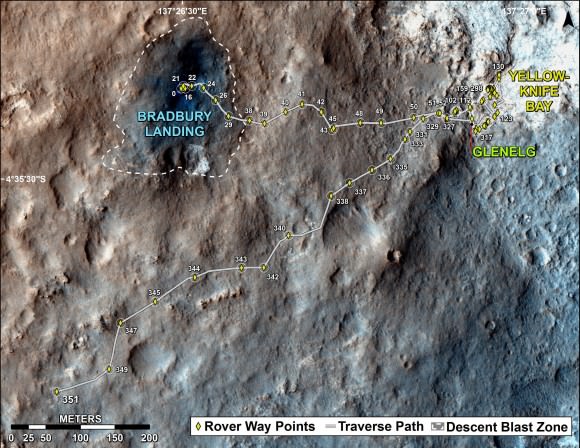
This map shows where NASA’s Mars rover Curiosity landed in August 2012 at “Bradbury Landing”; the area where the rover worked from November 2012 through May 2013 at and near the “John Klein” target rock in the “Glenelg” area; and the mission’s next major destination, the entry point to the base of Mount Sharp. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Univ. of Arizona
What’s The Asteroid Capture Mission Going to Look Like? NASA’s Starting Its Review
It’s still unclear if NASA will receive Congressional funding or authorization to do an asteroid retrieval proposal backed by President Barack Obama’s administration, but as missions take time to plan, the agency is moving ahead with its work for now.
NASA just did a mission formulation review this week to look at some internal studies on the mission. It also is starting to wade through hundreds of ideas the space community submitted concerning the mission.
“With the mission formulation review complete, agency officials now will begin integrating the most highly-rated concepts into an asteroid mission baseline concept to further develop in 2014,” NASA stated. The agency was light on details, but more information should be forthcoming when the process is further along.
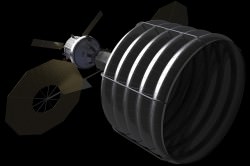
The agency’s fiscal 2014 budget proposal suggests robotically picking up an asteroid, steering it closer to Earth, and putting it in a safe orbit where probes and possibly astronauts could visit. The budget is still being moved through Congressional committees and we won’t know until later this year just how much money will be available for NASA, and what initiatives the agency will be allowed to do.
For more information, be sure to read this past article from Universe Today editor Nancy Atkinson looking in detail at NASA’s asteroid retrieval mission. It includes information on what technology could be used, and the history of NASA’s quest to explore asteroids.
Space rocks have hit the headlines several times this year, particularly when one exploded over the area of Chelyabinsk, Russia earlier in 2013. NASA and several other groups have ongoing searches for asteroids and other small bodies in our solar system to catalog and calculate the orbits for as many as they can find. No imminent threats are known.
What Happens To Your Skin in Space
The microgravity environment of the ISS poses many challenges to the human body — some more expected than others — but one that many people might not know about is the “molting” of dry skin, notably from the bottom of the feet. And while astronauts living aboard Space Station often spend their days working in socks, when they go to remove them they have to be especially careful to keep floating clouds of flakes at a minimum, lest they incite allergic reactions in their crewmates.
Yeah, you read that right. “Floating clouds of flakes.” Eeeewwwwww.
In the latest episode of ISS Science Garage NASA astronauts Mike Massimino and Don Pettit discuss some of the finer details of podiatric etiquette whilst sojourning aboard the ISS. (Unfortunately saying it fancy-like doesn’t make it any less gross.) All I have to say is, I wouldn’t want to be the one who has to clean out the vent filters.
MAVEN Takes Final Test Spins, Flexes Solar Panels Before Imminent Trek to Florida Launch Site
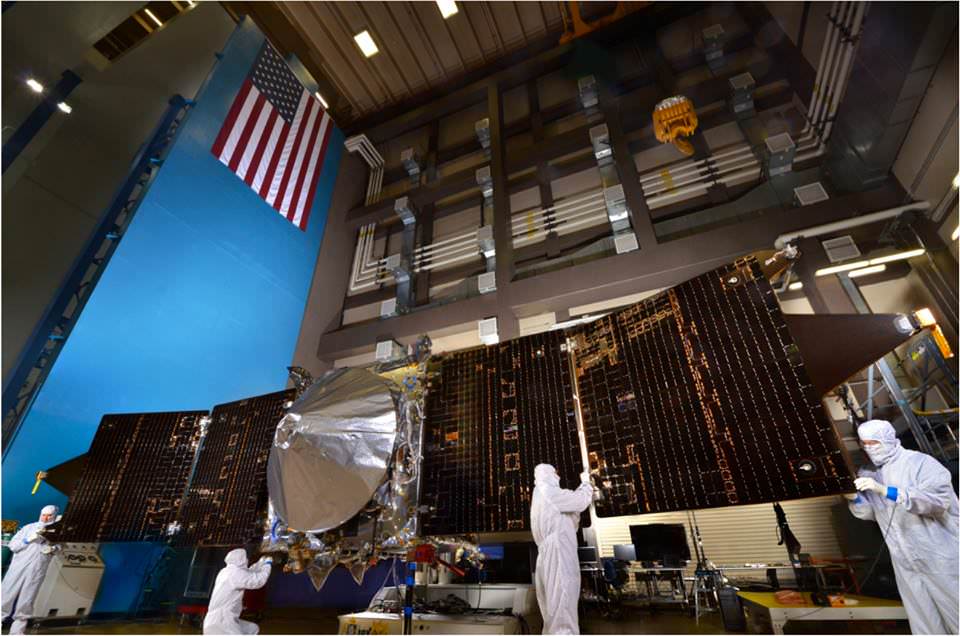

The solar panels on NASA’s MAVEN Mars orbiter are deployed as part of environmental testing procedures at Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Littleton, Colorado, before shipment to Florida on Aug. 2 and blastoff for Mars on Nov. 18, 2013. Credit: Lockheed Martin
Watch cool testing videos below![/caption]
MAVEN is NASA’s next mission to Mars and in less than three days time the spacecraft ships out on a cross country trek for the first step on the long sojourn to the Red Planet.
But before all that, technicians took MAVEN for a final spin test, flexed her solar arrays and bombarded her with sound and a whole lot more.
On Aug. 2, MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN Mission) journeys half a continent from its assembly facility at Lockheed Martin in Littleton, Colorado to the Kennedy Space Center and the Florida Space Coast aboard a USAF C-17.
Unlike Curiosity, which is roving across a crater floor on the Red Planet at this very moment, MAVEN is an orbiter with a first of its kind mission.
MAVEN is the first spacecraft from Earth devoted to investigating and understanding the upper atmosphere of Mars.
The goal is determining how and why Mars lost virtually all of its atmosphere billions of years ago, what effect that had on the climate and where did the atmosphere and water go?
To ensure that MAVEN is ready for launch, technicians have been busy this year with final tests of the integrated spacecraft.
Check out this video of MAVEN’s Dry Spin Balance Test
The spin balance test was conducted on the unfueled spacecraft on July 9, 2013 at Lockheed Martin Space Systems in Littleton, Colorado.
NASA says the purpose of the test “is to ensure that the fully integrated spacecraft is correctly balanced and to determine the current center of gravity. It allows the engineering team to fine-tune any necessary weight adjustments to precisely fix the center of gravity where they want it, so that it will perform as expected during the cruise to Mars.”
It was the last test to be completed on the integrated spacecraft before its shipment to Florida later this week.
This next video shows deployment tests of the two “gull-wing” solar panels at Lockheed Martin Space Systems.
Wingtip to wingtip, MAVEN measures 11.43 m (37.5 feet) in length.
In mid May, MAVEN was moved into a Thermal Vacuum Chamber at Lockheed Martin for 19 days of testing.
The TVAC test exposed MAVEN to the utterly harsh temperatures and rigors of space similar to those it will experience during its launch, cruise, and mission at Mars.
MAVEN is slated to blast off atop an Atlas V-401 rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida on Nov. 18, 2013. The 2000 pound (900 kg) spacecraft will be housed inside a 4 meter payload fairing.
After a 10 month interplanetary voyage it will join NASA’s armada of four robotic spacecraft when it arrives in Mars orbit in September 2014.
Scientists hope that measurements from MAVEN will help answer critical questions like whether, when and how long the Martian atmosphere was once substantial enough to sustain liquid water on its surface and support life.
“What we’re doing is measuring the composition of the atmosphere as a measure of latitude, longitude, time of day and solar activities,” said Paul Mahaffy, of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md, and the principal investigator for MAVEN’s mass spectrometer instrument.
“We’re trying to understand over billions of years how the atmosphere has been lost.”
…………….
Learn more about MAVEN, Cygnus, Antares, LADEE, Mars rovers and more at Ken’s upcoming lecture presentations
Aug 12: “RockSat-X Suborbital Launch, LADEE Lunar & Antares Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, 8 PM
Oct 3: “Curiosity and the Search for Life on Mars – (3-D)”, STAR Astronomy Club, Brookdale Community College & Monmouth Museum, Lincroft, NJ, 8 PM

Future Games: Astronauts Tele-Operate An Earth-Bound Rover … From Space!
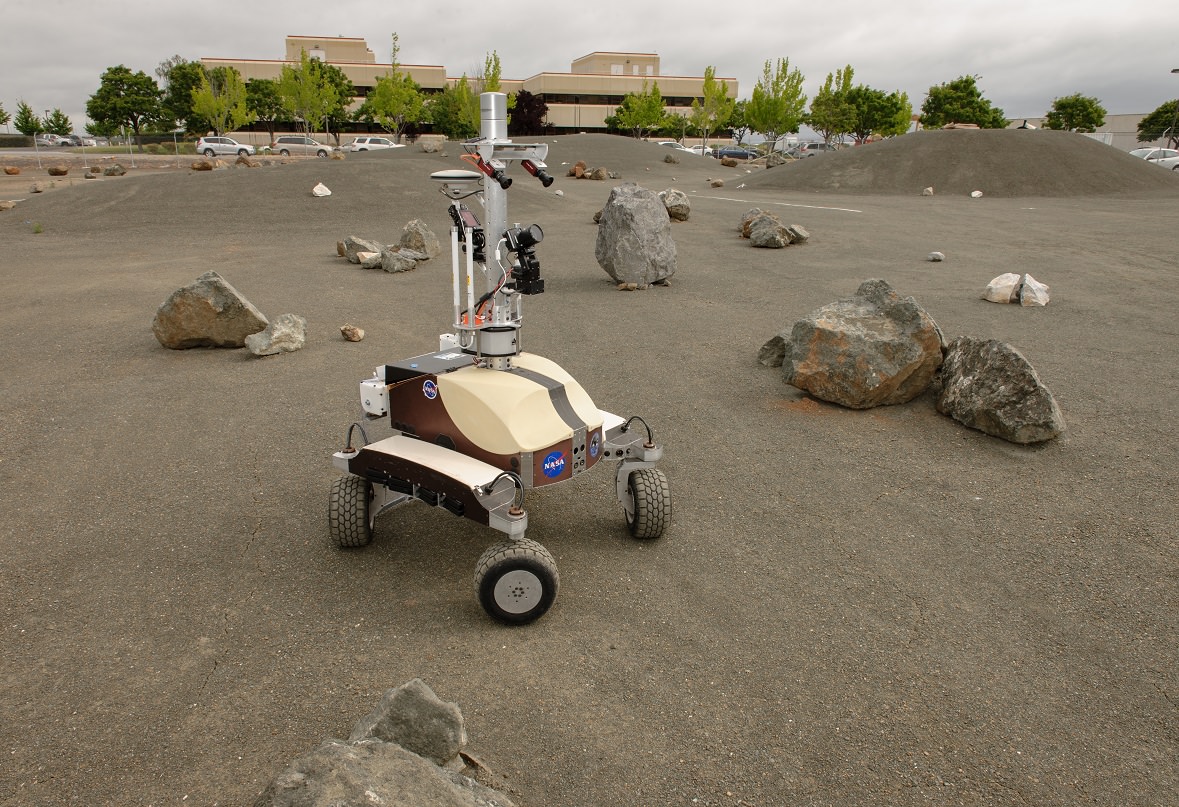

Astronauts, start your rover engines. Two astronauts recently remote-controlled a rover vehicle in California from their perch on the International Space Station — about 250 miles (400 kilometers) overhead.
The concept is cool in itself, but NASA has loftier aims. It’s thinking about those moon and asteroid and Mars human missions that the agency would really like to conduct one day, if it receives the money and authorization.
Potentially, say, you could have a Mars crew using rovers to explore as much of the surface as possible in a limited time.
Mars Curiosity and its predecessor rovers have found amazing things on Mars, but the challenge is the average 20-minute delay in communications between Mars and Earth. NASA deftly accounts for this problem through techniques such as hazard avoidance software so that Curiosity, say, wouldn’t crash into a big Martian boulder. (More techniques from NASA at this link.) But having astronauts above the surface would cut down on the time delay and potentially change Mars rover driving forever.

So about that test: two astronauts so far have run the K10 planetary vehicle prototype around a “Roverscape” at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California. NASA calls these runs the “first fully-interactive remote operation of a planetary rover by an astronaut in space.”
Expedition 36’s Chris Cassidy was first up on June 15, spending three hours moving the machine around in the rock-strewn area, which is about the size of two football fields. Then his crewmate Luca Parmitano took a turn on July 26, going so far as to deploy a simulated radio antenna. Another test session should take place in August.
“Whereas it is common practice in undersea exploration to use a joystick and have direct control of remote submarines, the K10 robots are more intelligent,” stated Terry Fong, human exploration telerobotics project manager at Ames.
“Astronauts interact with the robots at a higher level, telling them where to go, and then the robot itself independently and intelligently figures out how to safely get there,” added Fong, who is also director of Ames’ intelligent robotics group.
The tests simulated a mission to the moon’s L2 Lagrangian point, a spot where the combined gravity of the moon and Earth allow a spacecraft to remain virtually steady above the surface. One possibility for such a mission would be to deploy a radio telescope on the lunar side opposite from Earth, far from Earth’s radio noise, NASA said.
These tests also showcase a couple of technical firsts:
- NASA is testing a Robot Application Programming Interface Delegate (RAPID) robot data messaging system to control the robot from space, essentially working to strip down the information to the bare essentials to make communication as easy as possible. (RAPID has been tested before, but never in this way.)
- The agency is also using its Ensemble software in space for telerobotics for the first time. It describes this as “open architecture for the development, integration and deployment of mission operations software.”
Source: NASA
How Did That Spacesuit Water Leak Spread? New Video Has Clues
As NASA investigates how astronaut Luca Parmitano’s spacesuit filled with water during a spacewalk two weeks ago, a new video by fellow Expedition 36 astronaut Chris Cassidy demonstrated the path the pool took inside Parmitano’s helmet.
Cassidy described the situation as leaking “cooling water” that got “somehow into his ventilation system” and spread into Parmitano’s helmet. The cause is still being investigated.
From a ventilation port at the back of the helmet, “the water bubbles started to build up behind this white plastic piece,” Cassidy said in the video, pointing at a support that was behind Parmitano’s head.
Update: There’s now part 2 of Cassidy’s description of the leak, below:
“Once the water got big enough that it went all the way around and started coming outside the edge of the white plastic, then it saturated his communication cap and the … flow brought the water all around his head. And he had water filled up in his ear hubs, and it started to creep into his eyes, and cover his nose.”
Calling it a “scary situation”, Cassidy said that if the leak had continued, “it would have been very serious.” NASA, however, aborted the spacewalk quickly after Parmitano reported the problem. Parmitano and Cassidy, who were outside together, were back in the International Space Station in minutes.
Parmitano, for his part, has repeatedly said that he is doing all right. “Guys, I am doing fine and thanks for all the support. I am really okay and ready to move on,” he said, as reported in a July 18 ESA blog post.
NASA has at least two probes going on: an engineering analysis to find the cause, and a more wide-ranging mishap investigation to look at spacewalk procedures and overall crew safety during spaceflights. The agency also sent a spacesuit repair kit on the Progress spacecraft that docked with the International Space Station on July 27.
The July 16 spacewalk ended after just 1 hour, 32 minutes. All of the tasks for the planned 6.5-hour outing, which included preparing data cables and power for a forthcoming Russian module, are not urgent and can be done any time, NASA said. Further American spacewalks are suspended for the time being.
1st Operational Cygnus Module Bound for ISS Lands at NASA Wallops Launch Site
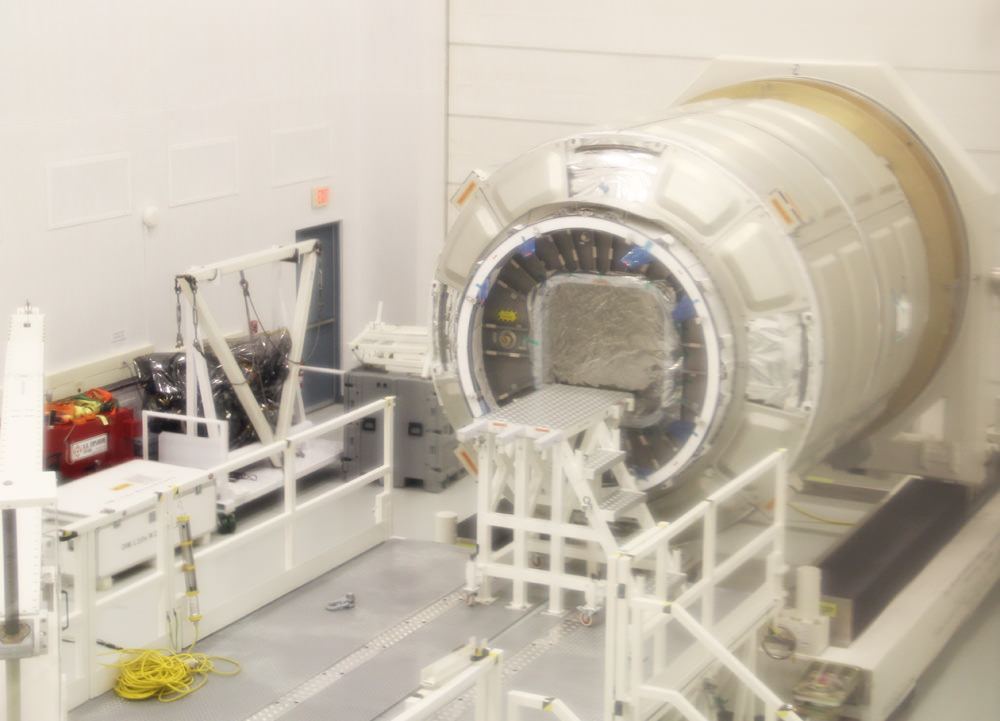
NASA WALLOPS ISLAND, VA – The 1st operational Cygnus cargo spacecraft slated to ferry crucial supplies to the International Space Station (ISS) under a commercial contract with NASA, has been delivered to NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
The privately built Cygnus Pressurized Cargo Module (PCM) was developed by Orbital Sciences Corp. & Thales Alenia Space under the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) cargo transport contract with NASA.
Universe Today took an exclusive look at the unmanned Cygnus cargo carrier housed inside the high bay facility where the vehicle is being processed for flight during a visit at NASA Wallops.
This Cygnus transport vessel is scheduled to lift off atop an Antares rocket bound for the ISS from the Wallops Island launch site towards the end of this year.
Cygnus is an essential lifeline to stock the station with all manner of equipment, science experiments, food, clothing, spare parts and gear for the international crew of six astronauts and cosmonauts.

The Cygnus PCM is manufactured by Thales Alenia Space at their production facility in Turin, Italy under a subcontract from Orbital.
The design is based on the Multi Purpose Logistic Module (MPLM) space shuttle cargo transporter.
The standard version has an internal volume of 18.9 cubic meters and can carry a total cargo mass of 2000 kg.
It was encased inside a special shipping container and flown from Italy to the US aboard an Antonov An-124 aircraft on July 17. The massive An-124 is the world’s second largest operating cargo aircraft.
After unloading from the An-124 and movement into a clean room high bay at Wallops Processing Building H-100, the shipping crate’s cover was raised using a 20 ton bridge crane. The PCM was unloaded and likewise gently craned over to an adjacent high bay work stand for flight processing.

Approximately a month and a half before launch, technicians mate the Cygnus PCM to the Service Module (SM) which houses the spacecraft’s avionics, propulsion and power systems and propels the combined vehicle to berth at the ISS.
The Cygnus SM is built by Orbital at their manufacturing facility in Dulles, VA., and shipped to Wallops for integration with the PCM in the processing building.
This particular vehicle is actually the second PCM bound for the ISS, but will be the first of eight operational cargo delivery runs to the space station over the next few years.
The first PCM to fly is set to blast-off on a Demonstration Mission (COTS 1) to the ISS in some six weeks on Sept. 14 atop Orbital’s privately developed Antares rocket. It is also in the midst of flight processing at Wallops inside a different building known as the Horizontal Integration Facility (HIF) where it is integrated with the Antares rocket.

Orbital says the Cygnus Demo vehicle is already fueled and will be loaded with about 1550 kg of cargo for the station crew.
The purpose of the demonstration flight is to prove that the unmanned spacecraft can safely and successfully rendezvous and dock with the orbiting outpost. The flight objectives are quite similar to the initial cargo delivery test flights successfully accomplished by Orbital’s commercial rival, SpaceX.
All of Orbital’s ISS cargo resupply missions will occur from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport’s (MARS) pad 0A at Wallops.
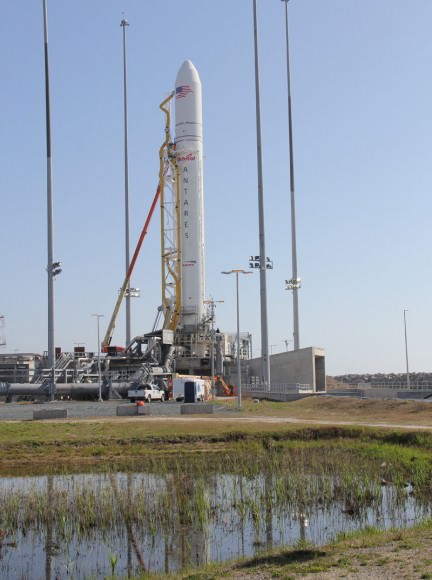

This past spring on April 21, Orbital successfully launched the 1st test flight of the Antares rocket. Read my articles here and here.
Orbital’s Antares/Cygnus system is similar in scope to the SpaceX Falcon 9/Dragon system.
Both firms won lucrative NASA contracts to deliver approximately 20,000 kilograms each of supplies and science equipment to the ISS during some 20 flights over the coming 3 to 4 years.

The goal of NASA’s CRS initiative is to achieve safe, reliable and cost-effective transportation to and from the ISS and low-Earth orbit (LEO) as a replacement for NASA’s now retired Space Shuttle Program.
Orbital’s contract with NASA for at least eight Antares/Cygnus resupply missions to the ISS is worth $1.9 Billion.

…………….
Learn more about Cygnus, Antares, LADEE, Mars rovers and more at Ken’s upcoming lecture presentations
Aug 12: “RockSat-X Suborbital Launch, LADEE Lunar & Antares Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, 8 PM
Alan Parson’s Project Dedicates Song to ISS Astronaut Parmitano
When we heard that the Alan Parsons Project song “Eye in the Sky” was beamed to humanity’s constant eye in the sky — the International Space Station — we just about exploded with space geekiness. It’s even more awesome that the video accompanying the song has tons of space scenes to enjoy.
Turns out the band’s song is Expedition 36 astronaut Luca Parmitano’s favorite, which is why Parsons dedicated that to him during a July 23 Alan Parsons Live Project concert at the Foro Italico in Rome.
Continue reading “Alan Parson’s Project Dedicates Song to ISS Astronaut Parmitano”



